
Calculate the area of the quadrilateral ABCD in which \[\angle A = {90^0}\], AB = 16 cm, AD = 12 cm and BC = CD =12.5 cm
\[
A.{\text{ 171c}}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
B.{\text{ 185c}}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
C.{\text{ 191c}}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
D.{\text{ 201c}}{{\text{m}}^2} \\
\]
Answer
616.8k+ views
Hint: First of all, Here we have to draw the diagram for quadrilateral ABCD. And to find the area of the quadrilateral we need to divide the quadrilateral into two triangles and then find the area of triangles by using the Pythagorean theorem and Heron’s formula.
Complete step-by-step answer:
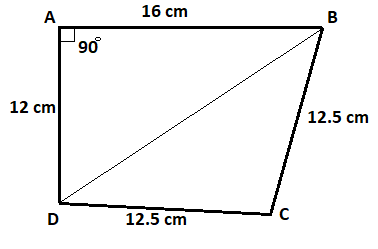
Now as we can see from the above figure ABCD that area of the quadrilateral ABCD = Area of the triangle ABD + Area of the triangle DBC.
As we now see from the above figure, the triangle ABD is the Pythagoras triangle because its one angle (angle A) is equal to \[{90^0}\].
And we know that the area of a Pythagoras triangle is calculated as \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times \](base length)\[ \times \](perpendicular height length).
So, the area of triangle ABD will be equal to \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times AB \times AD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 16 \times 12 = 96{\text{ }}c{m^2}\]
And we know that according to the Pythagorean theorem if XYZ is a Pythagoras triangle, right angled at Y. Then the square of its hypotenuse (XZ) is equal to the sum of squares of its other two sides (XY and YZ).
So, applying Pythagorean theorem in triangle ABD. We get,
\[
B{D^2} = A{B^2} + A{D^2} \\
B{D^2} = {\left( {16} \right)^2} + {\left( {12} \right)^2} = 256 + 144 = 400 \\
\]
So, BD = 20 cm
Now we had to find the area of triangle DBC.
So, we can find the area of triangle DBS by using Heron’ formula which states that if a, b and c are the sides of any triangle then s = \[\dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2}\]. And the area of this triangle is equal to \[\sqrt {s\left( {s - a} \right)\left( {s - b} \right)\left( {s - c} \right)} \].
So, applying Heron’s formula to find the area of triangle DBC.
s = \[\dfrac{{20 + 12.5 + 12.5}}{2} = 22.5\]
And area of triangle DBC = \[\sqrt {22.5\left( {22.5 - 20} \right)\left( {22.5 - 12.5} \right)\left( {22.5 - 12.5} \right)} = \sqrt {22.5 \times 2.5 \times 10 \times 10} = \sqrt {5625} = 75{\text{ }}c{m^2}\]
So, the area of quadrilateral ABCD will be = 96 + 75 = \[{\text{171c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Hence, the correct option will be A.
Note: Whenever we come up with this type of problem we can break the area of the quadrilateral into an area of different triangles and then find the area of the right-angled triangle. After that we have to find the unknown side of the right-angled triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem. After that we will find the area of another triangle by using Heron’s formula. This will be the easiest and most efficient way to find the solution to the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Now as we can see from the above figure ABCD that area of the quadrilateral ABCD = Area of the triangle ABD + Area of the triangle DBC.
As we now see from the above figure, the triangle ABD is the Pythagoras triangle because its one angle (angle A) is equal to \[{90^0}\].
And we know that the area of a Pythagoras triangle is calculated as \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times \](base length)\[ \times \](perpendicular height length).
So, the area of triangle ABD will be equal to \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times AB \times AD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 16 \times 12 = 96{\text{ }}c{m^2}\]
And we know that according to the Pythagorean theorem if XYZ is a Pythagoras triangle, right angled at Y. Then the square of its hypotenuse (XZ) is equal to the sum of squares of its other two sides (XY and YZ).
So, applying Pythagorean theorem in triangle ABD. We get,
\[
B{D^2} = A{B^2} + A{D^2} \\
B{D^2} = {\left( {16} \right)^2} + {\left( {12} \right)^2} = 256 + 144 = 400 \\
\]
So, BD = 20 cm
Now we had to find the area of triangle DBC.
So, we can find the area of triangle DBS by using Heron’ formula which states that if a, b and c are the sides of any triangle then s = \[\dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2}\]. And the area of this triangle is equal to \[\sqrt {s\left( {s - a} \right)\left( {s - b} \right)\left( {s - c} \right)} \].
So, applying Heron’s formula to find the area of triangle DBC.
s = \[\dfrac{{20 + 12.5 + 12.5}}{2} = 22.5\]
And area of triangle DBC = \[\sqrt {22.5\left( {22.5 - 20} \right)\left( {22.5 - 12.5} \right)\left( {22.5 - 12.5} \right)} = \sqrt {22.5 \times 2.5 \times 10 \times 10} = \sqrt {5625} = 75{\text{ }}c{m^2}\]
So, the area of quadrilateral ABCD will be = 96 + 75 = \[{\text{171c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Hence, the correct option will be A.
Note: Whenever we come up with this type of problem we can break the area of the quadrilateral into an area of different triangles and then find the area of the right-angled triangle. After that we have to find the unknown side of the right-angled triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem. After that we will find the area of another triangle by using Heron’s formula. This will be the easiest and most efficient way to find the solution to the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




