
Both $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$ and ${{[Ni{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ are diamagnetic. The hybridization of nickel in these complexes, respectively are:
(a)- $s{{p}^{3}},s{{p}^{3}}$
(b)- $s{{p}^{3}},ds{{p}^{2}}$
(c)- $ds{{p}^{2}},s{{p}^{3}}$
(d)- $ds{{p}^{2}},ds{{p}^{2}}$
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: First find the oxidation state of the central metal atom. Then according to the oxidation state, remove the electrons. If the ligand is a strong field then unpaired electrons will pair up and the number of electrons will occupy the next orbitals. If the ligand is a weak field ligand then, pairing will not occur and ligands will occupy the next orbitals. Based on the orbitals occupied by the hybridization is calculated.
Complete step by step answer:
In $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$, the oxidation number of nickel is:
The oxidation number of $CO$ is zero because it is a neutral ligand,
$x+4(0)=0$
$x=0$
So, the oxidation state of nickel in $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$ is zero, the electronic configuration of the atomic orbital of nickel and in zero oxidation is given in the diagram.
The $CO$is a strong field ligand, so the unpaired electrons will pair up, this will fill the 3d orbital. Now the orbitals next to 3d are 4s and 4p. So, there are 4 $CO$ molecules in $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$, hence they will occupy the 1 s-orbital and 3 p-orbitals.
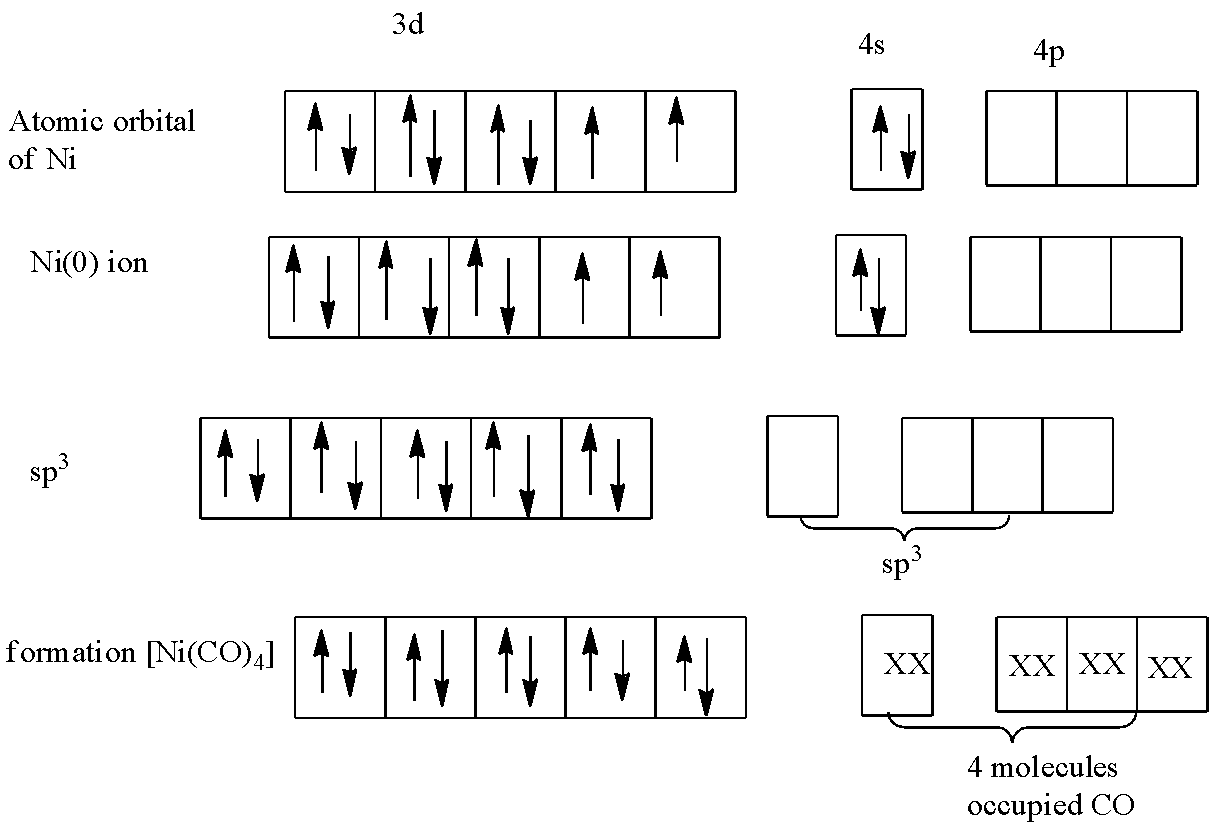
So, the hybridization of nickel in $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$ is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
In, ${{[Ni{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$the oxidation number of nickel is:
The oxidation number of $C{{N}^{-}}$ is -1 because it is a negative ligand. This overall charge on the molecule is -2.
$x+4(-1)=-2$
$x=+2$
So, the oxidation state of nickel in${{[Ni{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ is +2, the electronic configuration of atomic orbital of nickel and in +2 oxidation is given in the diagram.
The $C{{N}^{-}}$ is a strong field ligand, so the unpaired electrons will pair up, this will fill the 3d orbital. Now the orbitals next to 3d are 4s and 4p. So, there are 4 $CO$ molecules in $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$, hence they will occupy the 1 d-orbital, 1 s-orbital, and 2 p-orbitals.
