
Bacteria are called prokaryotes whereas higher organisms are called Eukaryotes. Why?
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The eukaryotes and prokaryotes are differentiated based on their cell characteristics. The term 'eukaryotes' consists of two words derived from Greek where 'EU' means true and 'Karyote' means nucleus.
Complete answer:
Organisms with organelles bounded by a cell membrane and have a differentiated nucleus are known as eukaryotic organisms and organisms without membrane-bounded organelles and do not have a well-differentiated nucleus are known as prokaryotes. Most of the prokaryotes are unicellular and find nutrition from different substrates. Unicellular cells without a well-differentiated nucleus is a common characteristic of bacteria, which is why bacteria are called prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes on the other hand have a well-differentiated nucleus with the nuclear membrane and membrane-bounded organelles. Cells of eukaryotes synchronize or join to form tissues. Different types of tissues join to form organs and various organs constitute an organism. Organisms with differentiated cells and for various purposes and have the division of labor are said to be higher organisms and these factors are due to eukaryotic cells. This is why higher organisms are called eukaryotes.
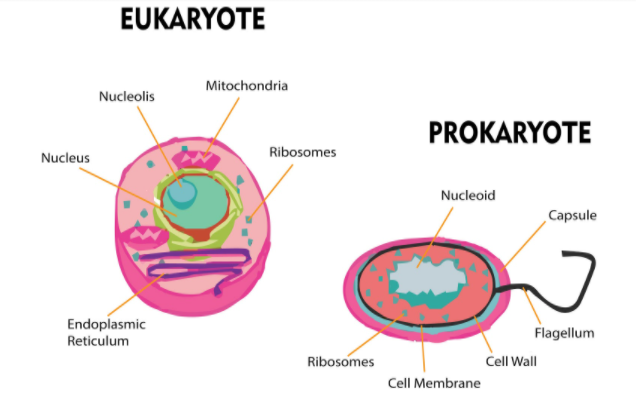
Note: -Prokaryotic cells are commonly tiny, with simple cells, and have a diameter of 0.1-5 μm. Eukaryotic cells are bigger and are about 10-100 μm and have complex cells. There are both unicellular and multicellular eukaryotic organisms.
-Prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound structure but they do have distinct cellular regions. In the cytoplasm, they have DNA bundles together in a region called the nucleoid.
-Prokaryotes are believed to be the first form of life before eukaryotes, which later evolved from prokaryotes almost 2.8 billion years ago.
Complete answer:
Organisms with organelles bounded by a cell membrane and have a differentiated nucleus are known as eukaryotic organisms and organisms without membrane-bounded organelles and do not have a well-differentiated nucleus are known as prokaryotes. Most of the prokaryotes are unicellular and find nutrition from different substrates. Unicellular cells without a well-differentiated nucleus is a common characteristic of bacteria, which is why bacteria are called prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes on the other hand have a well-differentiated nucleus with the nuclear membrane and membrane-bounded organelles. Cells of eukaryotes synchronize or join to form tissues. Different types of tissues join to form organs and various organs constitute an organism. Organisms with differentiated cells and for various purposes and have the division of labor are said to be higher organisms and these factors are due to eukaryotic cells. This is why higher organisms are called eukaryotes.

Note: -Prokaryotic cells are commonly tiny, with simple cells, and have a diameter of 0.1-5 μm. Eukaryotic cells are bigger and are about 10-100 μm and have complex cells. There are both unicellular and multicellular eukaryotic organisms.
-Prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound structure but they do have distinct cellular regions. In the cytoplasm, they have DNA bundles together in a region called the nucleoid.
-Prokaryotes are believed to be the first form of life before eukaryotes, which later evolved from prokaryotes almost 2.8 billion years ago.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




