
Cell in latin means______
Answer
513.6k+ views
Hint: All known species have a cell as their basic structural, functional, and biological unit. Because cells are the tiniest units of life, they are frequently referred to as "building blocks of life". Cell biology, cellular biology, or cytology are various terms for the study of cells.
There are two sorts of cells: eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and prokaryotic cells without one. Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular, whereas prokaryotes are single-celled organism
Complete explanation:
Every living creature is made up of cells, which are referred to as life's fundamental unit.
Cell is derived from the Latin word cellus, which means "little space".
It was first discovered by Robert Hooke, an English philosopher and architect.
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, two German scientists, proposed the cell hypothesis.
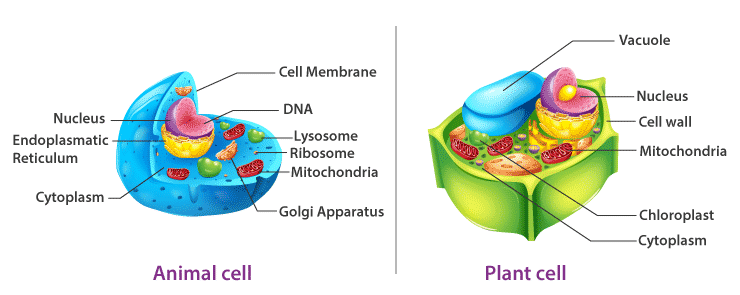
Additional information:
Functions of cell:
The cell provides support and structure to the body.
Facilitates growth by mitosis.
Helps in reproduction.
Provides energy and allows the transport of substances.
Note:
Bacteria and archaea, two of the three kingdoms of life, are prokaryotes. Prokaryotic cells were the first form of life on Earth, and they were distinguished by the presence of important biological processes such as cell signalling. They lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, making them simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotes include plants, mammals, fungi, slime moulds, protozoa, and algae. These cells are around fifteen times broader than a typical prokaryote and can have a thousand times the volume of a prokaryote. Compartmentalization is the presence of membrane-bound organelles (compartments) in which distinct processes take place, which distinguishes eukaryotes from prokaryotes.
There are two sorts of cells: eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and prokaryotic cells without one. Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular, whereas prokaryotes are single-celled organism
Complete explanation:
Every living creature is made up of cells, which are referred to as life's fundamental unit.
Cell is derived from the Latin word cellus, which means "little space".
It was first discovered by Robert Hooke, an English philosopher and architect.
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, two German scientists, proposed the cell hypothesis.

Additional information:
Functions of cell:
The cell provides support and structure to the body.
Facilitates growth by mitosis.
Helps in reproduction.
Provides energy and allows the transport of substances.
Note:
Bacteria and archaea, two of the three kingdoms of life, are prokaryotes. Prokaryotic cells were the first form of life on Earth, and they were distinguished by the presence of important biological processes such as cell signalling. They lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, making them simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotes include plants, mammals, fungi, slime moulds, protozoa, and algae. These cells are around fifteen times broader than a typical prokaryote and can have a thousand times the volume of a prokaryote. Compartmentalization is the presence of membrane-bound organelles (compartments) in which distinct processes take place, which distinguishes eukaryotes from prokaryotes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




