
${{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}$ shows how many benzenoid structural isomers?
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint:Compounds that have identical chemical formulas are known as isomers of each other. Benzenoid structural isomers mean the isomers that have benzene ring structure in common but the substituents are different.
Complete step by step answer:
Compounds that have identical chemical formulas are known as isomers of each other.
Benzenoid structural isomers mean the isomers that have benzene ring structure in common but the substituents are different.
${{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}$ is the chemical formula. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}$ shows five benzenoid structural isomers.
1.Benzyl alcohol
2.Anisole
3.o-cresol
4.m-cresol
5.p-cresol
The structures of benzenoid structural isomers of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}$ are as follows:
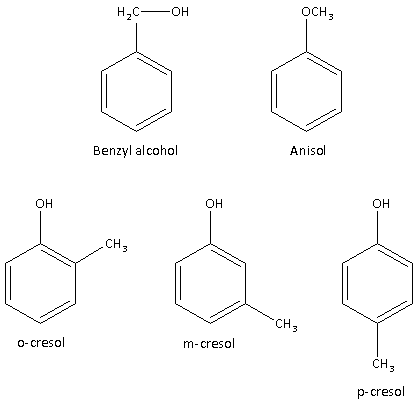
Thus, $C_7H_8O$ shows five benzenoid structural isomers.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Additional Information:
The chemical compounds have the same chemical formula but different structures are known as isomers of each other. There are two types of isomerisms:
Structural isomerism: In structural isomerism, the functional groups and the atoms of the isomers are linked in different ways. There are six types of structural isomerisms:
Chain or skeletal isomerism: Chain isomers have different branched structures.
Position isomerism: Position isomers have different positions of functional group or substituent atoms.
Functional or functional group isomerism: Functional isomers have the same chemical formula but different functional groups attached to them.
Metamerism: Metamers have different alkyl chains on each side of the functional group.
Tautomerism: Tautomers have different positions of protons and electrons.
Ring chain isomerism: in ring chain isomerism, one isomer has an open chain structure and the other isomer has a closed ring structure.
Stereo isomerism: In stereoisomerism, the chemical formula is the same but the orientation of atoms in the molecule in three-dimensional space is different. There are two types of stereoisomerism:
Geometric isomerism: Geometric isomers have different arrangements of atoms in three-dimensional space.
Optical isomerism: Optical isomers have the same bonds but different arrangement of atoms forming non-superimposable mirror images.
Note: In the compounds benzyl alcohol, anisole, o-cresol, m-cresol and p-cresol, the benzene ring has the chemical formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\]. The remaining ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ group is attached in different ways to get different isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
Compounds that have identical chemical formulas are known as isomers of each other.
Benzenoid structural isomers mean the isomers that have benzene ring structure in common but the substituents are different.
${{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}$ is the chemical formula. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}$ shows five benzenoid structural isomers.
1.Benzyl alcohol
2.Anisole
3.o-cresol
4.m-cresol
5.p-cresol
The structures of benzenoid structural isomers of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}$ are as follows:

Thus, $C_7H_8O$ shows five benzenoid structural isomers.
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Additional Information:
The chemical compounds have the same chemical formula but different structures are known as isomers of each other. There are two types of isomerisms:
Structural isomerism: In structural isomerism, the functional groups and the atoms of the isomers are linked in different ways. There are six types of structural isomerisms:
Chain or skeletal isomerism: Chain isomers have different branched structures.
Position isomerism: Position isomers have different positions of functional group or substituent atoms.
Functional or functional group isomerism: Functional isomers have the same chemical formula but different functional groups attached to them.
Metamerism: Metamers have different alkyl chains on each side of the functional group.
Tautomerism: Tautomers have different positions of protons and electrons.
Ring chain isomerism: in ring chain isomerism, one isomer has an open chain structure and the other isomer has a closed ring structure.
Stereo isomerism: In stereoisomerism, the chemical formula is the same but the orientation of atoms in the molecule in three-dimensional space is different. There are two types of stereoisomerism:
Geometric isomerism: Geometric isomers have different arrangements of atoms in three-dimensional space.
Optical isomerism: Optical isomers have the same bonds but different arrangement of atoms forming non-superimposable mirror images.
Note: In the compounds benzyl alcohol, anisole, o-cresol, m-cresol and p-cresol, the benzene ring has the chemical formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\]. The remaining ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$ group is attached in different ways to get different isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




