
Bulliform or motor cells are present in
(a)Dicot stem
(b)Upper epidermis of dicot leaves
(c)Lower epidermis of monocot leaves
(d)Upper epidermis of monocots leaves
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: They are present in the grass and grass-like flowering plants. This is one layer of cells containing few or no chloroplasts. The cells are quite transparent and permit most of the light that strikes them to undergo the underlying cells.
Complete answer:
Bulliform cells or motor cells are present on the upper surface of the leaves of many monocots. They are large, bubble-shaped epidermal cells that occur in groups on the upper surface of the leaves of the many monocots. They are colourless as there are few or no chloroplasts. They have central vacuole filled with water. They are hygroscopic (water absorbing) in nature, they absorb water and store in the vacuoles. They have an important role in leaf folding and unfolding. Example- grasses (they are present on the upper surface of the grass (monocots).
Additional Information: During drought, the loss of water through vacuoles induces the reduced bulliform cells to permit the leaves of the many grass species to shut and the two edges of the grass blade fold toward each other. Once enough water is available, these cells enlarge and the leaves open again.
Folded leaves offer less exposure to sunlight, in order that they are heated less thus reducing evaporation and conserving the remaining water within the plant. Bulliform cells occur on the leaves of a large variety of monocotyledon families but are probably best known in grasses.
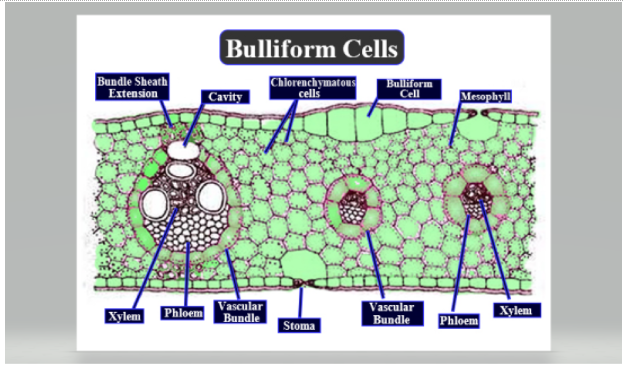
So, the correct answer is ‘Upper epidermis of monocots leaves’
Note: It is unclear if this mechanism applies in all monocots, however, or whether other components such as fibers are the pieces controlling the folding and unfolding of the leaf. What is observed is that the turgidity of the bulliform cells often coincide with the folding activity, though there are cases where folding happens long after the cells have gone turgid.
Complete answer:
Bulliform cells or motor cells are present on the upper surface of the leaves of many monocots. They are large, bubble-shaped epidermal cells that occur in groups on the upper surface of the leaves of the many monocots. They are colourless as there are few or no chloroplasts. They have central vacuole filled with water. They are hygroscopic (water absorbing) in nature, they absorb water and store in the vacuoles. They have an important role in leaf folding and unfolding. Example- grasses (they are present on the upper surface of the grass (monocots).
Additional Information: During drought, the loss of water through vacuoles induces the reduced bulliform cells to permit the leaves of the many grass species to shut and the two edges of the grass blade fold toward each other. Once enough water is available, these cells enlarge and the leaves open again.
Folded leaves offer less exposure to sunlight, in order that they are heated less thus reducing evaporation and conserving the remaining water within the plant. Bulliform cells occur on the leaves of a large variety of monocotyledon families but are probably best known in grasses.

So, the correct answer is ‘Upper epidermis of monocots leaves’
Note: It is unclear if this mechanism applies in all monocots, however, or whether other components such as fibers are the pieces controlling the folding and unfolding of the leaf. What is observed is that the turgidity of the bulliform cells often coincide with the folding activity, though there are cases where folding happens long after the cells have gone turgid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




