
CAM pathway is observed in
(a)Pineapple.
(b)Maize.
(c)Sunflower.
(d)Sugarcane.
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: CAM plants are the succulent plants that are exposed to high temperatures and grow in dry conditions and these plants, stomata open during the night and close during the daytime.
Complete answer:
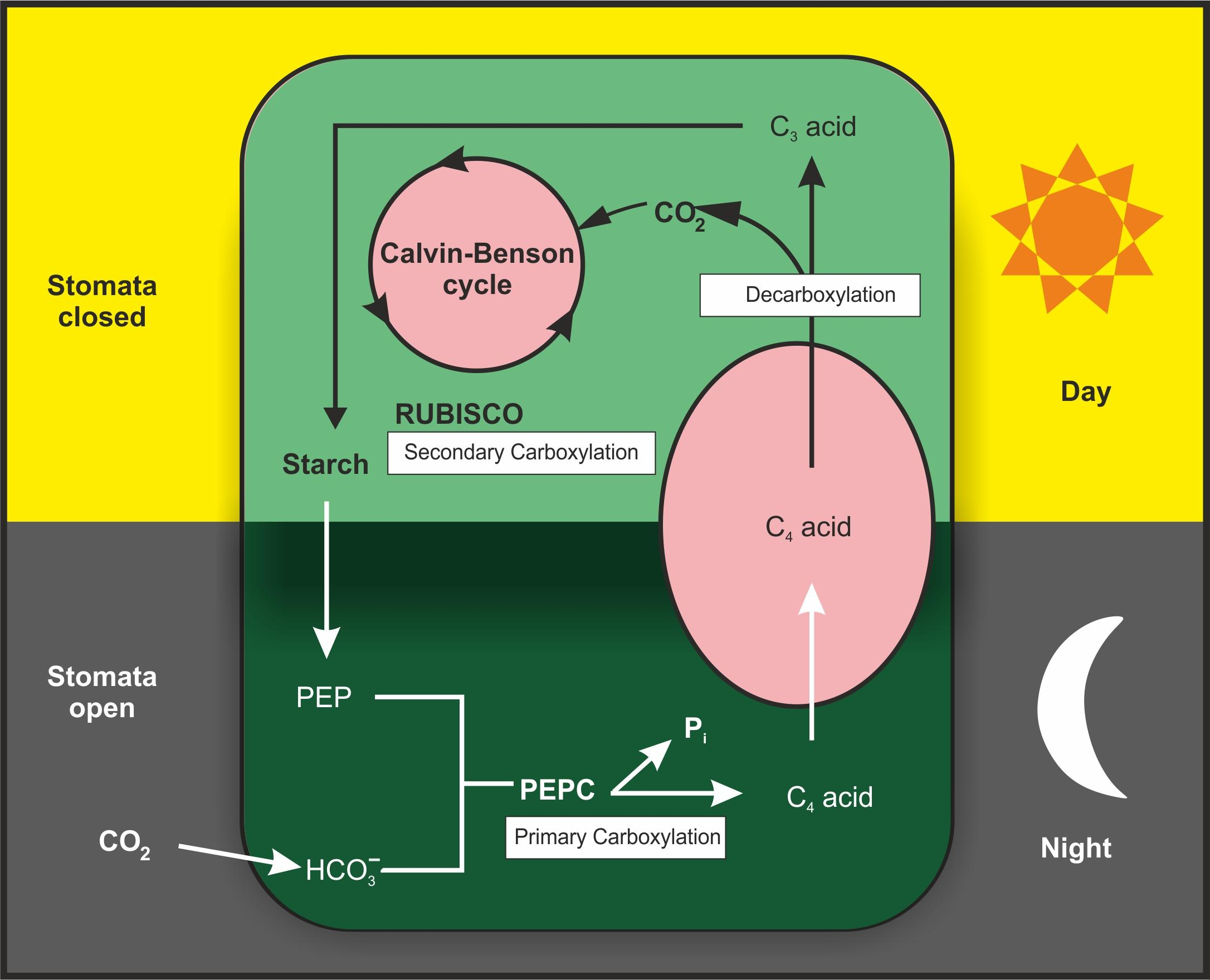
CAM metabolism is observed in Pineapple. CAM stands for Crassulacean Acid Metabolism. Since these plants are found in a stressful environment. They will lose much water during the day in hot conditions and perform the exchange of gases at night. At night, the CAM plants open their stomata, allowing the carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaves. In the mesophyll cells, this carbon dioxide is fixed into oxaloacetate by an enzyme PEP carboxylase(Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase ) that is converted to malate or other organic acids. During the daytime, the organic acids are broken down releasing carbon dioxide which enters the Calvin cycle (a process in plants that does not require sunlight for $CO_2$ fixation).
Additional Information: -CAM plants use the enzyme Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (Pepco) in the fixation of carbon dioxide at night.
-In the case of CAM plants, photosynthesis is not much efficient as in $C_3$ or $C_4$ plants.
-CAM plants can reduce the transpiration by performing gaseous exchange at night.
-CAM plants have a separate process of $CO_2$ fixation and electron transfer for the reduction of organic acids. Thus they can do one step during the day and the other during the night.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Pineapple.’
Note: CAM stands for Crassulacean Acid Metabolism because this particular phenomenon is observed in the members of the Crassulaceae family. Some members of this family contain a large amount of organic acid like malic acid and oxalic acid.
Complete answer:
CAM metabolism is observed in Pineapple. CAM stands for Crassulacean Acid Metabolism. Since these plants are found in a stressful environment. They will lose much water during the day in hot conditions and perform the exchange of gases at night. At night, the CAM plants open their stomata, allowing the carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaves. In the mesophyll cells, this carbon dioxide is fixed into oxaloacetate by an enzyme PEP carboxylase(Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase ) that is converted to malate or other organic acids. During the daytime, the organic acids are broken down releasing carbon dioxide which enters the Calvin cycle (a process in plants that does not require sunlight for $CO_2$ fixation).
Additional Information: -CAM plants use the enzyme Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (Pepco) in the fixation of carbon dioxide at night.
-In the case of CAM plants, photosynthesis is not much efficient as in $C_3$ or $C_4$ plants.
-CAM plants can reduce the transpiration by performing gaseous exchange at night.
-CAM plants have a separate process of $CO_2$ fixation and electron transfer for the reduction of organic acids. Thus they can do one step during the day and the other during the night.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Pineapple.’
Note: CAM stands for Crassulacean Acid Metabolism because this particular phenomenon is observed in the members of the Crassulaceae family. Some members of this family contain a large amount of organic acid like malic acid and oxalic acid.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




