
How do I calculate the bond order of $ H_2^ + $ and $ H_2^ - $ ?
Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint : To calculate the bond order of a diatomic species, we’ll have to refer to its Molecular orbital Diagram. The MO Diagram of Hydrogen Molecule consists of one Bonding and one Anti Bonding Orbitals.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We are given two species: $ H_2^ + $ and $ H_2^ - $ . The bond order is defined as the difference between the number of electrons in Bonding MO (B) and antibonding MO (AB). The formula can be given as:
$ Bond{\text{ Order}} = \dfrac{1}{2}(B - AB) $
Consider a neutral Hydrogen Molecules which consists of $ 2 $ electrons in total. The MO diagram is drawn as follows.
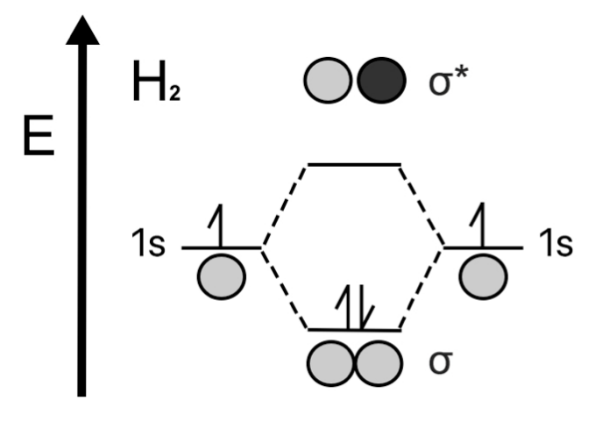
The bond order of neutral Hydrogen Molecule is $ = \dfrac{1}{2}(2 - 0) = 1 $
Hence it has a single bond between two hydrogen atoms.
In $ H_2^ + $ one atom is lost, which means that it has only one electron left. That electron will be in the bonding MO. The bond order of this molecule is $ = \dfrac{1}{2}(1 - 0) = 0.5 $
The bond order of $ H_2^ + $ is $ 0.5 $ .
In $ H_2^ - $ one electron is gained. Hence there are two electrons in bonding and one in antibonding MO. Total three electrons present in total. The bond order can be calculated as $ = \dfrac{1}{2}(2 - 1) = 0.5 $
The bond order of $ H_2^ - $ is also $ 0.5 $ .
The bond order of $ H_2^ - $ and $ H_2^ + $ is the same. In $ H_2^ + $ the electrons are present in the bonding MO only, hence it’ll be more stable and will have higher energy than $ H_2^ - $ . In $ H_2^ - $ there is one electron in the antibonding MO, hence the energy and stability are reduced.
Note :
Bond order is inversely proportional to bond length. Higher the bond order, the distance between the atoms will be less, hence the Bond length will reduce. But bond order and bond energy are directly proportional. The more the bond order, the more the Bond energy.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We are given two species: $ H_2^ + $ and $ H_2^ - $ . The bond order is defined as the difference between the number of electrons in Bonding MO (B) and antibonding MO (AB). The formula can be given as:
$ Bond{\text{ Order}} = \dfrac{1}{2}(B - AB) $
Consider a neutral Hydrogen Molecules which consists of $ 2 $ electrons in total. The MO diagram is drawn as follows.

The bond order of neutral Hydrogen Molecule is $ = \dfrac{1}{2}(2 - 0) = 1 $
Hence it has a single bond between two hydrogen atoms.
In $ H_2^ + $ one atom is lost, which means that it has only one electron left. That electron will be in the bonding MO. The bond order of this molecule is $ = \dfrac{1}{2}(1 - 0) = 0.5 $
The bond order of $ H_2^ + $ is $ 0.5 $ .
In $ H_2^ - $ one electron is gained. Hence there are two electrons in bonding and one in antibonding MO. Total three electrons present in total. The bond order can be calculated as $ = \dfrac{1}{2}(2 - 1) = 0.5 $
The bond order of $ H_2^ - $ is also $ 0.5 $ .
The bond order of $ H_2^ - $ and $ H_2^ + $ is the same. In $ H_2^ + $ the electrons are present in the bonding MO only, hence it’ll be more stable and will have higher energy than $ H_2^ - $ . In $ H_2^ - $ there is one electron in the antibonding MO, hence the energy and stability are reduced.
Note :
Bond order is inversely proportional to bond length. Higher the bond order, the distance between the atoms will be less, hence the Bond length will reduce. But bond order and bond energy are directly proportional. The more the bond order, the more the Bond energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




