
How do you calculate the formal charge of ${{O}_{3}}$ ?
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: There is a formula to calculate the formal charge of the molecules. First we have to calculate the formal charge of the individual atoms and we have to do the sum of the formal charges of all the individual atoms. The formula to calculate the formal charge is as follows.
Formal charge of the an atom = $\text{Valence electron - }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{bonding electrons - nonbonding electrons}\text{.}$
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is asked to calculate the formal charge of an ozone molecule.
- There are three oxygen atoms present in the structure of the ozone molecule.
- The structure of ozone is as follows:
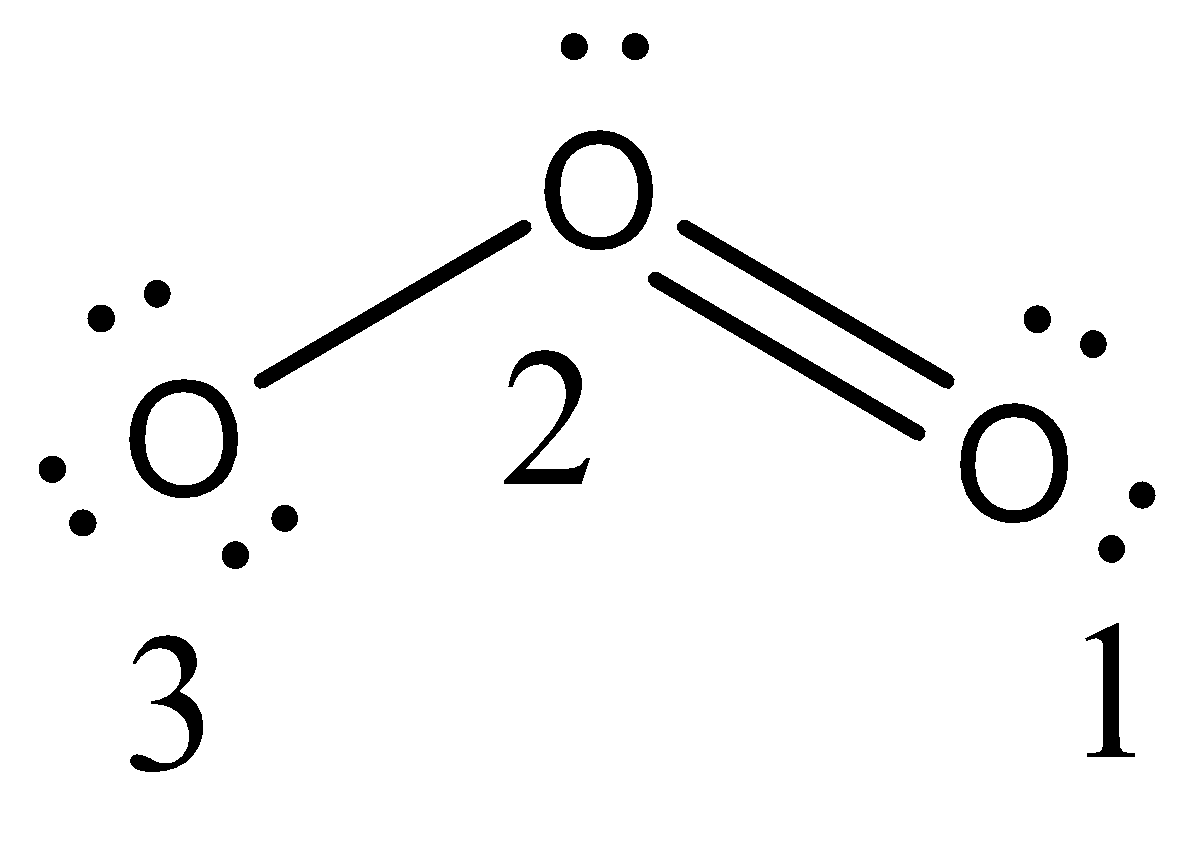
- The formal charge of the oxygen 1 is as follows.
- Formal charge of the oxygen atom 1= $\text{Valence electron - }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{bonding electrons - nonbonding electrons}\text{.}$
Formal charge of the oxygen atom 1= $\text{6 - }\dfrac{\text{4}}{\text{2}}\text{ - 4 = 0}$
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 1 is zero.
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 2 = $\text{6 - }\dfrac{\text{6}}{\text{2}}\text{ - 2 = 1}$
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 2 is ‘1’.
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 3 = $\text{6 - }\dfrac{\text{2}}{\text{2}}\text{ - 6 = -1}$
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 3 is ‘-1’.
- Now the total formal charge of the ozone = 0 + 1 - 1 = 0
- Therefore the formal charge of ozone is ‘0’.
Note: The formal charge of a molecule is equal to the sum of the formal charge of all the individual atoms present in the given molecule. The formal charge of the atoms is going to depend on the valence electrons, nodding electrons, and non-bonding electrons present in the given molecule.
Formal charge of the an atom = $\text{Valence electron - }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{bonding electrons - nonbonding electrons}\text{.}$
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is asked to calculate the formal charge of an ozone molecule.
- There are three oxygen atoms present in the structure of the ozone molecule.
- The structure of ozone is as follows:

- The formal charge of the oxygen 1 is as follows.
- Formal charge of the oxygen atom 1= $\text{Valence electron - }\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{bonding electrons - nonbonding electrons}\text{.}$
Formal charge of the oxygen atom 1= $\text{6 - }\dfrac{\text{4}}{\text{2}}\text{ - 4 = 0}$
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 1 is zero.
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 2 = $\text{6 - }\dfrac{\text{6}}{\text{2}}\text{ - 2 = 1}$
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 2 is ‘1’.
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 3 = $\text{6 - }\dfrac{\text{2}}{\text{2}}\text{ - 6 = -1}$
- The formal charge on oxygen atom 3 is ‘-1’.
- Now the total formal charge of the ozone = 0 + 1 - 1 = 0
- Therefore the formal charge of ozone is ‘0’.
Note: The formal charge of a molecule is equal to the sum of the formal charge of all the individual atoms present in the given molecule. The formal charge of the atoms is going to depend on the valence electrons, nodding electrons, and non-bonding electrons present in the given molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




