
How do I calculate the area of a hexagon?
Answer
546.6k+ views
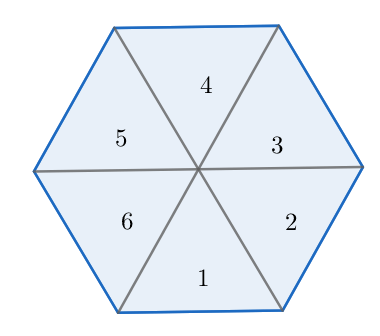
Hint: At first, we join all the opposite vertices of the hexagon. This gives rise to six equilateral and congruent triangles. We need to find the area of one of the triangles and multiply it with $6$ .
Complete step by step solution:
Hexagon can be of two types: regular and irregular. Regular hexagon is the one in which the lengths of all the sides are the same. We now join the opposite vertices of the hexagon. So, we get six diagonals and six internal triangles. Now, since the hexagon is regular, the six sides must subtend equal angles at the centre of the hexagon. The sum of the angles subtended is definitely ${{360}^{\circ }}$ and the six subtended angles being equal, each of them must be $\dfrac{{{360}^{\circ }}}{6}={{60}^{\circ }}$ . Also, all the diagonals are of equal lengths. This means that the sides of the internal triangles must also be same. This can only be possible if all the six triangles are equilateral.
Thus, the six triangles are equilateral and congruent. So, to find out the area of a regular hexagon, we need to only find out the area of one of the six equilateral triangles and multiply the area with $6$ . Now, let the side of the regular hexagon be of length $x$ (say). Then, the side of the equilateral triangle must also be $x$ . We know that if the length of the side of an equilateral triangle is $x$ , the formula for its area will be,
$area\left( \Delta \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{x}^{2}}$
The area of the hexagon will then be,
$\Rightarrow area\left( hexagon \right)=6\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}{{x}^{2}}$
Therefore, we have seen how to find the area of a regular hexagon.
Note: These types of problems are very easy, there are less chances of mistakes. Nevertheless, we should be careful and should remember to multiply the area of the equilateral triangle with $6$ . Also, there is a predefined formula for the area of a regular hexagon, which is $\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}{{x}^{2}}$ where, $x$ is the length of the side of the hexagon.

Complete step by step solution:
Hexagon can be of two types: regular and irregular. Regular hexagon is the one in which the lengths of all the sides are the same. We now join the opposite vertices of the hexagon. So, we get six diagonals and six internal triangles. Now, since the hexagon is regular, the six sides must subtend equal angles at the centre of the hexagon. The sum of the angles subtended is definitely ${{360}^{\circ }}$ and the six subtended angles being equal, each of them must be $\dfrac{{{360}^{\circ }}}{6}={{60}^{\circ }}$ . Also, all the diagonals are of equal lengths. This means that the sides of the internal triangles must also be same. This can only be possible if all the six triangles are equilateral.
Thus, the six triangles are equilateral and congruent. So, to find out the area of a regular hexagon, we need to only find out the area of one of the six equilateral triangles and multiply the area with $6$ . Now, let the side of the regular hexagon be of length $x$ (say). Then, the side of the equilateral triangle must also be $x$ . We know that if the length of the side of an equilateral triangle is $x$ , the formula for its area will be,
$area\left( \Delta \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{x}^{2}}$
The area of the hexagon will then be,
$\Rightarrow area\left( hexagon \right)=6\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{x}^{2}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}{{x}^{2}}$
Therefore, we have seen how to find the area of a regular hexagon.
Note: These types of problems are very easy, there are less chances of mistakes. Nevertheless, we should be careful and should remember to multiply the area of the equilateral triangle with $6$ . Also, there is a predefined formula for the area of a regular hexagon, which is $\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}{{x}^{2}}$ where, $x$ is the length of the side of the hexagon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





