
Why is it called a rectangular hyperbola?
Answer
507k+ views
Hint: For a hyperbola to be called a rectangular hyperbola, we must check for the eccentricity of the hyperbola. If the eccentricity of the hyperbola is \[\sqrt{2}\], then the hyperbola is considered as a rectangular hyperbola. The equation of the rectangular hyperbola is \[{{a}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\left( {{e}^{2}}-1 \right)\] where \[a=b\] for a rectangular hyperbola.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now let us learn more about rectangular hyperbola. In a rectangular hyperbola, \[a=b\] i.e. the length of the transverse axis = length of the conjugate axis. The asymptotes of the rectangular hyperbola are \[y=\pm x\]. When \[xy={{c}^{2}}\], the asymptotes are the coordinate axes. The equation of a normal rectangular hyperbola is \[y-\dfrac{c}{t}={{t}^{2}}\left( x-ct \right)\]. A hyperbola for which the asymptotes are perpendicular, it is called an equilateral hyperbola or right hyperbola. The main difference between a regular hyperbola and rectangular hyperbola is that the asymptotes are perpendicular in the rectangular hyperbola. The equation of a rectangular hyperbola is \[{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]. The AFC curve is represented by a rectangular hyperbola.
Now let us see why a hyperbola is called a rectangular hyperbola.
When a hyperbola has its asymptotes or the axes perpendicular to each other then it is called a rectangular hyperbola. Also, the eccentricity of a rectangular hyperbola is \[\sqrt{2}\].
Now, let us find the equation of the rectangular hyperbola whose asymptotes are \[3x-4y+9=0\] and \[4x+3y+1=0\] which passes through the origin.
We know that the join equation of the asymptotes and the equation of the hyperbola differs only by a constant \[r\].
So we get, \[\left( 3x-4y+9 \right)\left( 4x+3y+1 \right)+r=0\]
Since we are told that the hyperbola will be passing through the origin, we will be substituting \[x=y=0\].
Upon substituting we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 9+r=0 \\
& \Rightarrow r=-9 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we obtain the equation of hyperbola as
\[\begin{align}
& \left( 3x-4y+9 \right)\left( 4x+3y+1 \right)-9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 12{{x}^{2}}+9xy+3x-16xy-12{{y}^{2}}-4y+36x+27y+9-9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 12{{x}^{2}}-12{{y}^{2}}+39x+23y-7xy=0 \\
\end{align}\]
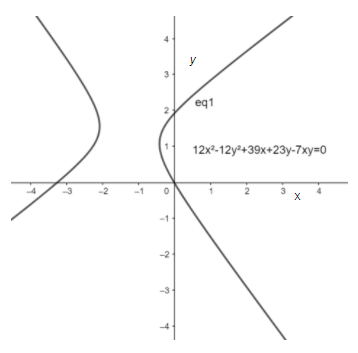
Note: e must always remember that the eccentricity of the rectangular hyperbola is \[\sqrt{2}\]. We must also note that the length of latus rectum can be calculated by the formula \[2\sqrt{2}c\] and when the vertices of a hyperbola are \[\left( c,c \right)\] and \[\left( -c,-c \right)\], then the focus of the hyperbola is \[\left( \sqrt{2}c,\sqrt{2}c \right)\] and \[\left( -\sqrt{2}c,-\sqrt{2}c \right)\].
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now let us learn more about rectangular hyperbola. In a rectangular hyperbola, \[a=b\] i.e. the length of the transverse axis = length of the conjugate axis. The asymptotes of the rectangular hyperbola are \[y=\pm x\]. When \[xy={{c}^{2}}\], the asymptotes are the coordinate axes. The equation of a normal rectangular hyperbola is \[y-\dfrac{c}{t}={{t}^{2}}\left( x-ct \right)\]. A hyperbola for which the asymptotes are perpendicular, it is called an equilateral hyperbola or right hyperbola. The main difference between a regular hyperbola and rectangular hyperbola is that the asymptotes are perpendicular in the rectangular hyperbola. The equation of a rectangular hyperbola is \[{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}\]. The AFC curve is represented by a rectangular hyperbola.
Now let us see why a hyperbola is called a rectangular hyperbola.
When a hyperbola has its asymptotes or the axes perpendicular to each other then it is called a rectangular hyperbola. Also, the eccentricity of a rectangular hyperbola is \[\sqrt{2}\].
Now, let us find the equation of the rectangular hyperbola whose asymptotes are \[3x-4y+9=0\] and \[4x+3y+1=0\] which passes through the origin.
We know that the join equation of the asymptotes and the equation of the hyperbola differs only by a constant \[r\].
So we get, \[\left( 3x-4y+9 \right)\left( 4x+3y+1 \right)+r=0\]
Since we are told that the hyperbola will be passing through the origin, we will be substituting \[x=y=0\].
Upon substituting we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 9+r=0 \\
& \Rightarrow r=-9 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we obtain the equation of hyperbola as
\[\begin{align}
& \left( 3x-4y+9 \right)\left( 4x+3y+1 \right)-9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 12{{x}^{2}}+9xy+3x-16xy-12{{y}^{2}}-4y+36x+27y+9-9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 12{{x}^{2}}-12{{y}^{2}}+39x+23y-7xy=0 \\
\end{align}\]

Note: e must always remember that the eccentricity of the rectangular hyperbola is \[\sqrt{2}\]. We must also note that the length of latus rectum can be calculated by the formula \[2\sqrt{2}c\] and when the vertices of a hyperbola are \[\left( c,c \right)\] and \[\left( -c,-c \right)\], then the focus of the hyperbola is \[\left( \sqrt{2}c,\sqrt{2}c \right)\] and \[\left( -\sqrt{2}c,-\sqrt{2}c \right)\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




