
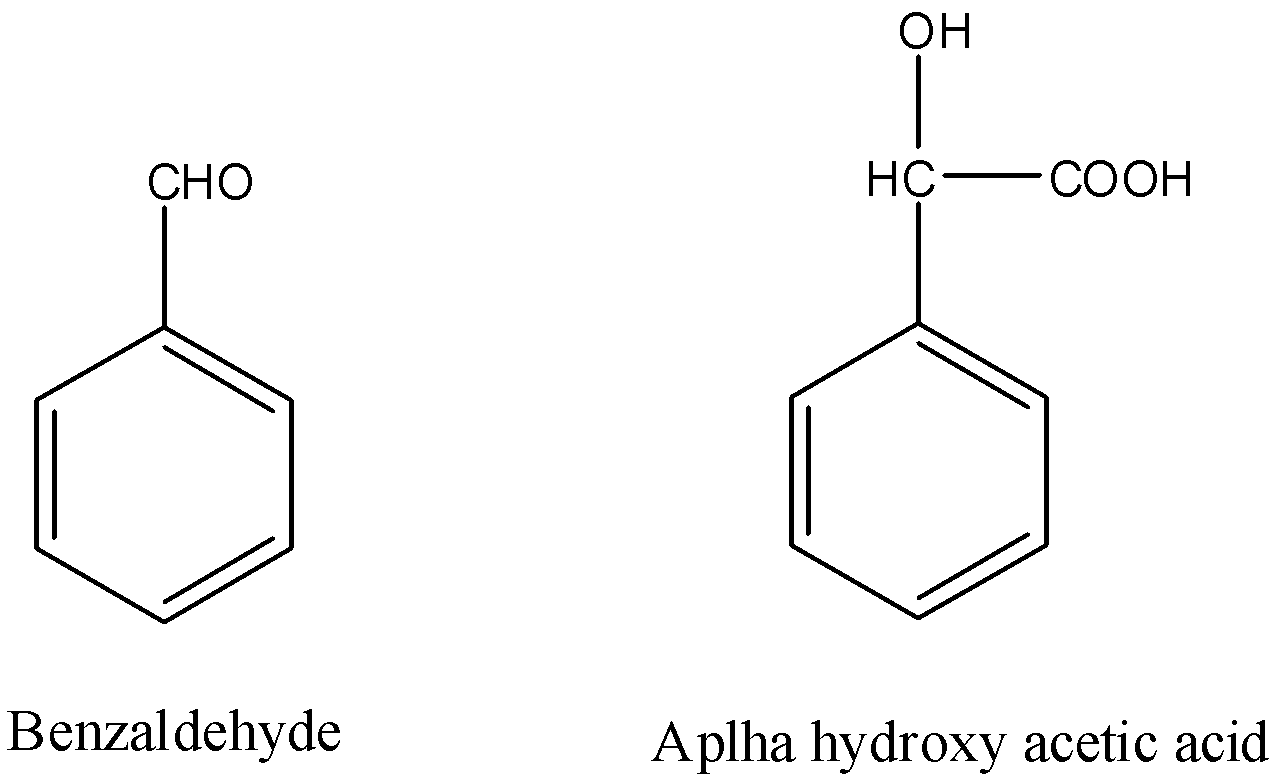
Benzaldehyde to \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid.
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: The structures of Benzaldehyde and \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid are as follows. So as we can see that one carbon has increased in the chain and that carbon is actually a carboxylic acid. We can use nucleophilic addition reactions to add a carbon atom in the aldehyde.
Complete step by step solution:
-The preparation of \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid from benzaldehyde contains two steps.
