
How many bonding orbitals in benzene?
Answer
546k+ views
Hint: This is easily find molecular orbital theory
Molecular orbital Theory-As per MO theory, one sigma orbital is lower in energy than both of the two secluded atomic \[1s\] orbitals – this lower sigma orbital is alluded to as a bonding molecular orbital. The second, 'sigma star' orbital is higher in energy than the two atomic \[1s\] orbitals, and is alluded to as an antibonding molecular orbital.
Complete step by step answer:
The Answer is \[15\] bonding orbitals
The valence bond (Lewis) structure of benzene draw as –
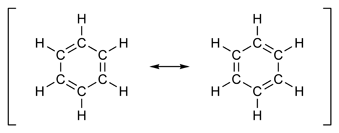
There are \[6C - C\sigma bonds\] , \[6C - H\sigma bonds\], and \[3C = C\pi bonds\] . This makes \[16\] bonding orbitals
As per molecular orbital theory, the σ molecular orbitals form from the three orbitals on every carbon atom and the \[1s\] orbitals on every hydrogen atom. These \[24\] atomic orbitals blend to form \[24\] molecular \[\sigma \] orbitals. Of these, \[12\] are bonding σ orbitals and \[12\] are antibonding \[\sigma ^*\] orbitals.
The \[6\] atomic p orbitals on the carbon atoms blend to form \[6\] molecular \[\pi \] orbitals.
There are \[3\] bonding \[\pi \] orbitals and \[3\] antibonding \[\pi ^*\] orbitals.
So, \[12\] bonding σ orbitals plus \[3\] bonding π orbitals give \[15\] bonding orbitals in benzene.
We see that benzene contains three bonding molecular orbitals that house the six pi electrons and three anti-bonding molecular orbitals that are higher in energy and in this manner don't contain any of the pi electrons. The most reduced in energy molecular orbital contains no nodal planes, two of the bonding molecular orbitals contain a solitary nodal plane each, two of the anti-bonding contain two nodal planes while the last contains three nodal planes
Note: It's difficult to draw a cyclic pi system with one node, however we can draw a system with one nodal plane. For benzene, the next level up has two nodal planes. Once more, there's two different ways to do it: cut through the bonds, or cut through the atoms. Once more, these are of a similar energy
Molecular orbital Theory-As per MO theory, one sigma orbital is lower in energy than both of the two secluded atomic \[1s\] orbitals – this lower sigma orbital is alluded to as a bonding molecular orbital. The second, 'sigma star' orbital is higher in energy than the two atomic \[1s\] orbitals, and is alluded to as an antibonding molecular orbital.
Complete step by step answer:
The Answer is \[15\] bonding orbitals
The valence bond (Lewis) structure of benzene draw as –

There are \[6C - C\sigma bonds\] , \[6C - H\sigma bonds\], and \[3C = C\pi bonds\] . This makes \[16\] bonding orbitals
As per molecular orbital theory, the σ molecular orbitals form from the three orbitals on every carbon atom and the \[1s\] orbitals on every hydrogen atom. These \[24\] atomic orbitals blend to form \[24\] molecular \[\sigma \] orbitals. Of these, \[12\] are bonding σ orbitals and \[12\] are antibonding \[\sigma ^*\] orbitals.
The \[6\] atomic p orbitals on the carbon atoms blend to form \[6\] molecular \[\pi \] orbitals.
There are \[3\] bonding \[\pi \] orbitals and \[3\] antibonding \[\pi ^*\] orbitals.
So, \[12\] bonding σ orbitals plus \[3\] bonding π orbitals give \[15\] bonding orbitals in benzene.
We see that benzene contains three bonding molecular orbitals that house the six pi electrons and three anti-bonding molecular orbitals that are higher in energy and in this manner don't contain any of the pi electrons. The most reduced in energy molecular orbital contains no nodal planes, two of the bonding molecular orbitals contain a solitary nodal plane each, two of the anti-bonding contain two nodal planes while the last contains three nodal planes
Note: It's difficult to draw a cyclic pi system with one node, however we can draw a system with one nodal plane. For benzene, the next level up has two nodal planes. Once more, there's two different ways to do it: cut through the bonds, or cut through the atoms. Once more, these are of a similar energy
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




