
Bring about the following conversion:
1-pentene to 1-pentyne.
Answer
544.5k+ views
Hint: In the above question, it is asked to convert 1-pentene to 1-pentyne. This can be done by adding bromine to 1-pentene followed by dehydrobromination in the presence of soda amine. This dehydrobromination is an example of double elimination reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the above question since we have to convert 1-pentane to1-pentyne, so we have to first convert it to 1,2-dibromo pentane such that after adding ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$, double elimination takes place resulting in formation of 1-pentyne.
So, the first step include conversion of 1-pentene to 1,2-dibromopentane with the help of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ and ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}$. The above reaction can be illustrated as:
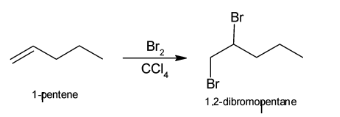
${\text{NaN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ helps in the formation of alkynes from halogens. Treatment of either geminal dihalides (i.e., two halogens on one carbon) or vicinal dihalides (halogens on adjacent carbons) with ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ results in the formation of alkynes. Hence, when vicinal dihalides or 1,2-dibromopentane reacts with
${\text{NaN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$, 1-pentyne is formed.
The above reaction can be illustrated as:
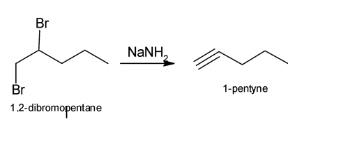
The complete reaction of conversion of 1-pentene to 1-pentyne can be illustrated as:
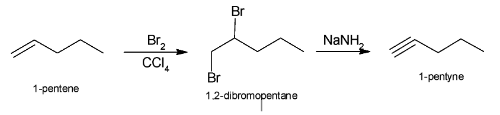
Note:Aromatic compounds require lewis acid like${\text{AlC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ for bromination. But the reaction that will take place will be substitution instead of addition.
Alkanes do not react with ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$.
NaNH2 is a strong base. It can be an excellent nucleophile. It is used for deprotonation of weak acids and also for elimination reactions.
As a strong base, NaNH2 will deprotonate alkynes, alcohols, and a host of other functional groups with acidic protons such as esters and ketones.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the above question since we have to convert 1-pentane to1-pentyne, so we have to first convert it to 1,2-dibromo pentane such that after adding ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$, double elimination takes place resulting in formation of 1-pentyne.
So, the first step include conversion of 1-pentene to 1,2-dibromopentane with the help of ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$ and ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}$. The above reaction can be illustrated as:

${\text{NaN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ helps in the formation of alkynes from halogens. Treatment of either geminal dihalides (i.e., two halogens on one carbon) or vicinal dihalides (halogens on adjacent carbons) with ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ results in the formation of alkynes. Hence, when vicinal dihalides or 1,2-dibromopentane reacts with
${\text{NaN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$, 1-pentyne is formed.
The above reaction can be illustrated as:

The complete reaction of conversion of 1-pentene to 1-pentyne can be illustrated as:

Note:Aromatic compounds require lewis acid like${\text{AlC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ for bromination. But the reaction that will take place will be substitution instead of addition.
Alkanes do not react with ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}$.
NaNH2 is a strong base. It can be an excellent nucleophile. It is used for deprotonation of weak acids and also for elimination reactions.
As a strong base, NaNH2 will deprotonate alkynes, alcohols, and a host of other functional groups with acidic protons such as esters and ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




