
What causes the movement of food in the alimentary canal?
Answer
606.9k+ views
Hint: Any kind of movement in the alimentary canal is usually associated with involuntary muscular movement.
Complete answer:
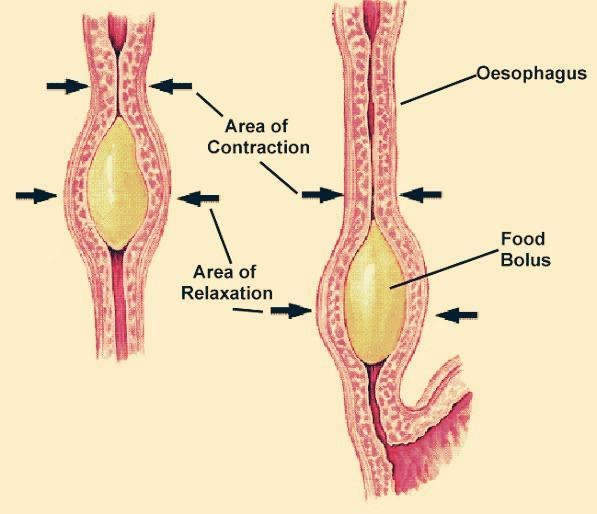
The movement of food in the alimentary canal occurs by peristalsis which includes rhythmic contraction and relaxation waves in the smooth muscles of the alimentary canal.
Primarily peristalsis is initiated due to stretching of the alimentary muscular walls when food enters it. This stimulus initiates a circular contraction behind it and relaxation in front of it. Resulting in a wave of contraction and relaxation which causes the movement of food.
Additional Information:
- Peristaltic movement always occurs from mouth end to anal end of the gut.
- When food after mastication is swallowed it is known as a bolus. Stretching of the alimentary canal by the bolus releases serotonin that activates the myenteric plexus which is present between inner circular and outer longitudinal muscles.
- A contracting segment is then formed behind the bolus and a relaxing segment is formed in front of the bolus.
- Three types of peristalsis are seen in the esophagus. Primary peristaltic contractions, it is progressive and moves at the rate of 2-4 cm/sec and it starts after swallowing or deglutition of food. Secondary peristaltic contraction is also progressive and generated due to stretching of the gut. Tertiary movement is nonprogressive and non peristaltic.
Note: Several other types of movement are seen in different regions of the alimentary canal but the predominant movement is the peristaltic movement, seen after the intake of food. Peristalsis is mainly seen in the esophagus, the small intestine, and the large intestine.
Complete answer:
The movement of food in the alimentary canal occurs by peristalsis which includes rhythmic contraction and relaxation waves in the smooth muscles of the alimentary canal.
Primarily peristalsis is initiated due to stretching of the alimentary muscular walls when food enters it. This stimulus initiates a circular contraction behind it and relaxation in front of it. Resulting in a wave of contraction and relaxation which causes the movement of food.
Additional Information:
- Peristaltic movement always occurs from mouth end to anal end of the gut.
- When food after mastication is swallowed it is known as a bolus. Stretching of the alimentary canal by the bolus releases serotonin that activates the myenteric plexus which is present between inner circular and outer longitudinal muscles.
- A contracting segment is then formed behind the bolus and a relaxing segment is formed in front of the bolus.
- Three types of peristalsis are seen in the esophagus. Primary peristaltic contractions, it is progressive and moves at the rate of 2-4 cm/sec and it starts after swallowing or deglutition of food. Secondary peristaltic contraction is also progressive and generated due to stretching of the gut. Tertiary movement is nonprogressive and non peristaltic.
Note: Several other types of movement are seen in different regions of the alimentary canal but the predominant movement is the peristaltic movement, seen after the intake of food. Peristalsis is mainly seen in the esophagus, the small intestine, and the large intestine.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




