
\[{{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{CHO}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{NaCN}}/{\text{HCl}}}}\left( {\text{X}} \right)\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}/{{\text{H}}^ + }/\Delta }}\] product of the reaction is:
A) Optically inactive acid
B) Optically inactive \[\alpha - {\text{hydroxy acid}}\]
C) Racemic mixture of two optically active \[\alpha - {\text{hydroxy acid}}\]
D) Racemic mixture of two optically active secondary alcohols.
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint:
If the formation of chiral carbon occurs in the compound X then there will be optical isomerism. The hydrolysis of cyanide gives us carboxylic acids.
Complete step by step solution:
When benzaldehyde is treated with sodium cyanide along with hydrochloric acid then additional reaction occurs. Cyanide gets attached to carbon and hydrogen gets attached to the oxygen. The whole reaction occurs as:
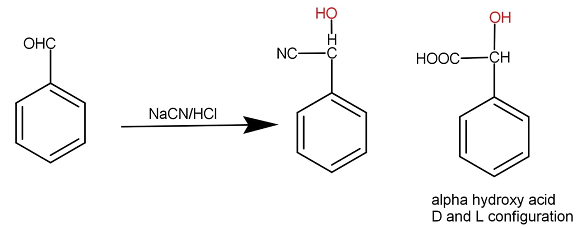
Carbon is tetravalent that means carbon forms 4 bonds. A chiral carbon is that carbon which has four different groups attached to it. As we can see that the compound X formed has all different groups attached hence it is chiral in nature. A chiral molecule shows optical activity. Optical activity is the property of compounds to rotate the plane polarised light towards the right or left side. If a molecule rotates the plane polarised light toward the right then the molecule is said to be dextrorotatory and if it rotates the plane polarised light to the lift then it is said to be Laevo rotatory. These two isomers are formed. In the above molecule too the two isomers will form. A racemic mixture is a mixture when both the isomers are present in the same proportion in the mixture. They both cancel their rotation and the solution becomes inactive in spite of the presence of optically active compounds.
The acids with racemic mixture forms, hence the correct option is C that is Racemic mixture of two optically active \[\alpha - {\text{hydroxy acid}}\].
Note:
The optically activity is also defined in terms of R and S isomers. Optical isomers or stereo isomerism arises due to difference in the arrangement in 3 dimensional spaces of the constituent’s species.
If the formation of chiral carbon occurs in the compound X then there will be optical isomerism. The hydrolysis of cyanide gives us carboxylic acids.
Complete step by step solution:
When benzaldehyde is treated with sodium cyanide along with hydrochloric acid then additional reaction occurs. Cyanide gets attached to carbon and hydrogen gets attached to the oxygen. The whole reaction occurs as:

Carbon is tetravalent that means carbon forms 4 bonds. A chiral carbon is that carbon which has four different groups attached to it. As we can see that the compound X formed has all different groups attached hence it is chiral in nature. A chiral molecule shows optical activity. Optical activity is the property of compounds to rotate the plane polarised light towards the right or left side. If a molecule rotates the plane polarised light toward the right then the molecule is said to be dextrorotatory and if it rotates the plane polarised light to the lift then it is said to be Laevo rotatory. These two isomers are formed. In the above molecule too the two isomers will form. A racemic mixture is a mixture when both the isomers are present in the same proportion in the mixture. They both cancel their rotation and the solution becomes inactive in spite of the presence of optically active compounds.
The acids with racemic mixture forms, hence the correct option is C that is Racemic mixture of two optically active \[\alpha - {\text{hydroxy acid}}\].
Note:
The optically activity is also defined in terms of R and S isomers. Optical isomers or stereo isomerism arises due to difference in the arrangement in 3 dimensional spaces of the constituent’s species.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




