
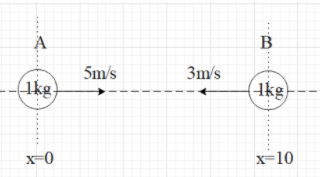
At t=0, the position and velocities of two particles are as shown in figure. They are kept on a smooth surface and are mutually attracted by gravitational force. Find the position of centre of mass at t = 2s.
A. x = 5m
B. x = 7m
C. x = 3m
D. x = 2m

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Check whether the net force on the system is zero. Then find the velocity of the centre of mass of the two particles at time t=0. Also find the position of the centre of mass at t=0. Then calculate the distance moved by the centre of mass in 2s. With this find the position of the centre of mass at t=2s.
Formula used:
${{v}_{com}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
${{x}_{com}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
$x=vt$
Complete answer:
The two particles are said to be mutually attracted by gravitational force. This means that particle A will attract particle B towards itself and particle B will attract particle A towards itself. As a result, the two will move towards each other.
The magnitude of the force that A exerts on B is equal to the magnitude of the force that B exerts on A. Therefore, there are two forces acting on the system of the two particles. However, the forces are opposite in direction and equal in magnitude. Hence, the net force on the given system is zero.
When the net force on a system of particles is zero, the velocity of the centre of mass of the system remains constant. Therefore, let us find the velocity of the centre of mass at time t=0.
The velocity of the centre of mass of a system of two particles (when the particles are moving in one dimension) is given as ${{v}_{com}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$ ….. (i).
Here, ${{m}_{1}}={{m}_{2}}=1kg$
${{v}_{1}}=5m{{s}^{-1}}$ and ${{v}_{3}}=-3m{{s}^{-1}}$ (because B is moving in the direction of negative x-axis).
Substitute the values in (i).
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{com}}=\dfrac{1(5)+1(-3)}{1+1}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1m{{s}^{-1}}$.
This means that constant velocity of the centre of mass is $1m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Therefore, in 2 seconds the centre of mass will be displaced to the right by $x=vt=1\times 2=2m$.
Let us now calculate the position of the centre of mass at t=0 by using the formula ${{x}_{com}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$ .
From the figure we get to know that ${{x}_{1}}=0$ and ${{x}_{2}}=10m$
${{x}_{com}}=\dfrac{1(0)+1(10)}{1+1}=\dfrac{10}{2}=5m$.
Therefore, the position of the centre of mass at t=2s is $5+2=7m$.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:
Note that in a system of two particles, the centre of mass of the two particles is always on the line joining the two particles. If the masses of the particles are equal then the centre of mass is located at the midpoint of the line segment joining the two.
Also note that only the centre of mass is moving with a constant velocity. Whereas the two particles are accelerating under force of gravity.
Formula used:
${{v}_{com}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
${{x}_{com}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$
$x=vt$
Complete answer:
The two particles are said to be mutually attracted by gravitational force. This means that particle A will attract particle B towards itself and particle B will attract particle A towards itself. As a result, the two will move towards each other.
The magnitude of the force that A exerts on B is equal to the magnitude of the force that B exerts on A. Therefore, there are two forces acting on the system of the two particles. However, the forces are opposite in direction and equal in magnitude. Hence, the net force on the given system is zero.
When the net force on a system of particles is zero, the velocity of the centre of mass of the system remains constant. Therefore, let us find the velocity of the centre of mass at time t=0.
The velocity of the centre of mass of a system of two particles (when the particles are moving in one dimension) is given as ${{v}_{com}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$ ….. (i).
Here, ${{m}_{1}}={{m}_{2}}=1kg$
${{v}_{1}}=5m{{s}^{-1}}$ and ${{v}_{3}}=-3m{{s}^{-1}}$ (because B is moving in the direction of negative x-axis).
Substitute the values in (i).
$\Rightarrow {{v}_{com}}=\dfrac{1(5)+1(-3)}{1+1}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1m{{s}^{-1}}$.
This means that constant velocity of the centre of mass is $1m{{s}^{-1}}$.
Therefore, in 2 seconds the centre of mass will be displaced to the right by $x=vt=1\times 2=2m$.
Let us now calculate the position of the centre of mass at t=0 by using the formula ${{x}_{com}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{1}}{{x}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{x}_{2}}}{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}$ .
From the figure we get to know that ${{x}_{1}}=0$ and ${{x}_{2}}=10m$
${{x}_{com}}=\dfrac{1(0)+1(10)}{1+1}=\dfrac{10}{2}=5m$.
Therefore, the position of the centre of mass at t=2s is $5+2=7m$.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:
Note that in a system of two particles, the centre of mass of the two particles is always on the line joining the two particles. If the masses of the particles are equal then the centre of mass is located at the midpoint of the line segment joining the two.
Also note that only the centre of mass is moving with a constant velocity. Whereas the two particles are accelerating under force of gravity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




