
At which temperature, the particles get converted into a liquid?
a.) Melting point
b.) Boiling point
c.) Freezing point
d.) None of the above
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: The kinetic theory of matter may be used to demonstrate how solid state, liquid state and gaseous states are interchangeable among themselves as a result of increase or decrease in heat energy inside them referring to the below change of states diagram. When an object is heated, the energy of the particles increases and change of state occurs. This theory can be used to proceed with the solution further.
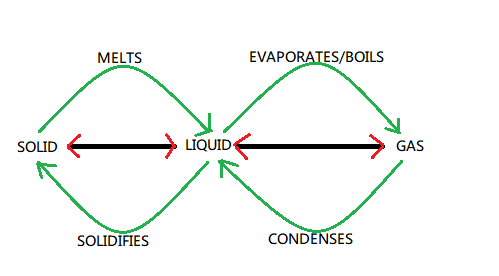
Complete step-by-step answer:
Melting
In the solid state the strong attractions amongst the particles hold them tightly packed together. Even though they are vibrating yet they are not free to move and hence this is not enough to disrupt the structure in the solid state.
But when a solid is heated the particles gain energy and momentum and start vibrating faster and faster. Resulting to which the internal structure of the solid is gradually weakened which has the effect of expanding the solid. Continued heating provides more energy until the particles start to break free of the structure and become random. Although the particles are still loosely connected they will be able to move around but not as freely as in the case of gas. At this particular point the solid is melting to form a liquid.
The particles in the liquid are the same as in the solid but they have more energy and their respective positioning is more random and loose. To melt a substance or material in the solid state, energy is required to overcome the attractions between the particles and allow them to pull them apart. The energy is supplied when the solid is heated up. The temperature at which some substance melts and changes a state is called its "melting point" or melting temperature.
At room temperature a material is generally “a solid, liquid or gas” depending on its melting temperature. Any substance that has a melting temperature higher than about $20^\circ C$ is likely to be a solid under normal situations. Materials have a wide range of different melting temperatures, e.g. for mercury the melting point or temperature is -39$^\circ C$ , for ice it is 0 $^\circ C$, for steel it is 1535 $^\circ C$ etc.
For instance if we consider the example of ice which is of course in solid state, it melts at room temperature only because the surrounding air is warmer than the ice itself and at a temperature above the melting temperature.
Hence the correct answer for the above question is option (A) as at melting point, the particles get converted into a liquid.
Note – Please remember that not all solids will melt when they are subjected to heat. Some may just undergo chemical changes as a result of heating or other deformation in their structure. For example paper burns rather than melting and gets converted to ash which is not liquid.

Complete step-by-step answer:
Melting
In the solid state the strong attractions amongst the particles hold them tightly packed together. Even though they are vibrating yet they are not free to move and hence this is not enough to disrupt the structure in the solid state.
But when a solid is heated the particles gain energy and momentum and start vibrating faster and faster. Resulting to which the internal structure of the solid is gradually weakened which has the effect of expanding the solid. Continued heating provides more energy until the particles start to break free of the structure and become random. Although the particles are still loosely connected they will be able to move around but not as freely as in the case of gas. At this particular point the solid is melting to form a liquid.
The particles in the liquid are the same as in the solid but they have more energy and their respective positioning is more random and loose. To melt a substance or material in the solid state, energy is required to overcome the attractions between the particles and allow them to pull them apart. The energy is supplied when the solid is heated up. The temperature at which some substance melts and changes a state is called its "melting point" or melting temperature.
At room temperature a material is generally “a solid, liquid or gas” depending on its melting temperature. Any substance that has a melting temperature higher than about $20^\circ C$ is likely to be a solid under normal situations. Materials have a wide range of different melting temperatures, e.g. for mercury the melting point or temperature is -39$^\circ C$ , for ice it is 0 $^\circ C$, for steel it is 1535 $^\circ C$ etc.
For instance if we consider the example of ice which is of course in solid state, it melts at room temperature only because the surrounding air is warmer than the ice itself and at a temperature above the melting temperature.
Hence the correct answer for the above question is option (A) as at melting point, the particles get converted into a liquid.
Note – Please remember that not all solids will melt when they are subjected to heat. Some may just undergo chemical changes as a result of heating or other deformation in their structure. For example paper burns rather than melting and gets converted to ash which is not liquid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE

What is the full form of pH?