Step-1:
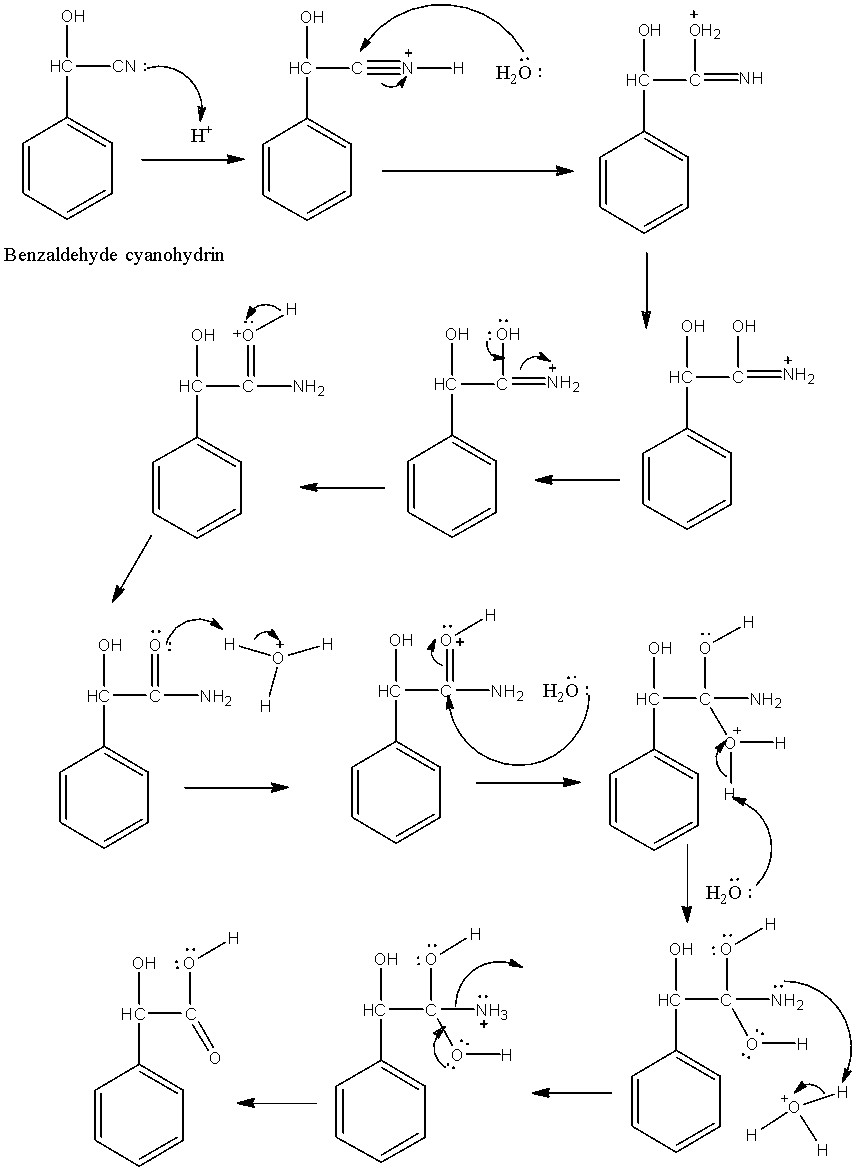
-Benzaldehyde undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction with sodium cyanide (NaCN) in the presence of hydrochloric acid and gives benzaldehyde cyanohydrin as the product at pH 9-10. Conversion of benzaldehyde to benzaldehyde cyanohydrin is as follows.
