
Car $A$ has an acceleration $2\,m{s^{ - 2}}$ due east and car $B$ has acceleration $4m{s^{ - 2}}$ due north. What is the acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$ ?
Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: We can find the acceleration of the car $B$ with respect to car $A$ by using the concept of motion in two dimensions in which two objects are moving along two different directions with different speeds. We use the concept of resultant acceleration of both the motions and find the magnitude and direction of the resultant acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assign some terminologies to the given data for better understanding.
${\bar a_A}$ - acceleration of car $A$.
\[{\bar a_B}\] - acceleration of car $B$.
\[{\bar a_{BA}}\] - acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$.
Car $A$ is travelling in the east direction with acceleration $2m{s^{ - 2}}$ while Car $B$ is travelling in the North direction with acceleration $4m{s^{ - 2}}$ .So,
$\left| {{{\bar a}_A}} \right| = 2m{s^{ - 2}}$ and $\left| {{{\bar a}_B}} \right| = 4m{s^{ - 2}}$
Let us draw the given situation.
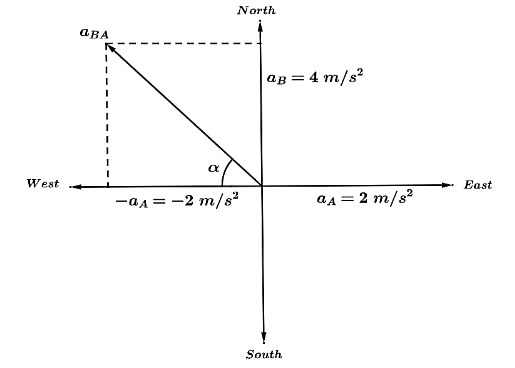
The acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$ is given by
\[{\bar a_{BA}} = {\bar a_B} - {\bar a_A} = {\bar a_B} + \left( { - {{\bar a}_A}} \right)\]
The magnitude of the acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$ is given by
\[\left| {{{\bar a}_{BA}}} \right| = \sqrt {{{\left| {{{\bar a}_B}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{{\bar a}_A}} \right|}^2}} = \sqrt {{4^2} + {2^2}} \]
\[\therefore \left| {{{\bar a}_{BA}}} \right| = 2\sqrt 5 m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Hence, the direction of the acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$ is North-west given by angle $\alpha $.
Note: The direction of the resultant acceleration changes when we are asked to find the acceleration of car $A$ with respect to car $B$ . The direction of resultant acceleration is given by $\alpha = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{a_B}}}{{{a_A}}}} \right)$ . The acceleration of the car $A$ with respect to car $B$ is just opposite that in direction but of the same magnitude.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assign some terminologies to the given data for better understanding.
${\bar a_A}$ - acceleration of car $A$.
\[{\bar a_B}\] - acceleration of car $B$.
\[{\bar a_{BA}}\] - acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$.
Car $A$ is travelling in the east direction with acceleration $2m{s^{ - 2}}$ while Car $B$ is travelling in the North direction with acceleration $4m{s^{ - 2}}$ .So,
$\left| {{{\bar a}_A}} \right| = 2m{s^{ - 2}}$ and $\left| {{{\bar a}_B}} \right| = 4m{s^{ - 2}}$
Let us draw the given situation.

The acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$ is given by
\[{\bar a_{BA}} = {\bar a_B} - {\bar a_A} = {\bar a_B} + \left( { - {{\bar a}_A}} \right)\]
The magnitude of the acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$ is given by
\[\left| {{{\bar a}_{BA}}} \right| = \sqrt {{{\left| {{{\bar a}_B}} \right|}^2} + {{\left| {{{\bar a}_A}} \right|}^2}} = \sqrt {{4^2} + {2^2}} \]
\[\therefore \left| {{{\bar a}_{BA}}} \right| = 2\sqrt 5 m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Hence, the direction of the acceleration of car $B$ with respect to car $A$ is North-west given by angle $\alpha $.
Note: The direction of the resultant acceleration changes when we are asked to find the acceleration of car $A$ with respect to car $B$ . The direction of resultant acceleration is given by $\alpha = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{a_B}}}{{{a_A}}}} \right)$ . The acceleration of the car $A$ with respect to car $B$ is just opposite that in direction but of the same magnitude.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




