
Back bonding in \[B{{F}_{3}}\] does not affect:
a.) Planarity, lewis acid strength and bond angle.
b.) Bond length, hybridisation and bond strength.
c.) Bond angle, planarity and geometry.
d.) Lewis acidity, bond length, bond order (\[B\to F\]).
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: \[B{{F}_{3}}\] has a trigonal planar structure and all the 3 \[B\to F\] bonds lie in the same plane. Therefore all the p orbitals of boron and fluorine are parallel to each other.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss how back bonding occurs in \[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecules.
-\[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecule has 2p orbitals of each fluorine which has fully filled orbitals and one of the 2p orbital of boron atoms is vacant.
-There will be a lateral overlap between the 2p orbitals involved in the formation of \[B\to F\] bond. This would result in the transfer of fluorine electrons into the vacant orbitals of the boron atom.
-There is an effective overlap between them because both the orbitals are of the same energy. We can say that an additional \[p\pi -p\pi \] bond is formed and the \[B\to F\] bond acquires a double bond character.
-Due to this back donation, the electron deficiency of boron is compensated and therefore Lewis acidity of \[B{{F}_{3}}\] decreases.
-The tendency of \[p\pi -p\pi \] bond formation is seen maximum in \[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecules.
-\[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecule forms a resonating structure. The lone pair of electrons between the boron and fluorine resonate giving it 3 resonating structures.
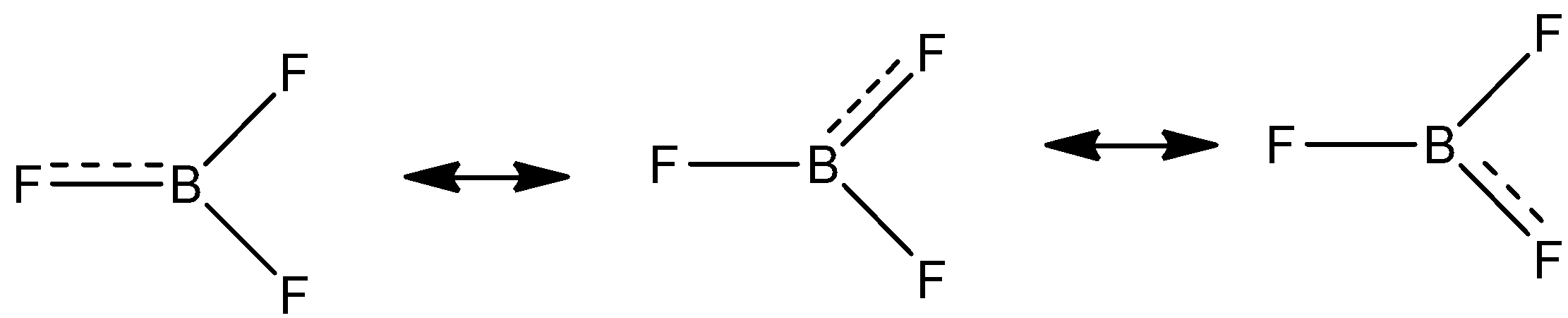
Back bonding \[B{{F}_{3}}\] does not affect the bond angle, planarity and the geometry of the molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: We should keep in mind that due to back bonding the hybridisation changes, bond strength increases and also bond length decreases. It is due to \[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecules planar structure and its bond angle, the overlapping of p orbitals occur.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss how back bonding occurs in \[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecules.
-\[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecule has 2p orbitals of each fluorine which has fully filled orbitals and one of the 2p orbital of boron atoms is vacant.
-There will be a lateral overlap between the 2p orbitals involved in the formation of \[B\to F\] bond. This would result in the transfer of fluorine electrons into the vacant orbitals of the boron atom.
-There is an effective overlap between them because both the orbitals are of the same energy. We can say that an additional \[p\pi -p\pi \] bond is formed and the \[B\to F\] bond acquires a double bond character.
-Due to this back donation, the electron deficiency of boron is compensated and therefore Lewis acidity of \[B{{F}_{3}}\] decreases.
-The tendency of \[p\pi -p\pi \] bond formation is seen maximum in \[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecules.
-\[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecule forms a resonating structure. The lone pair of electrons between the boron and fluorine resonate giving it 3 resonating structures.

Back bonding \[B{{F}_{3}}\] does not affect the bond angle, planarity and the geometry of the molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: We should keep in mind that due to back bonding the hybridisation changes, bond strength increases and also bond length decreases. It is due to \[B{{F}_{3}}\] molecules planar structure and its bond angle, the overlapping of p orbitals occur.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




