
How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps?
1. Propanone to Propene
2. Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
3. Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
4. Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone
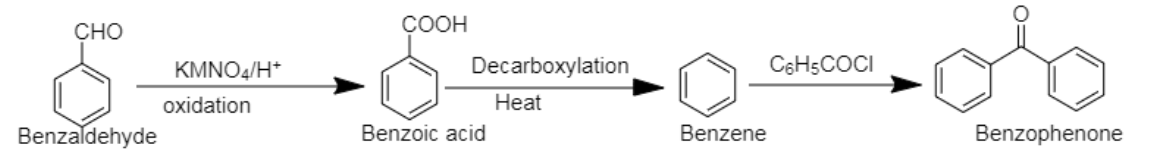
5. Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone
6. Bromobenzene to 1-Phenylethanol
7. Benzaldehyde to 3-Phenylpropan-1-ol
8. Benzaldehyde to $\alpha - $Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
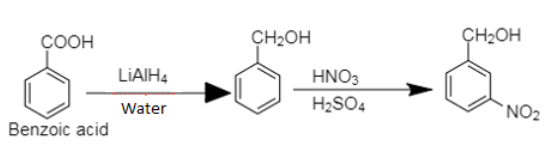
9. Benzoic acid to m-Nitrobenzyl alcohol
Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint:The chemical reactions mentioned in the question are either involved aldehydes or ketones or both. Aldehydes and ketones belong to the category of organic compounds, containing a carbonyl group that is a carbon atom in the molecule attached to one double bonded oxygen atom. For both aldehydes and ketones, the carbonyl group serves as the functional group.
Complete answer:
In the chemical conversions mentioned above, ketone is converted to aldehyde or vice-versa or aldehyde or a ketone undergoing a chemical reaction to produce different compounds. Let us see how these conversions are carried out in single or two steps.
1. Propanone, commonly known as acetone is a ketone containing 3 carbon atoms and one carbonyl group. The chemical formula of propanone is $[C{H_3}COC{H_3}]$.
Propene, an alkene, an unsaturated organic compound, containing one double bond.
Propanone is converted to 2-propanol on reduction by metal hydride in ether followed by dehydration to form propene.
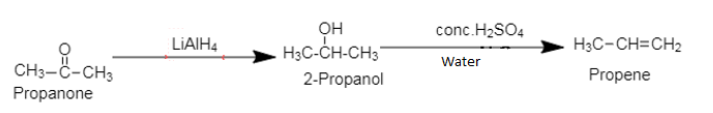
2. The compounds containing carboxylic group ($[ - COOH]$) as a functional group, that is compounds containing a carbonyl group bonded to the hydroxyl group are categorised as carboxylic acids.
Benzoic acid is a carboxylic acid of benzene.
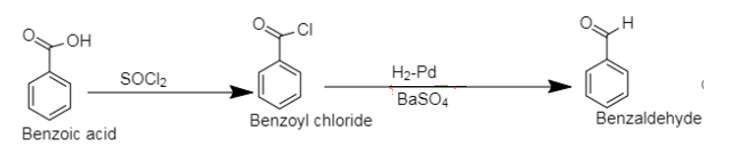
In the first step, chlorination of benzoic acid by thionyl chloride leads to the formation of benzoyl chloride followed by reduction using Rosenmund’s reduction. Rosenmund’s reduction is carried out using hydrogen over palladium, poisoned by barium sulphate which selectively reduces acyl chloride to aldehyde.
3. Ethanol, commonly known as ethyl alcohol or spirit is an alcohol. The compound, 3-hydroxybutanal is an aldol, a compound containing both hydroxyl ($[ - OH$]) group and aldehyde group ($[ - CHO$]).
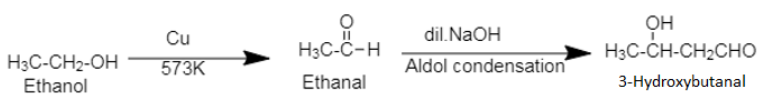
Ethanol when heated with copper produces an aldehyde, which then undergoes Aldol condensation to form 3-hydroxybutanal. During Aldol condensation, an alcohol with at least one α-H atom is converted into $\beta - $hydroxy aldehyde in presence of dilute alkali. The dilute alkali acts as a catalyst in Aldol condensation.
