
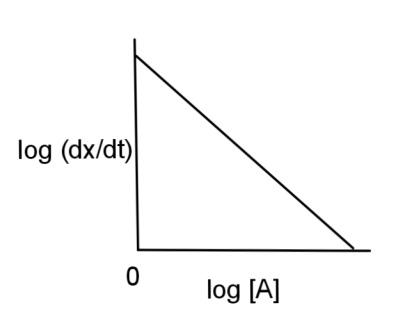
$A\to product$ and $\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)=K{{[A]}^{2}}$. If log$\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)$is plotted against log [A], then graph is of the type:
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: Rate law is the concentration of the reactants that is raised to their stoichiometric coefficients. Here ‘K’ is the rate constant. While, $\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)$ is the rate of a reaction in which the reactant is A. The graph of this expression can be identified by taking the log of the rate law, and then identifying the equation of slope, y = mx + c.
Complete answer:
The rate law of a reaction defines the rate of any reaction which is equal to the concentration of the species that are reacting and is raised to the power of their stoichiometric value. Rate constant of any reaction is the relationship between concentration of the reactants and the rate. The expression for which is $rate=K{{[A]}^{a}}$ where, ‘a’ is the stoichiometric coefficient and [A] is the concentration of reactant, and K is the rate constant.
We have been given graphs plotted between log forms of the integrated rate law. The integrated rate law is derived.
This is the second order reaction (involving one reactant A raised to power 2 as ${{[A]}^{2}}$), the equation will be $2A\to products$. Applying the law of mass action, the rate of this reaction will be, $\dfrac{dx}{dt}\propto {{[A]}^{2}}$
So, changing the proportionality with rate constant k, we have,
$\dfrac{dx}{dt}=k{{[A]}^{2}}$, now, taking log on both the sides we have,
$\log \,\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)\,=\log K+\,2\log [A]$
Rearranging this equation, $\log \,\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)\,=\,2\log [A]+\log \,K$
The rearranged equation is similar to the equation of slope for a graph as y = mx + c, where,
m is the slope, x is the x coordinate, y is the y coordinate, and c is the intercept.
Therefore, the graph will have a straight line with slope as 2 and the intercept as log K and the graph will be
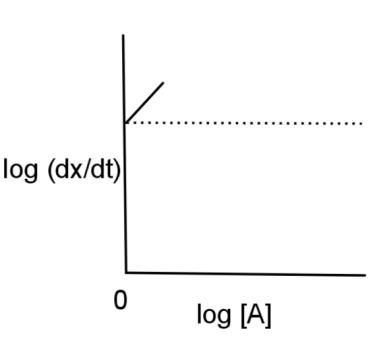
Hence, the log $\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)$ is plotted against log [A] and has a graph of option C.
Note:
The tan of the angle of the slope will give us the value of 2. The value of $\log \,{{a}^{b}}=b\,\log \,a$, is used in the log form of the equation, also the relation, log (ab) = log a + log b is used to derive the equation of slope in the log form. The slope- intercept form of the equation can tell us the value of rate constant, which is the slope of the graph between concentration and time.
Complete answer:
The rate law of a reaction defines the rate of any reaction which is equal to the concentration of the species that are reacting and is raised to the power of their stoichiometric value. Rate constant of any reaction is the relationship between concentration of the reactants and the rate. The expression for which is $rate=K{{[A]}^{a}}$ where, ‘a’ is the stoichiometric coefficient and [A] is the concentration of reactant, and K is the rate constant.
We have been given graphs plotted between log forms of the integrated rate law. The integrated rate law is derived.
This is the second order reaction (involving one reactant A raised to power 2 as ${{[A]}^{2}}$), the equation will be $2A\to products$. Applying the law of mass action, the rate of this reaction will be, $\dfrac{dx}{dt}\propto {{[A]}^{2}}$
So, changing the proportionality with rate constant k, we have,
$\dfrac{dx}{dt}=k{{[A]}^{2}}$, now, taking log on both the sides we have,
$\log \,\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)\,=\log K+\,2\log [A]$
Rearranging this equation, $\log \,\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)\,=\,2\log [A]+\log \,K$
The rearranged equation is similar to the equation of slope for a graph as y = mx + c, where,
m is the slope, x is the x coordinate, y is the y coordinate, and c is the intercept.
Therefore, the graph will have a straight line with slope as 2 and the intercept as log K and the graph will be

Hence, the log $\left( \dfrac{dx}{dt} \right)$ is plotted against log [A] and has a graph of option C.
Note:
The tan of the angle of the slope will give us the value of 2. The value of $\log \,{{a}^{b}}=b\,\log \,a$, is used in the log form of the equation, also the relation, log (ab) = log a + log b is used to derive the equation of slope in the log form. The slope- intercept form of the equation can tell us the value of rate constant, which is the slope of the graph between concentration and time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




