
By pulling the cord of a yo-yo just fast enough, a person manages to make the yo-yo spin counter-clockwise, while remaining at a constant height above the floor. Denoting the weight of the yo-yo by $W$ . The radius of the inner drum on which the cord is wound by $r$ , and the radius of gyration of the yo-yo by $k$ , determine;
(A) The tension in the cord
(B) The angular acceleration of the yo-yo
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint In this question, we need to determine the direction of the acceleration of the yo-yo. Newton’s laws of motion and the relation between the moment of inertia, torque, and the acceleration of the body are used to solve the question
Complete Step-by-step solution
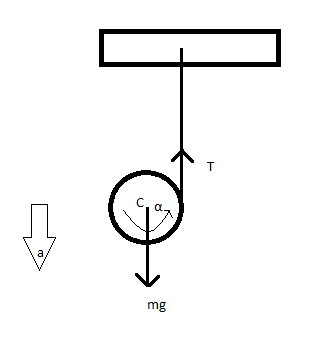
When the yo-yo is released from the hand, then the hand works as rigid support and the wrapped string starts unwrapping so that the yo-yo gains some instant. The linear acceleration $a$ in a vertically downward direction. Angular acceleration $\alpha $ about its center. The force $mg$ works vertically downward. The tension $T$ in an upward direction.
From FBD applying force equation,
$mg - T = ma$ ................... $\left( 1 \right)$
Applying torque equation about the center $C$, $\tau = I\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow T \times r + mg\left( 0 \right) = I\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow Tr = I\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{I\alpha }}{r}$..................... $\left( 2 \right)$
Moment of Inertia for yo-yo is:
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{1}{2}m{r^2}$
On putting the value of $I$in the equation$\left( 2 \right)$;
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{1}{2}m{r^2} \times \left( {\dfrac{\alpha }{r}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times r\alpha $
$ \therefore T = \dfrac{1}{2}ma$ $\left[ {\because a = r\alpha } \right]$............... $\left( 3 \right)$
On putting the value $T$ into the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ ;
$ \Rightarrow mg - \dfrac{1}{2}ma = ma$
$ \therefore mg = ma + \dfrac{1}{2}ma$
Taking $m$ common out and get canceled;
$ \Rightarrow g = \dfrac{3}{2}a$
$ \therefore a = \dfrac{2}{3}g$..............................$\left( 4 \right)$
As we know, the formula for angular acceleration is;
$ \therefore \alpha = \dfrac{a}{r}$
Substituting the value of $a$ from the equation$\left( 4 \right)$;
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{2g}}{{3r}}$
Hence, the Tension in the cord is $\dfrac{1}{2}ma$ and the angular acceleration of the yo-yo is $\left( {\dfrac{{2g}}{{3r}}} \right)$ .
Additional Information The torque of all the forces is zero, which passes through the point at which the torque has been computed. When a force is applied to the body, not only the applied force is acting, there are many other forces like gravitational force f and the normal force N that balances the other force. Therefore in the force equation
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{F_{net}}} = $$m\overrightarrow a $,
$ \therefore {\overrightarrow F _{net}} = {\overrightarrow F _{ex}} + \overrightarrow F g + \overrightarrow f + \overrightarrow N $
Note Students should keep in mind that the weight of an object is the gravitational force applied in a downward direction. Students also need to know that the unbalanced force is the cause of motion. So that they can easily compare the forces exerted on a mechanical system and determine the direction of motion.
Complete Step-by-step solution

When the yo-yo is released from the hand, then the hand works as rigid support and the wrapped string starts unwrapping so that the yo-yo gains some instant. The linear acceleration $a$ in a vertically downward direction. Angular acceleration $\alpha $ about its center. The force $mg$ works vertically downward. The tension $T$ in an upward direction.
From FBD applying force equation,
$mg - T = ma$ ................... $\left( 1 \right)$
Applying torque equation about the center $C$, $\tau = I\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow T \times r + mg\left( 0 \right) = I\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow Tr = I\alpha $
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{I\alpha }}{r}$..................... $\left( 2 \right)$
Moment of Inertia for yo-yo is:
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{1}{2}m{r^2}$
On putting the value of $I$in the equation$\left( 2 \right)$;
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{1}{2}m{r^2} \times \left( {\dfrac{\alpha }{r}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{1}{2}m \times r\alpha $
$ \therefore T = \dfrac{1}{2}ma$ $\left[ {\because a = r\alpha } \right]$............... $\left( 3 \right)$
On putting the value $T$ into the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ ;
$ \Rightarrow mg - \dfrac{1}{2}ma = ma$
$ \therefore mg = ma + \dfrac{1}{2}ma$
Taking $m$ common out and get canceled;
$ \Rightarrow g = \dfrac{3}{2}a$
$ \therefore a = \dfrac{2}{3}g$..............................$\left( 4 \right)$
As we know, the formula for angular acceleration is;
$ \therefore \alpha = \dfrac{a}{r}$
Substituting the value of $a$ from the equation$\left( 4 \right)$;
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{2g}}{{3r}}$
Hence, the Tension in the cord is $\dfrac{1}{2}ma$ and the angular acceleration of the yo-yo is $\left( {\dfrac{{2g}}{{3r}}} \right)$ .
Additional Information The torque of all the forces is zero, which passes through the point at which the torque has been computed. When a force is applied to the body, not only the applied force is acting, there are many other forces like gravitational force f and the normal force N that balances the other force. Therefore in the force equation
$ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {{F_{net}}} = $$m\overrightarrow a $,
$ \therefore {\overrightarrow F _{net}} = {\overrightarrow F _{ex}} + \overrightarrow F g + \overrightarrow f + \overrightarrow N $
Note Students should keep in mind that the weight of an object is the gravitational force applied in a downward direction. Students also need to know that the unbalanced force is the cause of motion. So that they can easily compare the forces exerted on a mechanical system and determine the direction of motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




