
At the temperature of liquefaction of air, the ratio of ortho and para hydrogen is:
A)1:1
B)1:3
C)3:1
D)3:2
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall the concept of the different spin of hydrogen nuclei that exist in nature. The molecule of dihydrogen consists of two atoms, in which the nuclei of both the atoms are spinning. Dihydrogen is of two types depending upon the direction of the spin of the two nuclei.
Complete Step by step solution:
We know that the Ortho hydrogen molecule is the one in which the spins of both the nuclei are in the same direction. Para hydrogen is the one in which the spins of both the nuclei are in the opposite direction Ordinary dihydrogen is an equilibrium mixture of ortho and para hydrogen. At the temperature of liquefaction of air, the ratio of ortho and para hydrogen is 1: 1. A diagrammatic representation of the nuclei can be shown as:
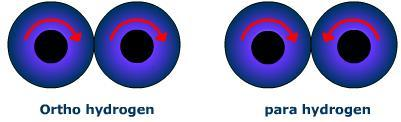
\[{\text{ortho hydrogen}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{para hydrogen}}\]
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option A
Note: The amount of ortho and para hydrogen is a variable that depends on temperature as, At 0°K, hydrogen contains mainly para-hydrogen which is more stable. Room temperature changes this ratio of ortho to para hydrogen to 3: 1. This is the maximum possible ratio. This means that even at very high temperatures, the ratio of ortho to para-hydrogen can never be more than 3: 1. Thus, it has been possible to get pure para-hydrogen by cooling ordinary hydrogen gas to very low temperature but it is impossible to get a sample of hydrogen which contains more than 75% of ortho hydrogen.
Complete Step by step solution:
We know that the Ortho hydrogen molecule is the one in which the spins of both the nuclei are in the same direction. Para hydrogen is the one in which the spins of both the nuclei are in the opposite direction Ordinary dihydrogen is an equilibrium mixture of ortho and para hydrogen. At the temperature of liquefaction of air, the ratio of ortho and para hydrogen is 1: 1. A diagrammatic representation of the nuclei can be shown as:

\[{\text{ortho hydrogen}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{para hydrogen}}\]
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option A
Note: The amount of ortho and para hydrogen is a variable that depends on temperature as, At 0°K, hydrogen contains mainly para-hydrogen which is more stable. Room temperature changes this ratio of ortho to para hydrogen to 3: 1. This is the maximum possible ratio. This means that even at very high temperatures, the ratio of ortho to para-hydrogen can never be more than 3: 1. Thus, it has been possible to get pure para-hydrogen by cooling ordinary hydrogen gas to very low temperature but it is impossible to get a sample of hydrogen which contains more than 75% of ortho hydrogen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




