
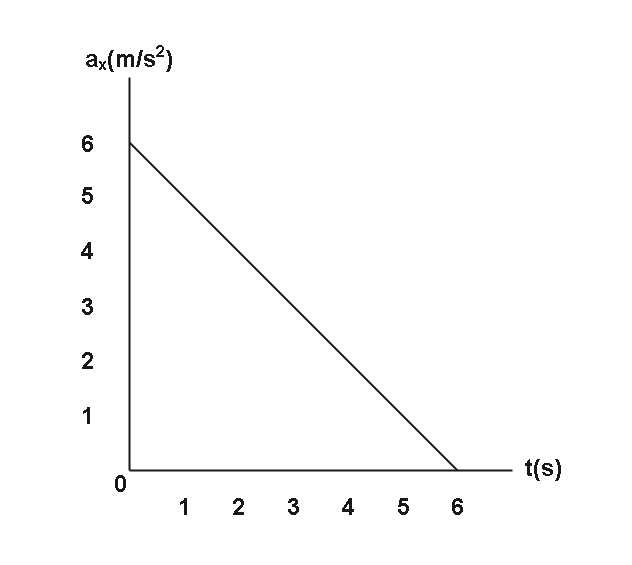
At \[t = 0\] is located at $x = 25m$ and has a velocity of $15m{\text{ }}{s^{ - 1}}$ in the positive $x$ direction. The acceleration of the particle varies with time as shown in the diagram. What is the position of the particle at $t = 5.0s$ ?

Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this type of question one must have the concept of integration and graph straight line (slope intercept form). Firstly, from the graph using slope intercept form we will find the equation of acceleration and time and then we know that integrating the acceleration time equation gives us change in velocity and integrating velocity time graph give us position time equation and at last simply substituting all the values in equation to get the required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
From the diagram we can see that it is a straight line and here we can apply slope intercept form to find the equation of the graph and we know that the acceleration-time graph says the change in velocity in the given interval of the time.
$a(t) = {a_i} - m \times t$
And ${a_i} = 6$
And we know that $m$ is the slope and slope is $\tan \theta $
$\therefore \tan \theta = \dfrac{6}{6} = 1$
So, we can rewrite the equation as,
$a(t) = 6 - t$
And we know that integrating the acceleration-time equation gives us velocity so integrating the above equation,
$
v(t) = \int {\left( {6 - t} \right)dt} \\
v(t) = 6t - \dfrac{1}{2}{t^2} + C \\
$
And according to the question it is given that, at $t = 0$ the velocity is $v = 15m{\text{ }}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ .
Substituting in the above equation to find $C$ .
$
v(t) = 6t - \dfrac{1}{2}{t^2} + C \\
15 = 6(0) - \dfrac{1}{2}{(0)^2} + C \\
\Rightarrow C = 15 \\
$
So, again integrating the equation to find the position,
$
v(t) = 6t - \dfrac{1}{2}{t^2} + 15 \\
x(t) = \int {v(t)dt = } \int {\left( {6t - \dfrac{1}{2}{t^2} + 15} \right)dt} \\
x(t) = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 6 \times {t^2} - \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{3} \times {t^3} + 15t + C \\
$
Now, solving the above equation,
$x(t) = 3{t^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{t^3} + 15t + C$
Now again at $t = 0,x = 25m$ we will get,
$
x(t) = 3{t^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{t^3} + 15t + C \\
25 = 3t{(0)^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{t^3} + 15(0) + C \\
\Rightarrow C = 25 \\
$
And we have to find the position of the particle at $x = 5s$ so putting the values in above equation we get,
$
x(t) = 3{t^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{t^3} + 15t + 25 \\
x(5) = 3{(5)^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{(5)^3} + 15(5) + 25 \\
x(5) = 75 - 20.83 + 75 + 25 \\
x(5) = 154.167m \\
$
Hence, the position of the particle at $x(5)$ is $154.167$.
Note: When solving for y in terms of x, the slope intercept form of a linear equation takes the following form:
$y = a + bx$
Where,
$b$ is the slope and
$a$ is the constant term.
Complete step by step answer:
From the diagram we can see that it is a straight line and here we can apply slope intercept form to find the equation of the graph and we know that the acceleration-time graph says the change in velocity in the given interval of the time.
$a(t) = {a_i} - m \times t$
And ${a_i} = 6$
And we know that $m$ is the slope and slope is $\tan \theta $
$\therefore \tan \theta = \dfrac{6}{6} = 1$
So, we can rewrite the equation as,
$a(t) = 6 - t$
And we know that integrating the acceleration-time equation gives us velocity so integrating the above equation,
$
v(t) = \int {\left( {6 - t} \right)dt} \\
v(t) = 6t - \dfrac{1}{2}{t^2} + C \\
$
And according to the question it is given that, at $t = 0$ the velocity is $v = 15m{\text{ }}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$ .
Substituting in the above equation to find $C$ .
$
v(t) = 6t - \dfrac{1}{2}{t^2} + C \\
15 = 6(0) - \dfrac{1}{2}{(0)^2} + C \\
\Rightarrow C = 15 \\
$
So, again integrating the equation to find the position,
$
v(t) = 6t - \dfrac{1}{2}{t^2} + 15 \\
x(t) = \int {v(t)dt = } \int {\left( {6t - \dfrac{1}{2}{t^2} + 15} \right)dt} \\
x(t) = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 6 \times {t^2} - \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{3} \times {t^3} + 15t + C \\
$
Now, solving the above equation,
$x(t) = 3{t^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{t^3} + 15t + C$
Now again at $t = 0,x = 25m$ we will get,
$
x(t) = 3{t^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{t^3} + 15t + C \\
25 = 3t{(0)^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{t^3} + 15(0) + C \\
\Rightarrow C = 25 \\
$
And we have to find the position of the particle at $x = 5s$ so putting the values in above equation we get,
$
x(t) = 3{t^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{t^3} + 15t + 25 \\
x(5) = 3{(5)^2} - \dfrac{1}{6}{(5)^3} + 15(5) + 25 \\
x(5) = 75 - 20.83 + 75 + 25 \\
x(5) = 154.167m \\
$
Hence, the position of the particle at $x(5)$ is $154.167$.
Note: When solving for y in terms of x, the slope intercept form of a linear equation takes the following form:
$y = a + bx$
Where,
$b$ is the slope and
$a$ is the constant term.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




