
What is the basicity of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$acid and why?
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: To find the basicity of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$, the term basicity need to be introduced first. Basicity means the number of replaceable or ionisable hydrogen atoms. In order to find basicity of an acid, the structure of that acid is to be drawn to find the number of replaceable hydrogen atoms present in it.
Complete answer:
Hypophosphorous acid, or phosphinic acid (${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$), is a phosphorus oxyacid and a reducing agent. It is a colourless low-melting compound. It is soluble in water and alcohol.
The basicity of an acid is the number of replaceable hydrogen atoms present in that molecule of an acid. The acids containing one, two or three replaceable hydrogen atoms in their respective molecules are called monobasic, dibasic acids or tribasic acids and their basicities will be 1, 2 or 3. Let us draw the structure of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$:
- 1 phosphorous or ($\text{P}$) atom
- 3 hydrogen or ($\text{H}$) atoms
- 2 oxygen or ($\text{O}$) atoms
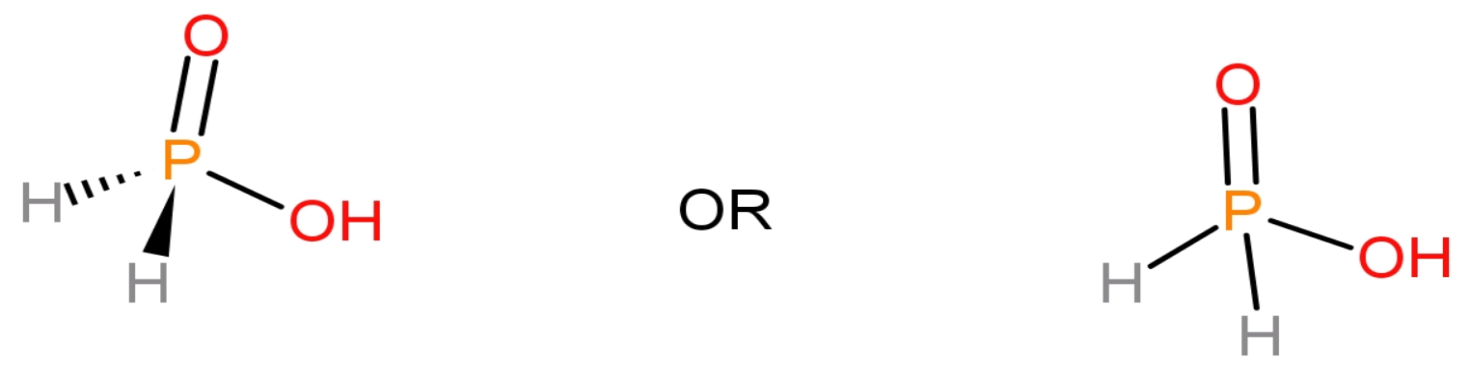
The number of hydrogen atoms counted in basicity of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ are 1. That is the number of hydrogen atoms attached to oxygen atoms is counted in the basicity of that acid. Thus, the basicity of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$: 1.
-The basicity of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ is 1.
Additional Information:
Uses of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ are:
(1) Hypo phosphorous Acid is used as a bleaching or decolorizing agent for plastics, chemicals, and synthetic fibers.
(2) Used as Catalyst: Hypophosphorous acid is used as a reducing agent to reduce Cu, Hg and Ag, to verify impurities, such as Nb and As. It is also used as a catalyst during esterification.
$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{COOH}+\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{OH}\xrightarrow{{{\text{H}}^{+}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{COOC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}$ (Esterification reaction)
(3) Used as a Reducing Agent.
Note: The hydrogen atoms attached to phosphorus are not to be considered as ionizable or replaceable atoms. The replaceable hydrogen atoms which are talked about here are that hydrogen atoms which are attached to oxygen means $-\text{OH}$ these hydrogen atoms. These hydrogen atoms are counted in basicity. Like in phosphoric acid, there are 3$-\text{OH}$ groups, so there are 3 replaceable hydrogen atoms present in it. So, the basicity of phosphoric acid is 3.
Complete answer:
Hypophosphorous acid, or phosphinic acid (${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$), is a phosphorus oxyacid and a reducing agent. It is a colourless low-melting compound. It is soluble in water and alcohol.
The basicity of an acid is the number of replaceable hydrogen atoms present in that molecule of an acid. The acids containing one, two or three replaceable hydrogen atoms in their respective molecules are called monobasic, dibasic acids or tribasic acids and their basicities will be 1, 2 or 3. Let us draw the structure of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$:
- 1 phosphorous or ($\text{P}$) atom
- 3 hydrogen or ($\text{H}$) atoms
- 2 oxygen or ($\text{O}$) atoms

The number of hydrogen atoms counted in basicity of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ are 1. That is the number of hydrogen atoms attached to oxygen atoms is counted in the basicity of that acid. Thus, the basicity of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$: 1.
-The basicity of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ is 1.
Additional Information:
Uses of ${{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{P}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$ are:
(1) Hypo phosphorous Acid is used as a bleaching or decolorizing agent for plastics, chemicals, and synthetic fibers.
(2) Used as Catalyst: Hypophosphorous acid is used as a reducing agent to reduce Cu, Hg and Ag, to verify impurities, such as Nb and As. It is also used as a catalyst during esterification.
$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{COOH}+\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{OH}\xrightarrow{{{\text{H}}^{+}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{COOC}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}+{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O}$ (Esterification reaction)
(3) Used as a Reducing Agent.
Note: The hydrogen atoms attached to phosphorus are not to be considered as ionizable or replaceable atoms. The replaceable hydrogen atoms which are talked about here are that hydrogen atoms which are attached to oxygen means $-\text{OH}$ these hydrogen atoms. These hydrogen atoms are counted in basicity. Like in phosphoric acid, there are 3$-\text{OH}$ groups, so there are 3 replaceable hydrogen atoms present in it. So, the basicity of phosphoric acid is 3.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




