
Check the correctness of the relation ${S_{nth}} = u + \dfrac{a}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)$, where $u$ is the initial velocity, $a$ is the acceleration and ${S_{nth}}$ is the distance travelled by the body in $nth$ second.
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: First consider the displacements for $n\sec $ and $\left( {n - 1} \right)\sec $. Now the equation can be obtained by integrating the kinematic equation $v = u + at$ (where $v = \dfrac{{ds}}{{dt}}$) and then apply the required limit. Here time is considered as a discrete number (i.e., $1$sec, $2$sec, $3$sec, … , $n$ sec).
Complete step by step answer:
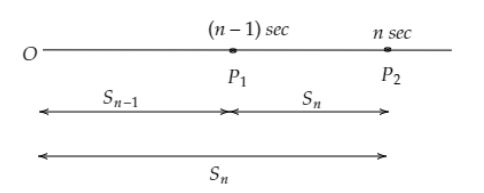
Let a body start from O to P1 in $\left( {n - 1} \right)$ second and to P2 in $n$ second as shown in the following figure. Then, ${P_1}{P_2}$ is the distance travelled by the body in $nth$ second.
${S_{nth}} = {S_n} - {S_{n - 1}}$
Where ${S_n}$ and ${S_{n - 1}}$ are the distances covered by the body in $n$ and $n - 1$ second respectively.
If $\overrightarrow {ds} $ be the small displacement moved by the body in a small time $dt$, instantaneous velocity $\vec v$ of the body is
$\vec v = \dfrac{{\vec ds}}{{dt}}$
$\Rightarrow ds = vdt$
We know that $v = u + at$
Where $u$ and $a$ are the initial velocity and acceleration of the body respectively.
$ \Rightarrow ds = \left( {u + at} \right)dt$
Integrating the above equation between the region P1P2 .
$\int_{{S_{n - 1}}}^{{S_n}} {ds} = \int_{n - 1}^n {\left( {u + at} \right)dt} $
On further simplification,
$\left[ S \right]_{{S_{n - 1}}}^{{S_n}} = u\left[ t \right]_{n - 1}^n + a\left[ {\dfrac{{{t^2}}}{2}} \right]_{n - 1}^n$
Substitute the limits and calculate
$ \Rightarrow {S_n} - {S_{n - 1}} = u\left[ {n - \left( {n - 1} \right)} \right] + a\left[ {\dfrac{{{n^2} - {{\left( {n - 1} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \right]$
Simplify further,
$ \Rightarrow {S_n} - {S_{n - 1}} = u + \dfrac{a}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)$
Since, ${S_n} - {S_{n - 1}} = {S_{nth}}$
Therefore, ${S_{nth}} = u + \dfrac{a}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)$ is the correct relation.
Note: While doing the integration, keep $u$ and $a$ constant. If a body starts from rest, $u = 0$.Therefore, displacement in nth second is ${S_{nth}} = \dfrac{a}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)$. It should be kept in mind that the equations of kinematics are valid only for uniformly accelerated motion i.e., when $a = $constant.
Complete step by step answer:
Let a body start from O to P1 in $\left( {n - 1} \right)$ second and to P2 in $n$ second as shown in the following figure. Then, ${P_1}{P_2}$ is the distance travelled by the body in $nth$ second.
${S_{nth}} = {S_n} - {S_{n - 1}}$
Where ${S_n}$ and ${S_{n - 1}}$ are the distances covered by the body in $n$ and $n - 1$ second respectively.

If $\overrightarrow {ds} $ be the small displacement moved by the body in a small time $dt$, instantaneous velocity $\vec v$ of the body is
$\vec v = \dfrac{{\vec ds}}{{dt}}$
$\Rightarrow ds = vdt$
We know that $v = u + at$
Where $u$ and $a$ are the initial velocity and acceleration of the body respectively.
$ \Rightarrow ds = \left( {u + at} \right)dt$
Integrating the above equation between the region P1P2 .
$\int_{{S_{n - 1}}}^{{S_n}} {ds} = \int_{n - 1}^n {\left( {u + at} \right)dt} $
On further simplification,
$\left[ S \right]_{{S_{n - 1}}}^{{S_n}} = u\left[ t \right]_{n - 1}^n + a\left[ {\dfrac{{{t^2}}}{2}} \right]_{n - 1}^n$
Substitute the limits and calculate
$ \Rightarrow {S_n} - {S_{n - 1}} = u\left[ {n - \left( {n - 1} \right)} \right] + a\left[ {\dfrac{{{n^2} - {{\left( {n - 1} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \right]$
Simplify further,
$ \Rightarrow {S_n} - {S_{n - 1}} = u + \dfrac{a}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)$
Since, ${S_n} - {S_{n - 1}} = {S_{nth}}$
Therefore, ${S_{nth}} = u + \dfrac{a}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)$ is the correct relation.
Note: While doing the integration, keep $u$ and $a$ constant. If a body starts from rest, $u = 0$.Therefore, displacement in nth second is ${S_{nth}} = \dfrac{a}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)$. It should be kept in mind that the equations of kinematics are valid only for uniformly accelerated motion i.e., when $a = $constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