4. Benzene, an aromatic compound of molecular formula $[{C_6}{H_6}$]. The compound m-nitroacetophenone is a derivative of acetophenone with molecular formula, $[{C_8}{H_7}N{O_3}$].
Through Friedel-Craft Acylation, benzene is first converted into acetophenone, followed by treatment with conc. nitric acid and conc. sulphuric acid to insert nitro group in the molecule.
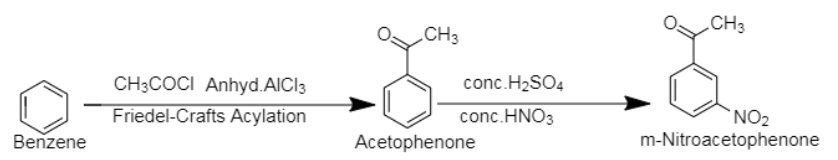
Friedel-Craft Acylation is an aromatic substitution reaction in which an acyl group is inserted on one of the carbon atoms of the aromatic ring.
Benzophenone is an aromatic compound containing two phenyl rings bonded with a carbonyl group.
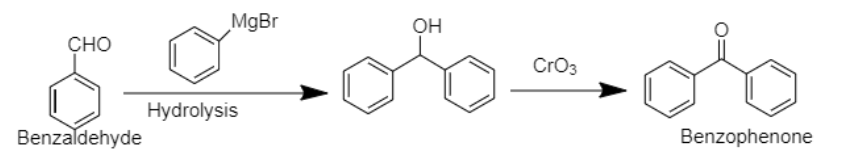
5. Benzophenone can be prepared using benzaldehyde by reacting it with Grignard reagent, followed by hydrolysis. In the next step, the compound formed can be oxidised using chromium trioxide to obtain benzophenone.
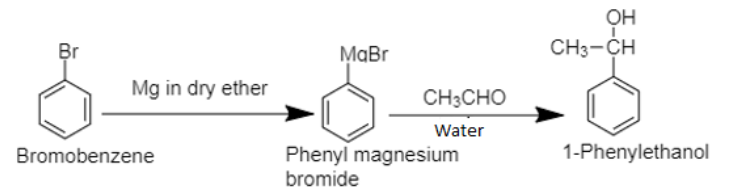
6. The bromobenzene, benzene’s halogen derivative, when treated with Grignard’s reagent yields Phenyl magnesium bromide in the first step. In the second step, phenyl magnesium bromide is treated with acetaldehyde and water respectively to produce 1-phenylethanol.
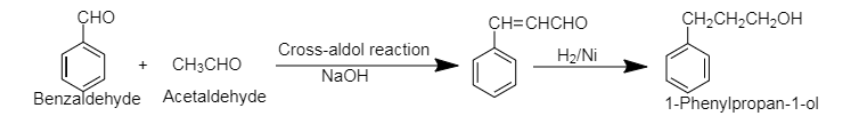
7. The cross-aldol condensation reaction between benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde produces cross aldol product which on catalytic hydrogenation yields 3-Phenylpropan-1-ol. The cross-aldol condensation takes place between either two different aldehydes or ketones.
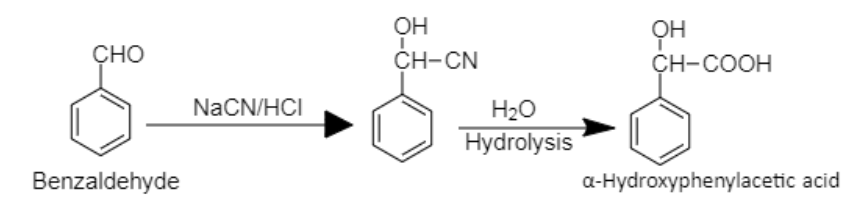
8. Benzaldehyde can be converted into $\alpha - $Hydroxyphenylacetic acid by insertion of cyano group followed by hydrolysis.
9. Benzoic acid on reduction followed by nitration produces m-nitrobenzyl alcohol.
Note:
1. While converting propanone to propene, reduction of propanone can be carried out by using $[NaB{H_4}]$ or $[{H_2}/Pt$].
2. The chlorination of benzoic acid to benzoyl chloride can be carried out using $[PC{l_5}]$ .
3. Ethanol can be converted into ethanal by using chromium trioxide, $[Cr{O_3}]$.
4. Benzaldehyde can be converted into Benzophenone by oxidation of benzaldehyde by $[KMN{O_4}$], followed by decarboxylation and benzoylation respectively.
Complete answer:
In the chemical conversions mentioned above, ketone is converted to aldehyde or vice-versa or aldehyde or a ketone undergoing a chemical reaction to produce different compounds. Let us see how these conversions are carried out in single or two steps.
1. Propanone, commonly known as acetone is a ketone containing 3 carbon atoms and one carbonyl group. The chemical formula of propanone is $[C{H_3}COC{H_3}]$.
Propene, an alkene, an unsaturated organic compound, containing one double bond.
Propanone is converted to 2-propanol on reduction by metal hydride in ether followed by dehydration to form propene.