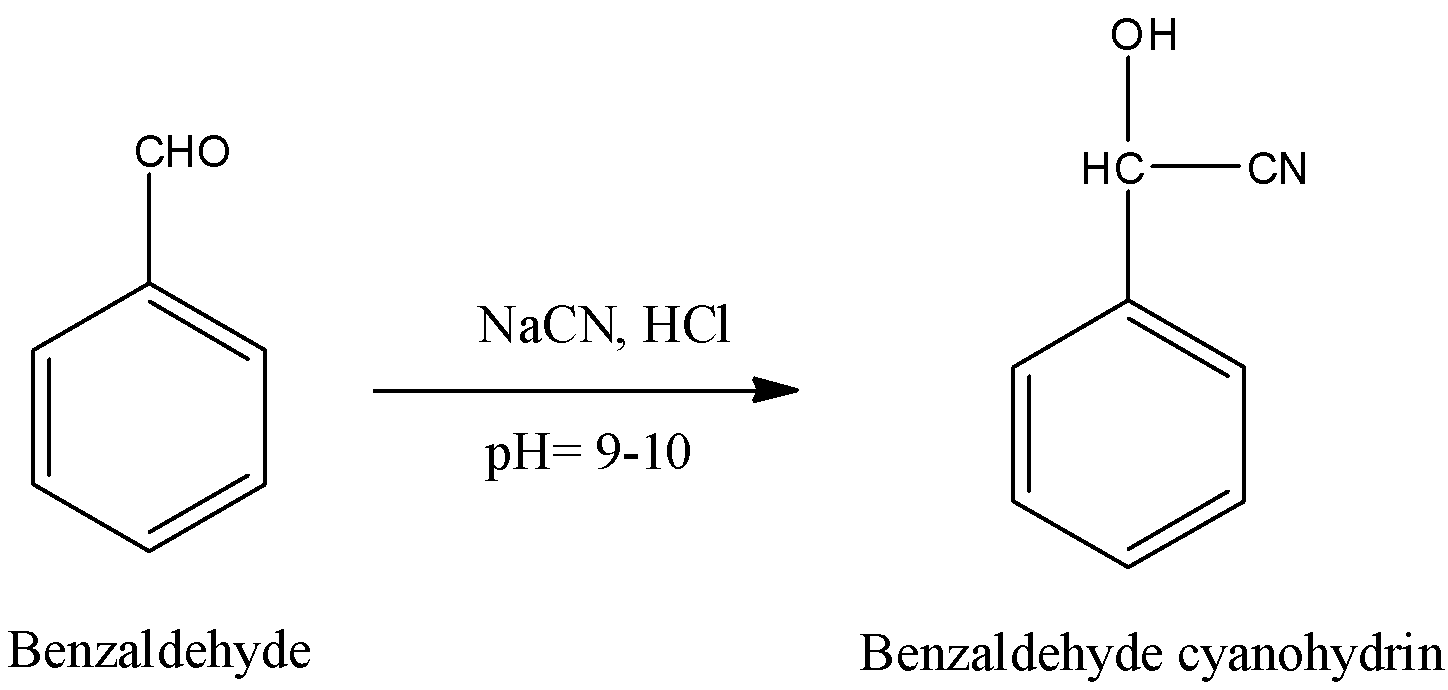
-In the above reaction Benzaldehyde undergoes bi molecular nucleophilic addition reaction with sodium cyanide to form benzaldehyde cyanohydrin as a product in step-1.
-The mechanism of nucleophilic addition reaction is as follows.
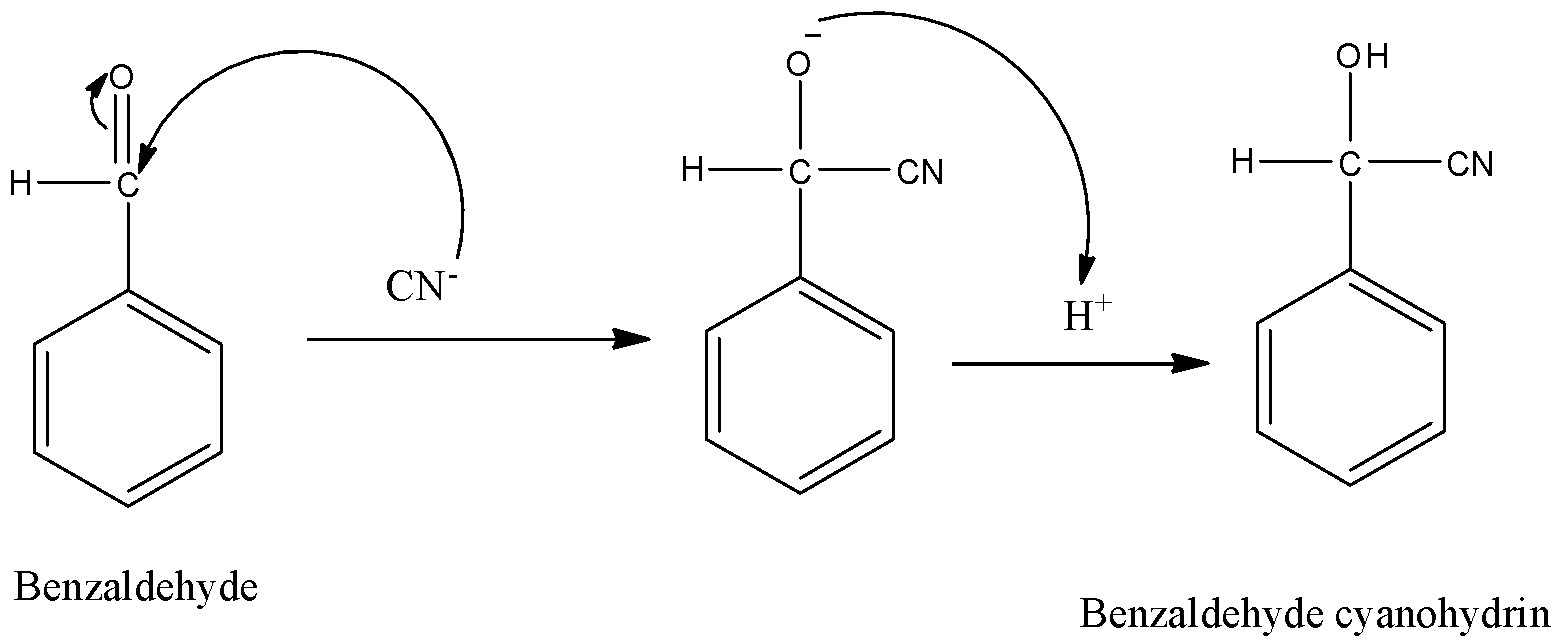
-Benzaldehyde cyanohydrin is also called as mandelonitrile.
Step-2:
-The formed benzaldehyde cyanohydrin undergoes hydrolysis in presence of acid and gives \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid. Conversion of benzaldehyde cyanohydrin to \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is as follows.
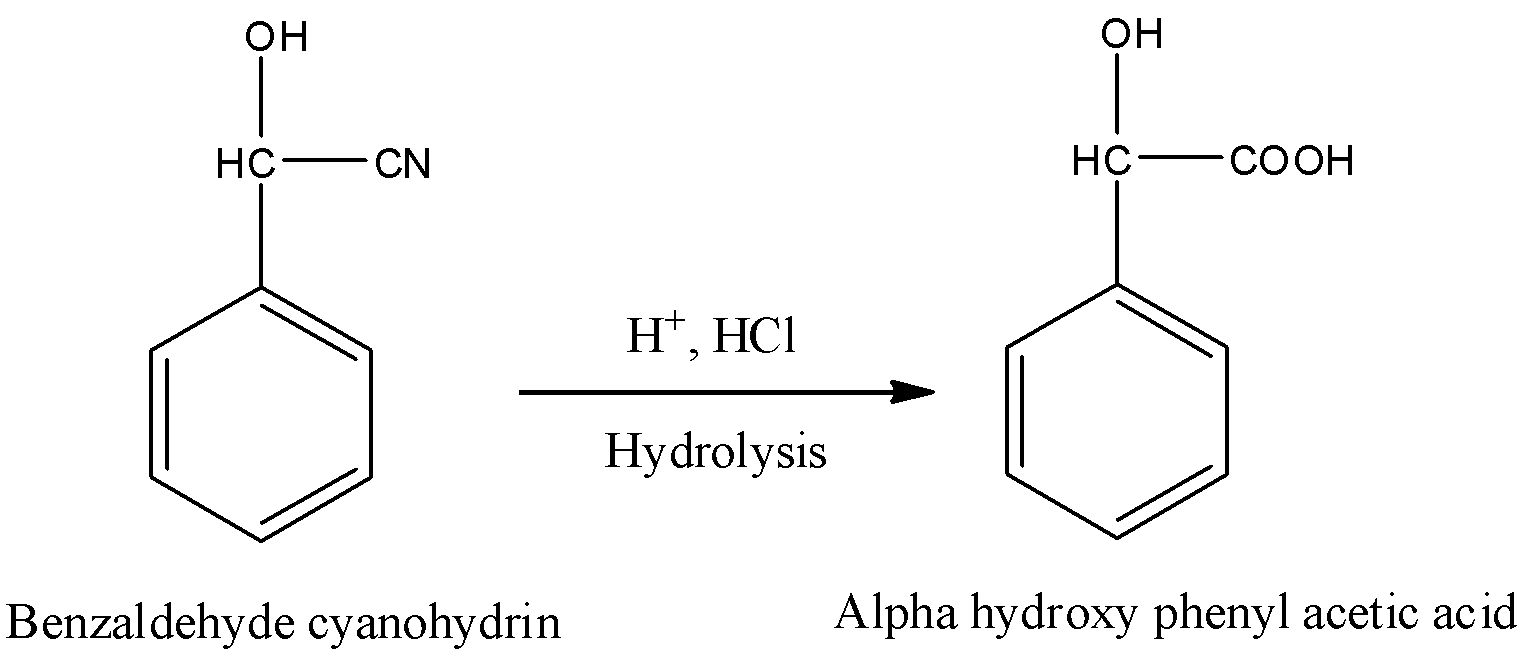
-In the above reaction cyanide undergoes hydrolysis in presence of acid and converts in to carboxylic acid in step-2.
-The mechanism of hydrolysis of cyanide is as follows.
Additional information:
-\[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is also called as Mandelic acid and it is white crystalline solid.
-Mandelic acid is partially soluble in water due to the presence of carboxylic acid (-COOH) and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups.
-Mandelic acid is completely soluble in organic solvents.
-Mandelic acid is used as a precursor in the preparation of drugs.
