
Calculate the lattice enthalpy (nearest integer value) in $kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ of $LiF$, given that enthalpy of
1.Sublimation of lithium is $155.3kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ ;
2.Dissociation of $\dfrac{1}{2}$ mole of ${{F}_{2}}$ is $75.3kJ$ ;
3.Ionization enthalpy of lithium is $520kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ ;
4.Electron gain enthalpy of $1$ mole of $F(g)$ is $-333kJ$ ;
5.${{\Delta }_{f}}H$ overall is $-594kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ .
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Born Haber Cycle is basically used to calculate the lattice energy by comparing the enthalpy change of formation of the ionic compound. Lattice energy is the amount of energy released when one mole of a lattice is formed from its constituent ion (in gaseous phase).
Complete step by step answer:
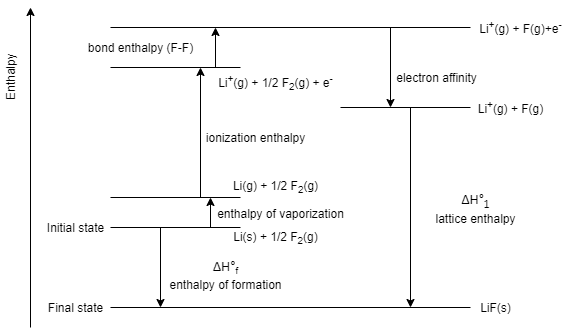
Here, it is given that, the sublimation of lithium, ${{\Delta }_{sub}}{{H}_{Li}}=155.2kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ ,
Dissociation of $\dfrac{1}{2}\Delta {{H}_{{{F}_{2}}}}=75.3kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ ,
Ionization enthalpy of lithium, ${{\Delta }_{f}}{{H}_{Li}}=520kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ ,
And, electron gain enthalpy, \[{{\Delta }_{F}}{{H}_{eg}}=-333kg\,mo{{l}^{-1}}\]
Overall ${{\Delta }_{f}}{{H}_{LiF}}=-594.1\,kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$
So, to calculate the lattice enthalpy of $LiF$ , we can use the equation given below
\[{{\Delta }_{f}}{{H}_{_{LiF}}}={{\Delta }_{sub}}{{H}_{Li}}+\Delta \dfrac{1}{2}{{H}_{{{F}_{2}}}}+{{\Delta }_{f}}{{H}_{Li}}+{{\Delta }_{F}}{{H}_{eg}}+{{\Delta }_{L}}{{H}_{LiF}}\]
On substituting the respective values , we get
\[\Rightarrow -594.1=155.2+75.3+520-333+{{\Delta }_{L}}{{H}_{LiF}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\Delta }_{L}}{{H}_{LiF}}=-1011.6\,kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}\]
Additional information:
To calculate the lattice enthalpy, it is done experimentally and theoretically. Experimentally it is calculated by Born Haber Cycle and theoretically, it is calculated by Born Lande equation.
Lattice energy is the amount of energy released when one mole of a lattice is formed from its constituent ion (in gaseous phase).
In this question, to calculate lattice energy, we have used the Born Haber cycle for ionic compounds. It consists of four steps:
1.Formation: In this step, elements get converted into the ionic state from standard state.
2.Atomization: In this step, elements lithium metal and fluoride get converted into gaseous atoms.
3.Ionization: In this step, electrons are removed from lithium and added to chlorine.
4.Lattice energy: This step involves the formation of ionic compounds from its gaseous ion.
Note: Factors that affect lattice enthalpy are as follows:
1.The charge on the ions: If the charge on ions is greater, attraction will be greater and lattice enthalpy will be high.
2.The radius of the ions: If the radius of the ions is smaller, it will increase the attraction and lattice enthalpy will be high.
Lattice enthalpy is calculated in $kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ .
Complete step by step answer:

Here, it is given that, the sublimation of lithium, ${{\Delta }_{sub}}{{H}_{Li}}=155.2kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ ,
Dissociation of $\dfrac{1}{2}\Delta {{H}_{{{F}_{2}}}}=75.3kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ ,
Ionization enthalpy of lithium, ${{\Delta }_{f}}{{H}_{Li}}=520kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ ,
And, electron gain enthalpy, \[{{\Delta }_{F}}{{H}_{eg}}=-333kg\,mo{{l}^{-1}}\]
Overall ${{\Delta }_{f}}{{H}_{LiF}}=-594.1\,kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$
So, to calculate the lattice enthalpy of $LiF$ , we can use the equation given below
\[{{\Delta }_{f}}{{H}_{_{LiF}}}={{\Delta }_{sub}}{{H}_{Li}}+\Delta \dfrac{1}{2}{{H}_{{{F}_{2}}}}+{{\Delta }_{f}}{{H}_{Li}}+{{\Delta }_{F}}{{H}_{eg}}+{{\Delta }_{L}}{{H}_{LiF}}\]
On substituting the respective values , we get
\[\Rightarrow -594.1=155.2+75.3+520-333+{{\Delta }_{L}}{{H}_{LiF}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\Delta }_{L}}{{H}_{LiF}}=-1011.6\,kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}\]
Additional information:
To calculate the lattice enthalpy, it is done experimentally and theoretically. Experimentally it is calculated by Born Haber Cycle and theoretically, it is calculated by Born Lande equation.
Lattice energy is the amount of energy released when one mole of a lattice is formed from its constituent ion (in gaseous phase).
In this question, to calculate lattice energy, we have used the Born Haber cycle for ionic compounds. It consists of four steps:
1.Formation: In this step, elements get converted into the ionic state from standard state.
2.Atomization: In this step, elements lithium metal and fluoride get converted into gaseous atoms.
3.Ionization: In this step, electrons are removed from lithium and added to chlorine.
4.Lattice energy: This step involves the formation of ionic compounds from its gaseous ion.
Note: Factors that affect lattice enthalpy are as follows:
1.The charge on the ions: If the charge on ions is greater, attraction will be greater and lattice enthalpy will be high.
2.The radius of the ions: If the radius of the ions is smaller, it will increase the attraction and lattice enthalpy will be high.
Lattice enthalpy is calculated in $kJ\,mo{{l}^{-1}}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




