
Calculate the relative acceleration of $A$ with respect to $B$ if $B$ is moving with acceleration ${a_0}$ towards the right.
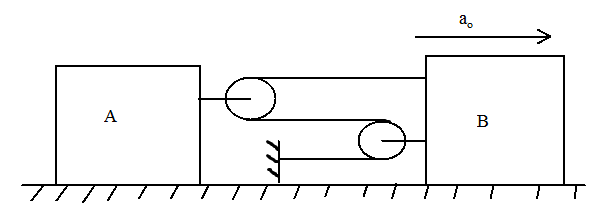

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint:First calculate the tensions in all the strings in the figure. Then use the formula which relates tension in string and object’s acceleration to calculate the acceleration of $A$ in terms of acceleration of $B$. After this is done, we have the acceleration of both the bodies. Subtract accordingly to get the acceleration of $A$ with respect to $B$ .
Formulas Used:
$\sum T{a_i}\cos \theta = 0$
Where, $T$ is the tension in the string attached to an object, ${a_i}$ is the acceleration of the ${i^{th}}$ object and $\theta $ is the angle between the directions of tension and acceleration of an object.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will calculate the tension in all the strings. We start from the top. Let the string at the top have a tension $T$ towards the object $B$. Therefore, the ${3^{rd}}$ string from the top, which connects the two pulleys together will also have a tension $T$ in the same direction and similarly, the string at the bottom will also have a tension $T$. Now, the string attached to $A$ is experiencing tension from two strings, therefore the tension in this string will be the sum of these two strings i.e. this string will have a tension of $2T$ in the same direction. The same is the case with the lower string attached to $B$. Tension in this string will also be equal to $2T$.
Since tension is always applied away from the body, the same will be the case here. These pulleys/strings do not have any velocity of their own, we can conclude that no net force is acting in them and these tensions are balanced. So, we assume that the same amount of force is acting on all the strings in opposite directions as the tensions we calculated above. The final diagram is shown below.
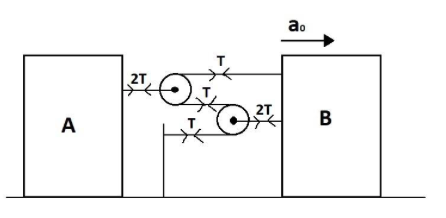
Now we use the formula $\sum T{a_i}\cos \theta = 0$. For $A$, tension is $2T$, let its acceleration be ${a_1}$ and the angle between them will be $0^\circ $ (tension is always applied away from the body). For $B$, tension is $(2T + T) = 3T$, its acceleration is ${a_0}$ (given) and the angle between them will be $180^\circ $. Therefore, the formula becomes $(2T \times {a_1} \times \cos 0) + (3T \times {a_0} \times \cos 180) = 0$
On solving this, we get $2T{a_1} - 3T{a_0} = 0$
Transposing, $2T{a_1} = 3T{a_0}$ $ \Rightarrow {a_1} = \dfrac{3}{2}{a_0}$
Or, ${a_1} = 1.5{a_0}$
We have the acceleration of $A$. The acceleration of $B$ is ${a_0}$. Therefore, relative acceleration of $A$ will be ${a_1} - {a_0} = 1.5{a_0} - {a_0} = 0.5{a_0}$ .
This is the required answer.
Note:Tension in a string is always applied away from the body it is attached to. If we do not balance the tension in the string it will mean that force is applied on the string and therefore, the string shall show motion in that direction which is not the case. Hence it is necessary to balance the tensions in the strings.
Formulas Used:
$\sum T{a_i}\cos \theta = 0$
Where, $T$ is the tension in the string attached to an object, ${a_i}$ is the acceleration of the ${i^{th}}$ object and $\theta $ is the angle between the directions of tension and acceleration of an object.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will calculate the tension in all the strings. We start from the top. Let the string at the top have a tension $T$ towards the object $B$. Therefore, the ${3^{rd}}$ string from the top, which connects the two pulleys together will also have a tension $T$ in the same direction and similarly, the string at the bottom will also have a tension $T$. Now, the string attached to $A$ is experiencing tension from two strings, therefore the tension in this string will be the sum of these two strings i.e. this string will have a tension of $2T$ in the same direction. The same is the case with the lower string attached to $B$. Tension in this string will also be equal to $2T$.
Since tension is always applied away from the body, the same will be the case here. These pulleys/strings do not have any velocity of their own, we can conclude that no net force is acting in them and these tensions are balanced. So, we assume that the same amount of force is acting on all the strings in opposite directions as the tensions we calculated above. The final diagram is shown below.

Now we use the formula $\sum T{a_i}\cos \theta = 0$. For $A$, tension is $2T$, let its acceleration be ${a_1}$ and the angle between them will be $0^\circ $ (tension is always applied away from the body). For $B$, tension is $(2T + T) = 3T$, its acceleration is ${a_0}$ (given) and the angle between them will be $180^\circ $. Therefore, the formula becomes $(2T \times {a_1} \times \cos 0) + (3T \times {a_0} \times \cos 180) = 0$
On solving this, we get $2T{a_1} - 3T{a_0} = 0$
Transposing, $2T{a_1} = 3T{a_0}$ $ \Rightarrow {a_1} = \dfrac{3}{2}{a_0}$
Or, ${a_1} = 1.5{a_0}$
We have the acceleration of $A$. The acceleration of $B$ is ${a_0}$. Therefore, relative acceleration of $A$ will be ${a_1} - {a_0} = 1.5{a_0} - {a_0} = 0.5{a_0}$ .
This is the required answer.
Note:Tension in a string is always applied away from the body it is attached to. If we do not balance the tension in the string it will mean that force is applied on the string and therefore, the string shall show motion in that direction which is not the case. Hence it is necessary to balance the tensions in the strings.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




