
How is benzamide converted into benzylamine?
Answer
538k+ views
Hint: Benzamide can be converted into benzylamine by using \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] or we can also use \[NaOH + B{r_2}\].
Complete step by step answer:
The most common method of converting benzamide to benzylamine is by \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] but it requires greater selection because \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] can also react with others. If there are no other groups that can be affected by \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \], in that case, \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] is probably the reagent of choice. The more \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] is required for reduction of amides to amines because the carbonyl carbon of amides is less electrophile, as the electron density is shared by resonance.
The step by step conversion of Benzyl amine into benzamide is as follows:
(i) The \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] is a strong reducing agent and is used to reduce the carbonyl group into corresponding saturated systems by the addition of hydrogen atoms and removal of oxygen atoms in the form of water.
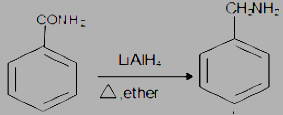
(ii) Heat the compound in the presence of dry ether.
We can also convert it by adding $Br_2$ and \[NaOH/KOH\] to benzamide and heat it which will convert it to amine with one carbon less than the reactant, this is called Hoffman Bromamide Degradation Reaction. Then treat it with \[HN{O_2}\] followed by \[HCN/CuCN\] to convert it into Benzene cyanate then treat it with \[{H_2}/Pd\]. By this way benzamide will convert into benzylamine.
Note:
Red phosphorus + HI can also reduce amides into amines. So, we can also use other reducing agents that can convert amides into amines.Catalytic hydrogenation can be used to reduce amides to amines; however, the process often requires high hydrogenation pressures and reaction temperatures to be effective
Complete step by step answer:
The most common method of converting benzamide to benzylamine is by \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] but it requires greater selection because \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] can also react with others. If there are no other groups that can be affected by \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \], in that case, \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] is probably the reagent of choice. The more \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] is required for reduction of amides to amines because the carbonyl carbon of amides is less electrophile, as the electron density is shared by resonance.
The step by step conversion of Benzyl amine into benzamide is as follows:
(i) The \[LiAl\mathop H\nolimits_4 \] is a strong reducing agent and is used to reduce the carbonyl group into corresponding saturated systems by the addition of hydrogen atoms and removal of oxygen atoms in the form of water.

(ii) Heat the compound in the presence of dry ether.
We can also convert it by adding $Br_2$ and \[NaOH/KOH\] to benzamide and heat it which will convert it to amine with one carbon less than the reactant, this is called Hoffman Bromamide Degradation Reaction. Then treat it with \[HN{O_2}\] followed by \[HCN/CuCN\] to convert it into Benzene cyanate then treat it with \[{H_2}/Pd\]. By this way benzamide will convert into benzylamine.
Note:
Red phosphorus + HI can also reduce amides into amines. So, we can also use other reducing agents that can convert amides into amines.Catalytic hydrogenation can be used to reduce amides to amines; however, the process often requires high hydrogenation pressures and reaction temperatures to be effective
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




