
At stable equilibrium position of a body where kinetic energy can’t be zero because it is the maximum. Why?
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint:An object is said to be in the stable equilibrium, if a small externally induced displacement is given to the object at equilibrium, creates a force which opposes the displacement of the object. The objects at the stable equilibrium is similar to the particle performing harmonic motion is at the mean position. Recall the velocity of the particle performing harmonic motion at the mean position. The kinetic energy is proportional to the square of the velocity.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, let us first understand the meaning of equilibrium. A system is said to be in the equilibrium if its state of motion and internal energy does not change with time. Now, there are two types of equilibrium: stable and unstable. An object is said to be in the stable equilibrium, if a small externally induced displacement is given to the object at equilibrium, creates a force which opposes the displacement of the object. And thus, the object again attains an equilibrium position. In the meantime, the object follows a simple harmonic motion about its mean position.
Consider the following situation in which a rectangular rod is at equilibrium (a) and then it has given a small horizontal force or we can say torque is applied at the top position. The rod follows a harmonic motion about its stable equilibrium position.
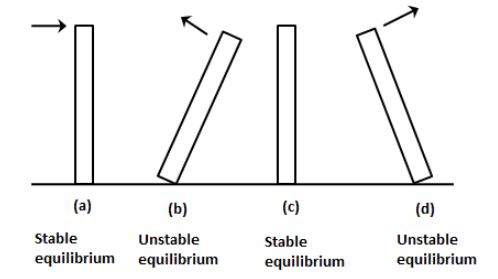
We know that the particle in the simple harmonic motion has the maximum velocity at the mean position. We have the expression for the kinetic energy,
\[K = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max }^2\]
Since the velocity is the maximum at the equilibrium or mean position, the kinetic energy also becomes the maximum. We can see the kinetic energy decrease from the equilibrium position to the extreme position and becomes zero at the extreme position.
So, the kinetic energy is the maximum at the stable equilibrium position.
Note: A stable position is not an equilibrium position. The stable position resembles the mean position in spring-mass arrangement. At a stable position, the kinetic energy is the maximum while the potential energy is the minimum since the potential energy is proportional to the square of the displacement from the equilibrium position.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, let us first understand the meaning of equilibrium. A system is said to be in the equilibrium if its state of motion and internal energy does not change with time. Now, there are two types of equilibrium: stable and unstable. An object is said to be in the stable equilibrium, if a small externally induced displacement is given to the object at equilibrium, creates a force which opposes the displacement of the object. And thus, the object again attains an equilibrium position. In the meantime, the object follows a simple harmonic motion about its mean position.
Consider the following situation in which a rectangular rod is at equilibrium (a) and then it has given a small horizontal force or we can say torque is applied at the top position. The rod follows a harmonic motion about its stable equilibrium position.

We know that the particle in the simple harmonic motion has the maximum velocity at the mean position. We have the expression for the kinetic energy,
\[K = \dfrac{1}{2}mv_{\max }^2\]
Since the velocity is the maximum at the equilibrium or mean position, the kinetic energy also becomes the maximum. We can see the kinetic energy decrease from the equilibrium position to the extreme position and becomes zero at the extreme position.
So, the kinetic energy is the maximum at the stable equilibrium position.
Note: A stable position is not an equilibrium position. The stable position resembles the mean position in spring-mass arrangement. At a stable position, the kinetic energy is the maximum while the potential energy is the minimum since the potential energy is proportional to the square of the displacement from the equilibrium position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




