
How many atoms of $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ lie in the same plane?
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ is known as perxenates which has octahedral molecular geometry and it was determined by Raman spectroscopy. We can synthesize perxenate by the disproportionation of xenon trioxide when it is dissolved in strong alkali. They are also strong oxidising agents.
Complete answer:
Synthesis of perxenates is done by disproportionation of Xenon trioxide when it is dissolved in strong alkali. In this, $Ba{{(OH)}_{2}}$ is an alkali.
To calculate the hybridization of $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ , firstly we should know the valence electron for $Xe$ which is equal to $8$ .
The covalency of $Xe$ is $8$
The number of sigma bond is $6$ and lone pair is $0$
To calculate the number of hybrid orbitals,
$H.O=\sigma \,bond+l.p$
where, $H.O$ is the hybrid orbital, $\sigma \,bond$ is the sigma bond and $lp$ is the lone pair on the central atom.
Now, substituting the values in the given formula, we get,
$H.O=6+0$
$\Rightarrow H.O=6$
Therefore, the hybridization for $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$
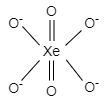
And the geometry formed is octahedral.
In $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ structure, two oxygen atoms form double bonds and four oxygen atoms form single bonds to complete the octet of xenon.
$XeO_{6}^{-4}$ is a strong oxidizing agent. In acidic solution, perxenate ion is unstable.
$XeO_{6}^{-4}$ has a hybridization of $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ and the shape of its molecule is octahedral. It has five atoms in one plane, that is, four oxygen and one xenon.
Hence, the number of atoms of $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ in the same plane is $5$ .
Note: Xenon having $+8$ charge does not have an outer valence electron for lone pairs, therefore, the number of lone pairs on the central atom is zero.
-In the structure of $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ , oxides are equivalent.
-The number of sigma bonds in $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ is six.
Complete answer:
Synthesis of perxenates is done by disproportionation of Xenon trioxide when it is dissolved in strong alkali. In this, $Ba{{(OH)}_{2}}$ is an alkali.
To calculate the hybridization of $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ , firstly we should know the valence electron for $Xe$ which is equal to $8$ .
The covalency of $Xe$ is $8$
The number of sigma bond is $6$ and lone pair is $0$
To calculate the number of hybrid orbitals,
$H.O=\sigma \,bond+l.p$
where, $H.O$ is the hybrid orbital, $\sigma \,bond$ is the sigma bond and $lp$ is the lone pair on the central atom.
Now, substituting the values in the given formula, we get,
$H.O=6+0$
$\Rightarrow H.O=6$
Therefore, the hybridization for $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ is $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$

And the geometry formed is octahedral.
In $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ structure, two oxygen atoms form double bonds and four oxygen atoms form single bonds to complete the octet of xenon.
$XeO_{6}^{-4}$ is a strong oxidizing agent. In acidic solution, perxenate ion is unstable.
$XeO_{6}^{-4}$ has a hybridization of $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ and the shape of its molecule is octahedral. It has five atoms in one plane, that is, four oxygen and one xenon.
Hence, the number of atoms of $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ in the same plane is $5$ .
Note: Xenon having $+8$ charge does not have an outer valence electron for lone pairs, therefore, the number of lone pairs on the central atom is zero.
-In the structure of $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ , oxides are equivalent.
-The number of sigma bonds in $XeO_{6}^{-4}$ is six.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




