
Chemical composition of chromosome:
(a)DNA and lipids
(b)DNA and carbohydrates
(c)Proteins and lipids
(d)DNA and proteins
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Their combination is also known as nucleosomes. One part of the chromosome is a two-stranded molecule and has a unique ‘double helix’ shape, like a twisted ladder. The other is the building blocks of the body, containing chains of amino acids.
Complete answer:
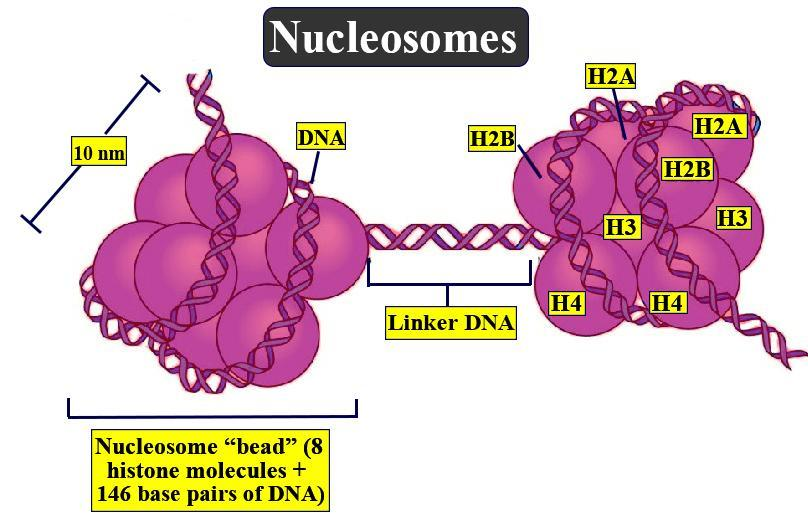
The chemical composition of a chromosome is DNA and histone proteins. The DNA molecules are very long, yet they are packed with the help of positively charged histones into a smaller diameter. Histones are rich in arginine and lysine (amino acid residues), which form the core around which a double-stranded DNA fragment is wounded.
Additional Information: -The term nucleosome was given by P. Oudet in 1975.
-The nucleosomes give chromatin its-beads-on-a-string appearance under the electron microscope.
-The nucleosome bead appears as a disc-shaped particle with a diameter of about 11nm.
-Each nucleosome bead consists of 8 histone molecules (octamer) copies.
-Each of these highly conserved nucleosomal histones, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 are two in number, so it makes 8 histone molecules.
-The histone octamer is also called a nu(v8)body.
-Each histone molecule has two parts, an uncharged hydrophobic region and a charged region having basic amino acid.
-Each nucleosome bead is separated from the next by a region of linker DNA which is approximately 60 base pairs long.
-The linker DNA plus the nucleosome bead form the entire nucleosome which therefore contains about 200 base pairs of DNA.
-The nucleosomes coil up tightly to create chromatin loops. The chromatin loops are then wrapped around each other, which makes a full chromosome.
So, the correct answer is, ‘DNA and proteins.’
Note: The DNA is wrapped over the histone octamer of the nucleosome in a superhelical manner forming 1.75 turns. DNA also extends as a continuous thread from one end to another end of the nucleosome.
Complete answer:
The chemical composition of a chromosome is DNA and histone proteins. The DNA molecules are very long, yet they are packed with the help of positively charged histones into a smaller diameter. Histones are rich in arginine and lysine (amino acid residues), which form the core around which a double-stranded DNA fragment is wounded.
Additional Information: -The term nucleosome was given by P. Oudet in 1975.
-The nucleosomes give chromatin its-beads-on-a-string appearance under the electron microscope.
-The nucleosome bead appears as a disc-shaped particle with a diameter of about 11nm.
-Each nucleosome bead consists of 8 histone molecules (octamer) copies.
-Each of these highly conserved nucleosomal histones, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 are two in number, so it makes 8 histone molecules.
-The histone octamer is also called a nu(v8)body.
-Each histone molecule has two parts, an uncharged hydrophobic region and a charged region having basic amino acid.
-Each nucleosome bead is separated from the next by a region of linker DNA which is approximately 60 base pairs long.
-The linker DNA plus the nucleosome bead form the entire nucleosome which therefore contains about 200 base pairs of DNA.
-The nucleosomes coil up tightly to create chromatin loops. The chromatin loops are then wrapped around each other, which makes a full chromosome.
So, the correct answer is, ‘DNA and proteins.’
Note: The DNA is wrapped over the histone octamer of the nucleosome in a superhelical manner forming 1.75 turns. DNA also extends as a continuous thread from one end to another end of the nucleosome.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