2. The compounds containing carboxylic group ($[ - COOH]$) as a functional group, that is compounds containing a carbonyl group bonded to the hydroxyl group are categorised as carboxylic acids.
Benzoic acid is a carboxylic acid of benzene.

In the first step, chlorination of benzoic acid by thionyl chloride leads to the formation of benzoyl chloride followed by reduction using Rosenmund’s reduction. Rosenmund’s reduction is carried out using hydrogen over palladium, poisoned by barium sulphate which selectively reduces acyl chloride to aldehyde.
3. Ethanol, commonly known as ethyl alcohol or spirit is an alcohol. The compound, 3-hydroxybutanal is an aldol, a compound containing both hydroxyl ($[ - OH$]) group and aldehyde group ($[ - CHO$]).

Ethanol when heated with copper produces an aldehyde, which then undergoes Aldol condensation to form 3-hydroxybutanal. During Aldol condensation, an alcohol with at least one α-H atom is converted into $\beta - $hydroxy aldehyde in presence of dilute alkali. The dilute alkali acts as a catalyst in Aldol condensation.
4. Benzene, an aromatic compound of molecular formula $[{C_6}{H_6}$]. The compound m-nitroacetophenone is a derivative of acetophenone with molecular formula, $[{C_8}{H_7}N{O_3}$].
Through Friedel-Craft Acylation, benzene is first converted into acetophenone, followed by treatment with conc. nitric acid and conc. sulphuric acid to insert nitro group in the molecule.

Friedel-Craft Acylation is an aromatic substitution reaction in which an acyl group is inserted on one of the carbon atoms of the aromatic ring.
Benzophenone is an aromatic compound containing two phenyl rings bonded with a carbonyl group.
5. Benzophenone can be prepared using benzaldehyde by reacting it with Grignard reagent, followed by hydrolysis. In the next step, the compound formed can be oxidised using chromium trioxide to obtain benzophenone.

6. The bromobenzene, benzene’s halogen derivative, when treated with Grignard’s reagent yields Phenyl magnesium bromide in the first step. In the second step, phenyl magnesium bromide is treated with acetaldehyde and water respectively to produce 1-phenylethanol.

7. The cross-aldol condensation reaction between benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde produces cross aldol product which on catalytic hydrogenation yields 3-Phenylpropan-1-ol. The cross-aldol condensation takes place between either two different aldehydes or ketones.

8. Benzaldehyde can be converted into $\alpha - $Hydroxyphenylacetic acid by insertion of cyano group followed by hydrolysis.

9. Benzoic acid on reduction followed by nitration produces m-nitrobenzyl alcohol.

Note:
1. While converting propanone to propene, reduction of propanone can be carried out by using $[NaB{H_4}]$ or $[{H_2}/Pt$].
2. The chlorination of benzoic acid to benzoyl chloride can be carried out using $[PC{l_5}]$ .
3. Ethanol can be converted into ethanal by using chromium trioxide, $[Cr{O_3}]$.
4. Benzaldehyde can be converted into Benzophenone by oxidation of benzaldehyde by $[KMN{O_4}$], followed by decarboxylation and benzoylation respectively.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