-Mandelic acid is used to treat urinary tract infections.
-Mandelic acid acts as an antibacterial agent.
Note: IUPAC name of\[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is 2-hydroxy-2phenylacetic acid. \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid has one chiral center in its structure. Generally \[\alpha \]-hydroxy acids (AHA) are used in cosmetics. Mandelic acid has two enantiomers called D- and L-Mandelic acid.

Complete step by step solution:
-The preparation of \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid from benzaldehyde contains two steps.
Step-1:
-Benzaldehyde undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction with sodium cyanide (NaCN) in the presence of hydrochloric acid and gives benzaldehyde cyanohydrin as the product at pH 9-10. Conversion of benzaldehyde to benzaldehyde cyanohydrin is as follows.

-In the above reaction Benzaldehyde undergoes bi molecular nucleophilic addition reaction with sodium cyanide to form benzaldehyde cyanohydrin as a product in step-1.
-The mechanism of nucleophilic addition reaction is as follows.

-Benzaldehyde cyanohydrin is also called as mandelonitrile.
Step-2:
-The formed benzaldehyde cyanohydrin undergoes hydrolysis in presence of acid and gives \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid. Conversion of benzaldehyde cyanohydrin to \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is as follows.

-In the above reaction cyanide undergoes hydrolysis in presence of acid and converts in to carboxylic acid in step-2.
-The mechanism of hydrolysis of cyanide is as follows.

Additional information:
-\[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is also called as Mandelic acid and it is white crystalline solid.
-Mandelic acid is partially soluble in water due to the presence of carboxylic acid (-COOH) and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups.
-Mandelic acid is completely soluble in organic solvents.
-Mandelic acid is used as a precursor in the preparation of drugs.
-Mandelic acid is used to treat urinary tract infections.
-Mandelic acid acts as an antibacterial agent.
Note: IUPAC name of\[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is 2-hydroxy-2phenylacetic acid. \[\alpha \]-hydroxyphenylacetic acid has one chiral center in its structure. Generally \[\alpha \]-hydroxy acids (AHA) are used in cosmetics. Mandelic acid has two enantiomers called D- and L-Mandelic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE




