
At the point of maximum compression, which of the following must be true?
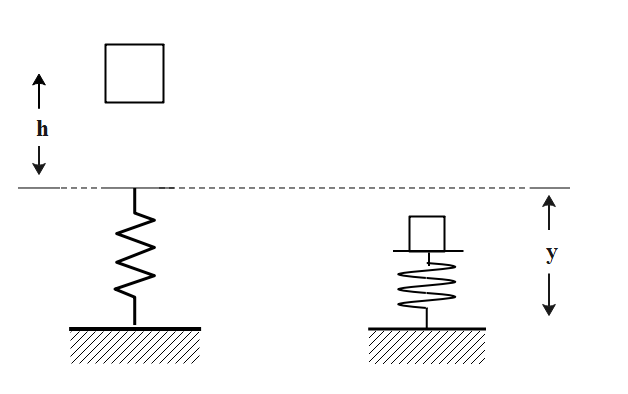
A. The speed of the block is maximum.
B. The acceleration of the block is not zero.
C. The potential energy of the block is zero.
D. The kinetic energy of the block is maximum.
E. The potential energy of the spring is zero.

Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: A compression spring has elasticity born within the spring wire used for storing mechanical energy. The force of a spring is calculated according to Hooke’s law. We will consider all these concepts of spring mechanics to find the correct option among the given ones.
Formula used: $F \propto x$
$ \Rightarrow {F_{spring}} = - kx$
Complete step by step answer:
We know Hookes’s law states that, the force of the spring is directly proportional to the extension of the spring i.e. $F \propto x$
The spring force is the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it. An object that compresses or stretches a spring is usually acted upon by a force that restores the object to its rest or equilibrium position.
According to the question, we get to understand that the block is momentarily at rest, but it will not occupy the rest position because the spring is accelerating the block upward with a spring. This state is similar to that of a ball when thrown up into the air at top of the flight it comes to rest, at that point it has no velocity but does have an acceleration. Therefore, acceleration of the ball is not zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information: Potential energy is the stored energy of position possessed by an object. Elastic potential energy refers to the position of the mass on the spring relative to its equilibrium position. Whenever the spring is compressed or stretched relative to its relaxed position, the elastic potential energy increases. The amount of elastic potential energy depends on the quantity of stretch or compression of the spring.
${\text{P}}{{\text{E}}_{{\text{spring}}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$ where $k$ is the spring constant and $x$ is the distance that the spring is stretched or compressed relative to the unstretched position.
Note: Compression springs are coil springs storing energy when they are closed by a force. Stored energy within the spring is brought back to original state after force is removed to lengthen the spring and push against the object that compressed it.
Formula used: $F \propto x$
$ \Rightarrow {F_{spring}} = - kx$
Complete step by step answer:
We know Hookes’s law states that, the force of the spring is directly proportional to the extension of the spring i.e. $F \propto x$
The spring force is the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it. An object that compresses or stretches a spring is usually acted upon by a force that restores the object to its rest or equilibrium position.
According to the question, we get to understand that the block is momentarily at rest, but it will not occupy the rest position because the spring is accelerating the block upward with a spring. This state is similar to that of a ball when thrown up into the air at top of the flight it comes to rest, at that point it has no velocity but does have an acceleration. Therefore, acceleration of the ball is not zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information: Potential energy is the stored energy of position possessed by an object. Elastic potential energy refers to the position of the mass on the spring relative to its equilibrium position. Whenever the spring is compressed or stretched relative to its relaxed position, the elastic potential energy increases. The amount of elastic potential energy depends on the quantity of stretch or compression of the spring.
${\text{P}}{{\text{E}}_{{\text{spring}}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$ where $k$ is the spring constant and $x$ is the distance that the spring is stretched or compressed relative to the unstretched position.
Note: Compression springs are coil springs storing energy when they are closed by a force. Stored energy within the spring is brought back to original state after force is removed to lengthen the spring and push against the object that compressed it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




