
How do you calculate the height of an equilateral triangle?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:In the given question, we have been asked how we can calculate the height of any given equilateral triangle. For that, we assume any one side of the triangle to be any variable. Then we cut the equilateral triangle in half and apply the Pythagoras theorem to calculate the height on the terms of the side of the triangle.
Formula Used:
We are going to use the Pythagoras theorem, which is,
\[{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} + {\left( {base} \right)^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Let the side of the equilateral triangle be ‘\[a\]’.
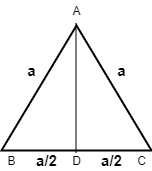
Now, we have to calculate the length of \[AD\].
In \[\Delta ADC\], using Pythagoras theorem, we have,
\[{\left( {AD} \right)^2} + {\left( {DC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AC} \right)^2}\]
Now, from the figure,
\[DC = \dfrac{a}{2}\] and \[AC = a\]
Putting the values into the formula, we have,
\[{\left( {AD} \right)^2} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4} = {a^2}\]
Taking all like terms on one side,
\[AD = \sqrt {{a^2} - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3{a^2}}}{4}} = \dfrac{{a\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
Hence, \[height = \dfrac{{a\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
Note: In the given question we had to calculate the height of an equilateral triangle. An equilateral triangle is a triangle with all sides equal. Then we cut the triangle in half. Then we applied the Pythagoras theorem on the half triangle and calculated the height on the basis of the assumed side of the triangle.
Formula Used:
We are going to use the Pythagoras theorem, which is,
\[{\left( {hypotenuse} \right)^2} = {\left( {perpendicular} \right)^2} + {\left( {base} \right)^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Let the side of the equilateral triangle be ‘\[a\]’.

Now, we have to calculate the length of \[AD\].
In \[\Delta ADC\], using Pythagoras theorem, we have,
\[{\left( {AD} \right)^2} + {\left( {DC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AC} \right)^2}\]
Now, from the figure,
\[DC = \dfrac{a}{2}\] and \[AC = a\]
Putting the values into the formula, we have,
\[{\left( {AD} \right)^2} + \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4} = {a^2}\]
Taking all like terms on one side,
\[AD = \sqrt {{a^2} - \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3{a^2}}}{4}} = \dfrac{{a\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
Hence, \[height = \dfrac{{a\sqrt 3 }}{2}\]
Note: In the given question we had to calculate the height of an equilateral triangle. An equilateral triangle is a triangle with all sides equal. Then we cut the triangle in half. Then we applied the Pythagoras theorem on the half triangle and calculated the height on the basis of the assumed side of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




