
What is the bond angle of a molecule undergoing $ s{p^2} $ hybridization?
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint :VSEPR (valence shell electron pair repulsion theory) gives a basic idea about the shape of a molecule depending upon its electron pair present in the valence shell.
This concept of hybridization was first introduced by Pauling. According to Pauli, the atomic orbitals combine to form a new set of equivalent orbitals which are commonly known as hybrid orbitals.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Hybridization is used to explain the characteristic shapes of molecules made up of 2 or more atoms.
Any molecule undergoes $ s{p^2} $ hybridization, one $ s $ orbital and one $ p $ orbital combine together to form $ s{p^2} $ hybridized orbital which are equivalent in terms of orbital energy.
For example, boron trichloride molecules undergo $ s{p^2} $ hybridization.
Boron acts as a central atom of the molecule with electronic configuration $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^1} $ .
Boron extends its valency by transferring one electron from $ 2s $ to $ 2p $ orbital.
Now the final configuration of boron becomes $ 1{s^2}2{s^1}2{p^2} $ with three valence.
finally, one $ 2s $ orbital and two $ 2p $ orbital of boron undergo hybridization to from $ s{p^2} $ hybridized
orbital.
These hybridized orbitals undergoes overlapping with $ 2p $ orbital of three chlorine atom
to form boron trichloride.
Chlorine atoms are arranged at $ {120^ \circ } $ with the central metal atom to form a geometry known as trigonal planar.
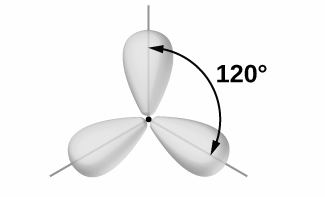
molecules undergoing $ s{p^2} $ hybridization includes- $ B{F_3} $ , $ AlC{l_3} $ , $ {C_2}{H_4} $ , $ N{O_3}^ - $ .
Hence, the bond angle of molecule undergoes $ sp^2 $ Hybridization is 120 degrees.
Note :
Remember that the total number of hybridized orbitals is always a sum of all the orbital undergoes hybridization. Hybrid orbital rearrange into a specific angle to form a stable arrangement. Angle in different molecules changes with change in hybridization for example molecule undergo $ sp $ hybridization form angle of $ {180^ \circ } $ while $ {109.5^ \circ } $ angle is formed by $ s{p_3} $ hybridized molecules.
This concept of hybridization was first introduced by Pauling. According to Pauli, the atomic orbitals combine to form a new set of equivalent orbitals which are commonly known as hybrid orbitals.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Hybridization is used to explain the characteristic shapes of molecules made up of 2 or more atoms.
Any molecule undergoes $ s{p^2} $ hybridization, one $ s $ orbital and one $ p $ orbital combine together to form $ s{p^2} $ hybridized orbital which are equivalent in terms of orbital energy.
For example, boron trichloride molecules undergo $ s{p^2} $ hybridization.
Boron acts as a central atom of the molecule with electronic configuration $ 1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^1} $ .
Boron extends its valency by transferring one electron from $ 2s $ to $ 2p $ orbital.
Now the final configuration of boron becomes $ 1{s^2}2{s^1}2{p^2} $ with three valence.
finally, one $ 2s $ orbital and two $ 2p $ orbital of boron undergo hybridization to from $ s{p^2} $ hybridized
orbital.
These hybridized orbitals undergoes overlapping with $ 2p $ orbital of three chlorine atom
to form boron trichloride.
Chlorine atoms are arranged at $ {120^ \circ } $ with the central metal atom to form a geometry known as trigonal planar.

molecules undergoing $ s{p^2} $ hybridization includes- $ B{F_3} $ , $ AlC{l_3} $ , $ {C_2}{H_4} $ , $ N{O_3}^ - $ .
Hence, the bond angle of molecule undergoes $ sp^2 $ Hybridization is 120 degrees.
Note :
Remember that the total number of hybridized orbitals is always a sum of all the orbital undergoes hybridization. Hybrid orbital rearrange into a specific angle to form a stable arrangement. Angle in different molecules changes with change in hybridization for example molecule undergo $ sp $ hybridization form angle of $ {180^ \circ } $ while $ {109.5^ \circ } $ angle is formed by $ s{p_3} $ hybridized molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




