
Beginning in town A, Biker Bob rides his bike 10 miles west, 3 miles north, 5 miles east, and 9 miles north, to town B. How far apart are town A and town B? (Assume perfectly flat terrain)
(a) 12
(b) 11
(c) 13
(d) 15
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Here, we need to distance between town A and town B. We will use Pythagoras’s theorem to find the required distance between town A and town B. The Pythagoras’s theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will draw a figure to show the path taken by Biker Bob to reach town B from town A.
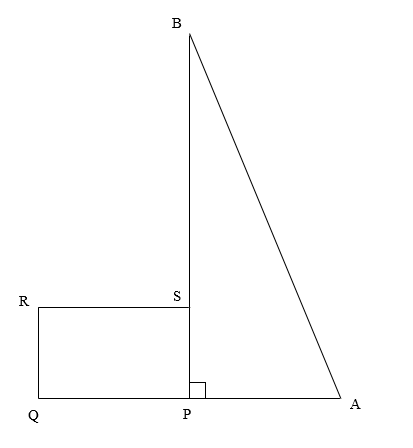
Here, A represents town A.
Biker Bob moves 10 miles west from point A to Q.
Thus, we get
\[AQ = 10\] miles
Biker Bob moves 3 miles north from point Q to R.
Thus, we get
\[QR = 3\] miles
Biker Bob moves 5 miles east from point R to S.
Thus, we get
\[RS = 5\] miles
Finally, biker Bob moves 9 miles north from point S to town B.
Thus, we get
\[SB = 9\] miles
We have extended SB to reach the line segment AQ at point P, such that BP is perpendicular to AQ.
Now, in the figure, we can observe that PQRS is a rectangle.
Therefore, we get
\[QP = SR = 5\] miles
\[QR = PS = 3\] miles
We can observe that the line segment AQ is the sum of the line segments QP and PA.
Therefore, we get
\[AQ = QP + PA\]
Substituting \[QP = 5\] miles and \[AQ = 10\] miles in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 10 = 5 + PA\]
Subtracting 5 from both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow PA = 5\] miles
Also, we can observe that the line segment BP is the sum of the line segments BS and SP.
Therefore, we get
\[BP = BS + SP\]
Substituting \[BS = 9\] miles and \[PS = 3\] miles in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow BP = 9 + 3\]
Adding the terms in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow BP = 12\] miles
Now, we can observe that the distance between town A and town B is the length of the line segment AB.
We will use the Pythagoras’s theorem, \[{\rm{Hypotenus}}{{\rm{e}}^2} = {\rm{Perpendicula}}{{\rm{r}}^2} + {\rm{Bas}}{{\rm{e}}^2}\], in the right angled triangle APB.
In the right angled triangle APB, AB is the hypotenuse, AP is the base, and BP is the perpendicular.
Using the Pythagoras’s theorem in right angled triangle ADB, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = B{P^2} + A{P^2}\]
Substituting \[BP = 12\] miles and \[AP = 5\] miles in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = {12^2} + {5^2}\]
Applying the exponents on the bases, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 144 + 25\]
Adding the terms in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 169\]
Taking the square root on both the sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow AB = 13\] miles
Therefore, the distance between town A and town B is 13 miles.
Thus, the correct option is option (c).
Note: We found \[QP = SR = 5\] miles and \[QR = PS = 3\] miles in the rectangle PQRS. This is because the opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length. It is a direction based question so it is important to draw the diagram based on the given information.
Also, we have used Pythagoras theorem to solve this question. If the triangle is not a right angled triangle then we cannot apply Pythagoras theorem on it.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will draw a figure to show the path taken by Biker Bob to reach town B from town A.

Here, A represents town A.
Biker Bob moves 10 miles west from point A to Q.
Thus, we get
\[AQ = 10\] miles
Biker Bob moves 3 miles north from point Q to R.
Thus, we get
\[QR = 3\] miles
Biker Bob moves 5 miles east from point R to S.
Thus, we get
\[RS = 5\] miles
Finally, biker Bob moves 9 miles north from point S to town B.
Thus, we get
\[SB = 9\] miles
We have extended SB to reach the line segment AQ at point P, such that BP is perpendicular to AQ.
Now, in the figure, we can observe that PQRS is a rectangle.
Therefore, we get
\[QP = SR = 5\] miles
\[QR = PS = 3\] miles
We can observe that the line segment AQ is the sum of the line segments QP and PA.
Therefore, we get
\[AQ = QP + PA\]
Substituting \[QP = 5\] miles and \[AQ = 10\] miles in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 10 = 5 + PA\]
Subtracting 5 from both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow PA = 5\] miles
Also, we can observe that the line segment BP is the sum of the line segments BS and SP.
Therefore, we get
\[BP = BS + SP\]
Substituting \[BS = 9\] miles and \[PS = 3\] miles in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow BP = 9 + 3\]
Adding the terms in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow BP = 12\] miles
Now, we can observe that the distance between town A and town B is the length of the line segment AB.
We will use the Pythagoras’s theorem, \[{\rm{Hypotenus}}{{\rm{e}}^2} = {\rm{Perpendicula}}{{\rm{r}}^2} + {\rm{Bas}}{{\rm{e}}^2}\], in the right angled triangle APB.
In the right angled triangle APB, AB is the hypotenuse, AP is the base, and BP is the perpendicular.
Using the Pythagoras’s theorem in right angled triangle ADB, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = B{P^2} + A{P^2}\]
Substituting \[BP = 12\] miles and \[AP = 5\] miles in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = {12^2} + {5^2}\]
Applying the exponents on the bases, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 144 + 25\]
Adding the terms in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 169\]
Taking the square root on both the sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow AB = 13\] miles
Therefore, the distance between town A and town B is 13 miles.
Thus, the correct option is option (c).
Note: We found \[QP = SR = 5\] miles and \[QR = PS = 3\] miles in the rectangle PQRS. This is because the opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length. It is a direction based question so it is important to draw the diagram based on the given information.
Also, we have used Pythagoras theorem to solve this question. If the triangle is not a right angled triangle then we cannot apply Pythagoras theorem on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




