
Blocking of the active site of an enzyme is a kind of
A. Non-competitive inhibition
B. Competitive inhibition
C. Allosteric inhibition
D. Feedback inhibition
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: Enzymes are biochemical substances that accelerate the rate of a reaction. In the body, processes like respiration, excretion, digestion and other metabolic reactions are catalyzed or accelerated by enzymes. The active site of the enzyme is a region where reactants bind. It can be blocked by some similar to reactant molecules or by other ways.
Complete answer: Enzymes are protein molecules having catalytic activities that are crucial and aid in different life processes. Various chemical reactions and metabolic processes are catalyzed by enzymes. Enzymes simply speed up the reaction rates. Enzymes react with reactant molecules called substrates. These substrates are converted into products with the help of enzymes. The enzymes are made of a linear chain of amino acids. Due to this, they have three-dimensional structures and the amino acid sequences specify the catalytic activity of enzymes.
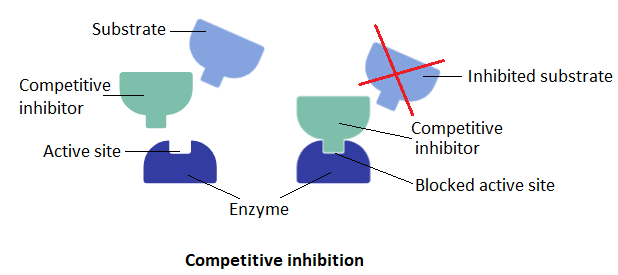
Only a small region of amino acids in an enzyme is involved in the catalysis of the substrate. This region is situated next to the binding site. The binding site is a region where substrates bind. This region is also called an active site as it is the primary region containing active amino acid chains. It is a cleft or pocket-like structure. The active sites are very specific for the substrates to which they bind. There are sometimes molecules that resemble the substrates and compete with them for binding to the active site of enzymes. These are called competitive inhibitors. They resemble the substrates in their structure. If they bind before substrates, the substrates cannot bind to enzymes. This results in competitive inhibition leading to blocking of the active site.
Non-competitive inhibition occurs when inhibitor molecules bind to the active site. Allosteric inhibition occurs when some molecules cause conformational changes in an enzyme’s active site. Allosteric molecules bind elsewhere than the active site. Feedback inhibition occurs when an accumulation of a product causes inhibition of enzyme causing its production.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Note: The inhibition mechanism of enzymes is used in pharmacology. Several drugs are made that resemble substrates and they bind to the active site of enzymes. They compete with the actual substrate so that they cause inhibition of unwanted products which results from substrate binding. Hence, the study of active sites and molecular modelling of active sites is very helpful in drug designing.
Complete answer: Enzymes are protein molecules having catalytic activities that are crucial and aid in different life processes. Various chemical reactions and metabolic processes are catalyzed by enzymes. Enzymes simply speed up the reaction rates. Enzymes react with reactant molecules called substrates. These substrates are converted into products with the help of enzymes. The enzymes are made of a linear chain of amino acids. Due to this, they have three-dimensional structures and the amino acid sequences specify the catalytic activity of enzymes.

Only a small region of amino acids in an enzyme is involved in the catalysis of the substrate. This region is situated next to the binding site. The binding site is a region where substrates bind. This region is also called an active site as it is the primary region containing active amino acid chains. It is a cleft or pocket-like structure. The active sites are very specific for the substrates to which they bind. There are sometimes molecules that resemble the substrates and compete with them for binding to the active site of enzymes. These are called competitive inhibitors. They resemble the substrates in their structure. If they bind before substrates, the substrates cannot bind to enzymes. This results in competitive inhibition leading to blocking of the active site.
Non-competitive inhibition occurs when inhibitor molecules bind to the active site. Allosteric inhibition occurs when some molecules cause conformational changes in an enzyme’s active site. Allosteric molecules bind elsewhere than the active site. Feedback inhibition occurs when an accumulation of a product causes inhibition of enzyme causing its production.
Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Note: The inhibition mechanism of enzymes is used in pharmacology. Several drugs are made that resemble substrates and they bind to the active site of enzymes. They compete with the actual substrate so that they cause inhibition of unwanted products which results from substrate binding. Hence, the study of active sites and molecular modelling of active sites is very helpful in drug designing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




