
Briefly describe the various types of composite fruits?
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: Fruit is the fleshy or dry ripened ovary of an angiosperm or flowering plant. Angiosperms are characterized by seeds enclosed in a fruit. Fruit is a mature or ripened ovary formed after the fertilization.
Complete answer:
Fruit wall: Fruit wall develops from the wall of the ovary and it can be dry or fleshy. Fruit wall develops in three layers in the basis of thickness and fleshiness:
> Epicarp (outer layer)
> Mesocarp (middle layer)
> Endocarp (inner layer)
Types of fruit:
> Simple fruits: These fruits formed from the syncarpous ovary of the single flower.
> Aggregate fruits: These fruits formed from polycarpellary, apocarpous ovary.
> Multiple fruits: These fruits formed from the entire fluorescence.
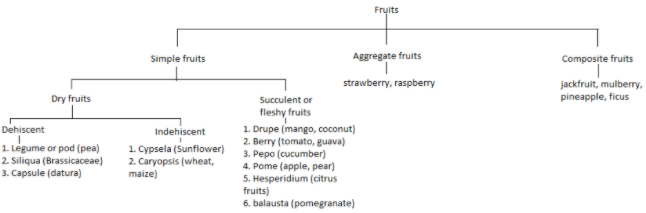
Multiple or Composite Fruits: The multiple fruits develop from the entire fluorescence. There fruits are of two types:
Sorosis: These fruits develop from spike, spadix or catkin inflorescence. Flower fuses together with their sepals or perianth and the whole inflorescence forms a compact mass. e.g., Jackfruit, mulberry and pineapple.
Syconus: These fruits develop from hypanthodium inflorescence. e.g., Ficus species (Fig, gular, banyan, peepal). Fruitlets of these fruits are achenial in nature.
Note: In some plants ovary grows into fruit without fertilization known as Parthenocarpic fruits. Fruits are seedless. e.g., Banana, Grapes. False fruits are the fruits in which any other floral part takes part in fruit formation. e.g., Apple, pear. The fruit which is developed from the ovary is called true fruit. Most of the fruits are true fruits.
Complete answer:
Fruit wall: Fruit wall develops from the wall of the ovary and it can be dry or fleshy. Fruit wall develops in three layers in the basis of thickness and fleshiness:
> Epicarp (outer layer)
> Mesocarp (middle layer)
> Endocarp (inner layer)
Types of fruit:
> Simple fruits: These fruits formed from the syncarpous ovary of the single flower.
> Aggregate fruits: These fruits formed from polycarpellary, apocarpous ovary.
> Multiple fruits: These fruits formed from the entire fluorescence.

Multiple or Composite Fruits: The multiple fruits develop from the entire fluorescence. There fruits are of two types:
Sorosis: These fruits develop from spike, spadix or catkin inflorescence. Flower fuses together with their sepals or perianth and the whole inflorescence forms a compact mass. e.g., Jackfruit, mulberry and pineapple.
Syconus: These fruits develop from hypanthodium inflorescence. e.g., Ficus species (Fig, gular, banyan, peepal). Fruitlets of these fruits are achenial in nature.
Note: In some plants ovary grows into fruit without fertilization known as Parthenocarpic fruits. Fruits are seedless. e.g., Banana, Grapes. False fruits are the fruits in which any other floral part takes part in fruit formation. e.g., Apple, pear. The fruit which is developed from the ovary is called true fruit. Most of the fruits are true fruits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