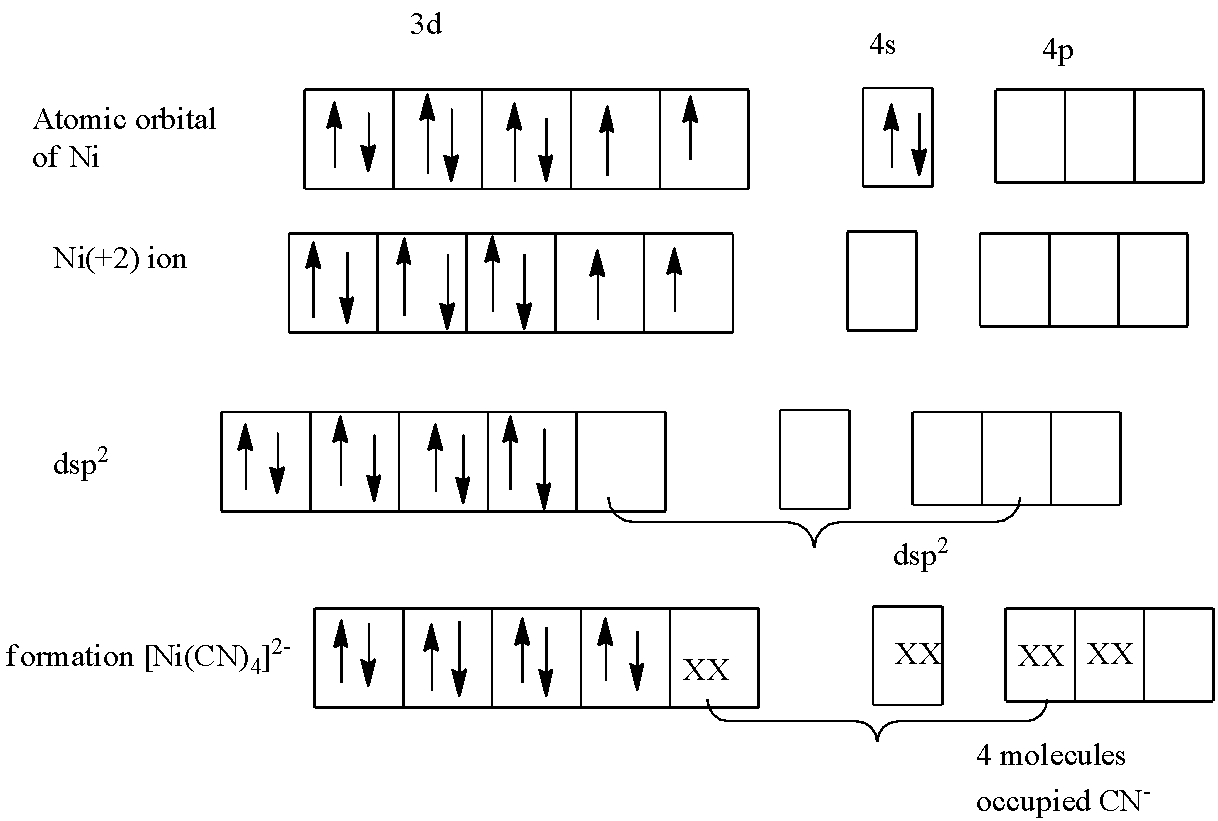
So, the hybridization of nickel in ${{[Ni{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ is $ds{{p}^{2}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The pairing of electrons is based on strong field ligand and weak field ligand. The examples of strong-field ligands are $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}, C{{N}^{-}}, CO$, etc and examples of weak field ligands are all halogens, water molecule, etc.
Complete step by step answer:
In $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$, the oxidation number of nickel is:
The oxidation number of $CO$ is zero because it is a neutral ligand,
$x+4(0)=0$
$x=0$
So, the oxidation state of nickel in $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$ is zero, the electronic configuration of the atomic orbital of nickel and in zero oxidation is given in the diagram.
The $CO$is a strong field ligand, so the unpaired electrons will pair up, this will fill the 3d orbital. Now the orbitals next to 3d are 4s and 4p. So, there are 4 $CO$ molecules in $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$, hence they will occupy the 1 s-orbital and 3 p-orbitals.

So, the hybridization of nickel in $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$ is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
In, ${{[Ni{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$the oxidation number of nickel is:
The oxidation number of $C{{N}^{-}}$ is -1 because it is a negative ligand. This overall charge on the molecule is -2.
$x+4(-1)=-2$
$x=+2$
So, the oxidation state of nickel in${{[Ni{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ is +2, the electronic configuration of atomic orbital of nickel and in +2 oxidation is given in the diagram.
The $C{{N}^{-}}$ is a strong field ligand, so the unpaired electrons will pair up, this will fill the 3d orbital. Now the orbitals next to 3d are 4s and 4p. So, there are 4 $CO$ molecules in $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$, hence they will occupy the 1 d-orbital, 1 s-orbital, and 2 p-orbitals.

So, the hybridization of nickel in ${{[Ni{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ is $ds{{p}^{2}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The pairing of electrons is based on strong field ligand and weak field ligand. The examples of strong-field ligands are $N{{O}_{2}}^{-}, C{{N}^{-}}, CO$, etc and examples of weak field ligands are all halogens, water molecule, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




