
Benzene with molecular formula ${C_6}{H_6}$ has:
Option:
A.$6$ Single bond and $6$ double bond
B.$12$ Single bond and $3$ double bond
C.$18$ Single bond only
D.$12$ double bond only
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: Benzene is defined as an aromatic compound which is composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms therefore it is also known as aromatic hydrocarbon. Structure of benzene was successfully described by Kekule.
Complete answer:
As we know, the molecular formula of benzene is ${C_6}{H_6}$. According to the basic concept of orbital theory, all the $6$ carbon atoms of benzene are $s{p^2}$ hybridized. When a carbon atom undergoes overlapping, out of three hybrid orbital of the carbon atom two undergoes axillary overlapping with the adjacent carbon atoms to form the bond. While the remaining last hybrid orbital of carbon undergoes overlapping with the hydrogen atom to form a bond with it.
From the above discussion we finally draw the structure of benzene:
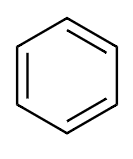
All the carbon atoms of benzene attached to one hydrogen atom to complete its valency to $4$. So the final structure of benzene will be:
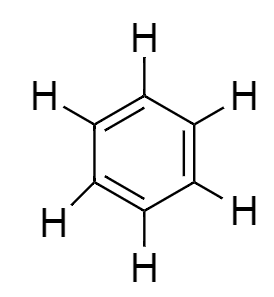
From the above diagram we easily calculate that there are $6$ single bonds formed between all the six-carbon atoms along with $6$single bonds with hydrogen atoms. So, there are a total number of $12$ single bonds in a single benzene.
Now we see that there are $3$ more bonds present in structure between carbon atoms. These are double bonds formed between adjacent carbon atoms of benzene.
$ \Rightarrow $ There are $12$ Single bonds and $3$ double bonds that are present in benzene molecules.
Therefore, option $\left( B \right)$ is the correct option.
Note:
Benzene possesses a very distinctive odour which helps in identification of it. Benzene is unsaturated in nature due to presence of $3$ double bonds but still it does not participate in decolorization reaction with bromine in $CC{l_4}$ and $KMn{O_4}$ alkaline solution.
Complete answer:
As we know, the molecular formula of benzene is ${C_6}{H_6}$. According to the basic concept of orbital theory, all the $6$ carbon atoms of benzene are $s{p^2}$ hybridized. When a carbon atom undergoes overlapping, out of three hybrid orbital of the carbon atom two undergoes axillary overlapping with the adjacent carbon atoms to form the bond. While the remaining last hybrid orbital of carbon undergoes overlapping with the hydrogen atom to form a bond with it.
From the above discussion we finally draw the structure of benzene:

All the carbon atoms of benzene attached to one hydrogen atom to complete its valency to $4$. So the final structure of benzene will be:

From the above diagram we easily calculate that there are $6$ single bonds formed between all the six-carbon atoms along with $6$single bonds with hydrogen atoms. So, there are a total number of $12$ single bonds in a single benzene.
Now we see that there are $3$ more bonds present in structure between carbon atoms. These are double bonds formed between adjacent carbon atoms of benzene.
$ \Rightarrow $ There are $12$ Single bonds and $3$ double bonds that are present in benzene molecules.
Therefore, option $\left( B \right)$ is the correct option.
Note:
Benzene possesses a very distinctive odour which helps in identification of it. Benzene is unsaturated in nature due to presence of $3$ double bonds but still it does not participate in decolorization reaction with bromine in $CC{l_4}$ and $KMn{O_4}$ alkaline solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




