
Calculate the mass of lead which will be required to just submerge in water a block of wood weighing \[50{\text{ }}g\] (a) when lead is attached underneath, (b) when lead is placed on the top of the block. Take sp. gravity of lead = \[11.3\] and of wood = \[0.75.\].
A. \[\left( a \right)28.28g \\
\left( b \right)16.67g \\ \]
B. $\left( a \right)18.28g \\
\left( b \right)26.67g \\ $
C. $\left( a \right)18.28g \\
\left( b \right)16.67g \\ $
D. $\left( a \right)18.28g \\
\left( b \right)50.67g $
Answer
520.5k+ views
Hint:In order to calculate the mass of the lead under two conditions one is when the lead is attached underneath and when the lead is placed on the top of the block we will use Archimedes’ principle.
Formula used:
Apparent immersed weight = Weight of object- weight of displaced fluid
$\dfrac{\text{density of object}}{\text{density of fluid}} = \dfrac{\text{Weight}}{\text{Weight of displaced fluid}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let the mass of the lead is = $m$
Mass of block, $M$ = $50g$
Sp. gravity of lead = ${\rho _L}$ = $11.3$
Sp. gravity of wood = ${\rho _W}$ = \[0.75\]
(a) When lead is attached underneath
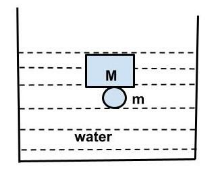
By Archimedes’ Principle volume of a body submerged = volume of water displaced due to submerged volume.
\[\dfrac{m}{{{\rho _L}}} + \dfrac{M}{{{\rho _W}}} = \dfrac{{\left( {m + M} \right)}}{{{\rho _{water}}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{m}{{11.3}} + \dfrac{{50}}{{0.75}} = \dfrac{{\left( {m + 50} \right)}}{1} \\
\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{16.66 \times 11.3}}{{10.3}} \\
\therefore m = 18.28\,g \]
Thus, the mass of lead required is $18.28\,g$.
(b) when lead is placed on the top of the block.
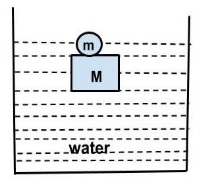
Weight of body = weight of water displaced due to submerged weight
\[\left( {50 + m} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{50}}{{0.75}}} \right){\rho _{water}} \times g \\
\Rightarrow m = \,\dfrac{{50}}{{0.75}} - 50 \\
\therefore m = 16.67\,g \]
Thus mass of lead required in this case is $16.67\,g$.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:The definition of displaced volume is one of the most frequently misunderstood aspects of Archimedes' theory. In most demonstrations, the displaced water is calculated by measuring the rise in water level when an object floats on the surface. When measuring a buoyant submerged object, this method fails because the rise in water level is proportional to the object's volume rather than its mass (except if the effective density of the object equals exactly the fluid density).
Formula used:
Apparent immersed weight = Weight of object- weight of displaced fluid
$\dfrac{\text{density of object}}{\text{density of fluid}} = \dfrac{\text{Weight}}{\text{Weight of displaced fluid}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let the mass of the lead is = $m$
Mass of block, $M$ = $50g$
Sp. gravity of lead = ${\rho _L}$ = $11.3$
Sp. gravity of wood = ${\rho _W}$ = \[0.75\]
(a) When lead is attached underneath

By Archimedes’ Principle volume of a body submerged = volume of water displaced due to submerged volume.
\[\dfrac{m}{{{\rho _L}}} + \dfrac{M}{{{\rho _W}}} = \dfrac{{\left( {m + M} \right)}}{{{\rho _{water}}}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{m}{{11.3}} + \dfrac{{50}}{{0.75}} = \dfrac{{\left( {m + 50} \right)}}{1} \\
\Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{16.66 \times 11.3}}{{10.3}} \\
\therefore m = 18.28\,g \]
Thus, the mass of lead required is $18.28\,g$.
(b) when lead is placed on the top of the block.

Weight of body = weight of water displaced due to submerged weight
\[\left( {50 + m} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{50}}{{0.75}}} \right){\rho _{water}} \times g \\
\Rightarrow m = \,\dfrac{{50}}{{0.75}} - 50 \\
\therefore m = 16.67\,g \]
Thus mass of lead required in this case is $16.67\,g$.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:The definition of displaced volume is one of the most frequently misunderstood aspects of Archimedes' theory. In most demonstrations, the displaced water is calculated by measuring the rise in water level when an object floats on the surface. When measuring a buoyant submerged object, this method fails because the rise in water level is proportional to the object's volume rather than its mass (except if the effective density of the object equals exactly the fluid density).
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




