
Briefly describe the structure and functions of the nephron with a neat labelled diagram.
Answer
522.7k+ views
Hint: It is the unit of the kidney which helps to clean and detoxify our body. Accumulation of toxic substances can even lead to death. This is the reason dialysis is performed when the kidneys of a person are failing. A single healthy kidney can also help us to survive throughout our life.
Complete answer:
What is a nephron? The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is made up of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle has two parts-glomerulus and a Bowman's capsule. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons per kidney.
Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers- the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, the podocytes of the lining of the capsule.
There is a maximum reabsorption of all the minerals and substances that are not to be flushed out. At the end of the tubule, urine is flushed out which is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.
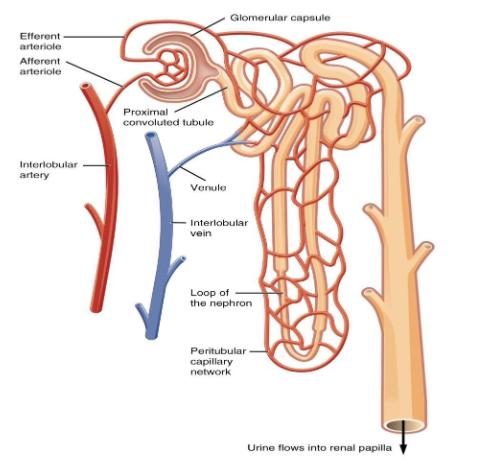
Let us study the different parts of the nephron.
1. Bowman’s capsule- It is a cup-like sac at the beginning of the nephron. It surrounds the glomerulus. It has a visceral cell layer which has thickened membranes.
2. Glomerulus- It is a capillary tuft which receives blood from the renal circulation. The blood is filtered here by ultrafiltration into the bowman’s capsule.
3. The proximal convoluted tubule- It is the first site for the reabsorption of the water and salts into the bloodstream. It occurs by passive diffusion.
4. The Loop of Henle- It is a U-shaped tube having a descendent and ascendant limb. The descending tube is permeable to water whereas the ascending tube is permeable to the ions.
5. Distal Convoluted Tubule- It is the final site for reabsorption. To maintain the blood osmolarity, the water is diffused. The antidiuretic hormone increases the permeability of the tubule.
Functions-
1. The nephron uses four mechanisms to convert blood into the urine. They are filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion.
2. The primary function of nephrons is to remove all waste products from the blood.
3. The blood passes via the glomerulus with high pressure, the small molecules are moved into the glomerular capsules.
4. The cells present in each tube absorb different molecules excluding the glucose, water, and others. It regulates the fluid volume in our body.
Note: A decomposition reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which a single element breaks down into two or more new elements. These decomposition reactions often involve an energy source such as heat, light, or electricity that breaks apart the bonds of elements.
Complete answer:
What is a nephron? The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is made up of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle has two parts-glomerulus and a Bowman's capsule. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons per kidney.
Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers- the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, the podocytes of the lining of the capsule.
There is a maximum reabsorption of all the minerals and substances that are not to be flushed out. At the end of the tubule, urine is flushed out which is composed of water, metabolic waste, and toxins.

Let us study the different parts of the nephron.
1. Bowman’s capsule- It is a cup-like sac at the beginning of the nephron. It surrounds the glomerulus. It has a visceral cell layer which has thickened membranes.
2. Glomerulus- It is a capillary tuft which receives blood from the renal circulation. The blood is filtered here by ultrafiltration into the bowman’s capsule.
3. The proximal convoluted tubule- It is the first site for the reabsorption of the water and salts into the bloodstream. It occurs by passive diffusion.
4. The Loop of Henle- It is a U-shaped tube having a descendent and ascendant limb. The descending tube is permeable to water whereas the ascending tube is permeable to the ions.
5. Distal Convoluted Tubule- It is the final site for reabsorption. To maintain the blood osmolarity, the water is diffused. The antidiuretic hormone increases the permeability of the tubule.
Functions-
1. The nephron uses four mechanisms to convert blood into the urine. They are filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion.
2. The primary function of nephrons is to remove all waste products from the blood.
3. The blood passes via the glomerulus with high pressure, the small molecules are moved into the glomerular capsules.
4. The cells present in each tube absorb different molecules excluding the glucose, water, and others. It regulates the fluid volume in our body.
Note: A decomposition reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which a single element breaks down into two or more new elements. These decomposition reactions often involve an energy source such as heat, light, or electricity that breaks apart the bonds of elements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




