
Cercaria is the larva of
A. Schistosoma
B. Fasciola
C. Both A and B
D. Taenia
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: It is a parasitic flatworm of class Trematoda that specifically consists of two suckers, one ventral and other oral.
Complete answer:
A cercaria is the larva form of fasciola and Schistosoma which develops inside the germinal cells of the sporocyst. The motile cercaria moves and settles in a host where it will become either an adult, or a mesocercaria, or a metacercaria, depending on the species.
Structure of cercaria: A cercaria is usually prepared with a tail that helps it to swim. The mouth is situated at the anterior part of the body and bounded by the oral sucker and finally leads into the foregut and paired ceca. There is an unevenly positioned ventral sucker whose location remains fixed throughout adulthood. In many cercariae, there are several types of glands present that open anteriorly. The name of a gland itself indicates its expected function. Such as a pair of escape glands lying near the mouth in schistosome cercariae, the cytogenic glands secrete constituents to form a cyst wall, and remaining glands like penetration glands and mucous glands play a role in host penetration.
The shape of the metacercarial cyst is variable from one species to others and it can be spherical, ovoidal, flask-shaped, or hemispherical. In closely related species, cercariae seem similar in body type and are difficult to distinguish by morphology only.
So, the correct answer is ‘Both A and B’.
Note:
- The trematode’s life cycle involves the mammalian as definitive hosts and molluscan as intermediate hosts. The transmission takes place within water between the two hosts.
- Mammals get infected when they ingest metacercariae with food and water.
- Subacute and chronic infections like Fascioliasis are treated with triclabendazole or bithionol.
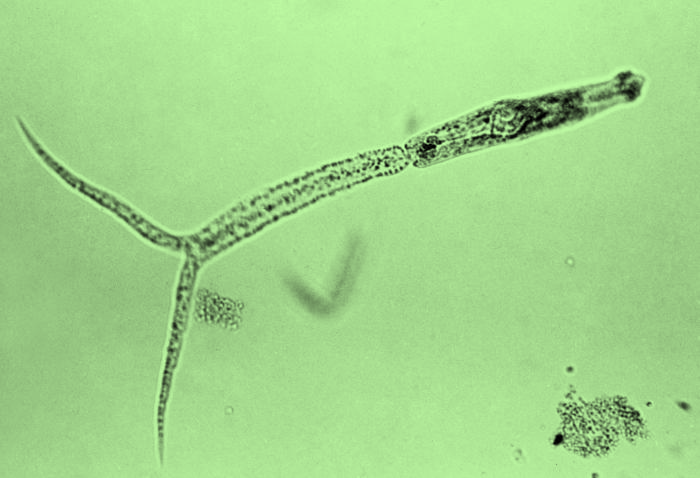
Figure: Schistosoma larva
Complete answer:
A cercaria is the larva form of fasciola and Schistosoma which develops inside the germinal cells of the sporocyst. The motile cercaria moves and settles in a host where it will become either an adult, or a mesocercaria, or a metacercaria, depending on the species.
Structure of cercaria: A cercaria is usually prepared with a tail that helps it to swim. The mouth is situated at the anterior part of the body and bounded by the oral sucker and finally leads into the foregut and paired ceca. There is an unevenly positioned ventral sucker whose location remains fixed throughout adulthood. In many cercariae, there are several types of glands present that open anteriorly. The name of a gland itself indicates its expected function. Such as a pair of escape glands lying near the mouth in schistosome cercariae, the cytogenic glands secrete constituents to form a cyst wall, and remaining glands like penetration glands and mucous glands play a role in host penetration.
The shape of the metacercarial cyst is variable from one species to others and it can be spherical, ovoidal, flask-shaped, or hemispherical. In closely related species, cercariae seem similar in body type and are difficult to distinguish by morphology only.
So, the correct answer is ‘Both A and B’.
Note:
- The trematode’s life cycle involves the mammalian as definitive hosts and molluscan as intermediate hosts. The transmission takes place within water between the two hosts.
- Mammals get infected when they ingest metacercariae with food and water.
- Subacute and chronic infections like Fascioliasis are treated with triclabendazole or bithionol.

Figure: Schistosoma larva
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




