
At lower temperature, most gases show:
(A) Negative deviation
(B) Positive deviation
(C) Positive and negative deviation
(D) None of the above
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: Kinetic theory and the ideal gas equation is followed by ideal gases. Real gases behave as ideal only under low pressure and high temperature. Real gases deviate from the ideal gas behaviour when they are under higher temperature and lower pressure.
Complete step by step answer:
When real gases are under higher temperature and lower pressures, they deviate from the behaviour of ideal gases significantly. This was understood by Van der Waals as he saw that two assumptions of kinetic molecular theory do not satisfy the behaviour of real gases.
The first assumption of kinetic theory, which does not fit into the real gases, was that a negligible fraction of the total volume of the gas is occupied by gas particles. The thing is that it only works till one atmospheric pressure. When the gas gets compressed, this does not apply. As we apply high pressure to compress the gas, real gases do not compress to a higher extent which was believed to be true in case of an ideal gas.
The second assumption was that the attraction between the gas molecules. Also, the ideal gas is zero. Which is not in the case of the real gases they do possess is an attraction between the molecules.
These two factors lead to the deviation of real gases from the behaviour of ideal gas.
The below-given diagram shows the deviation of real gases from the ideal gases under lower and higher temperature.
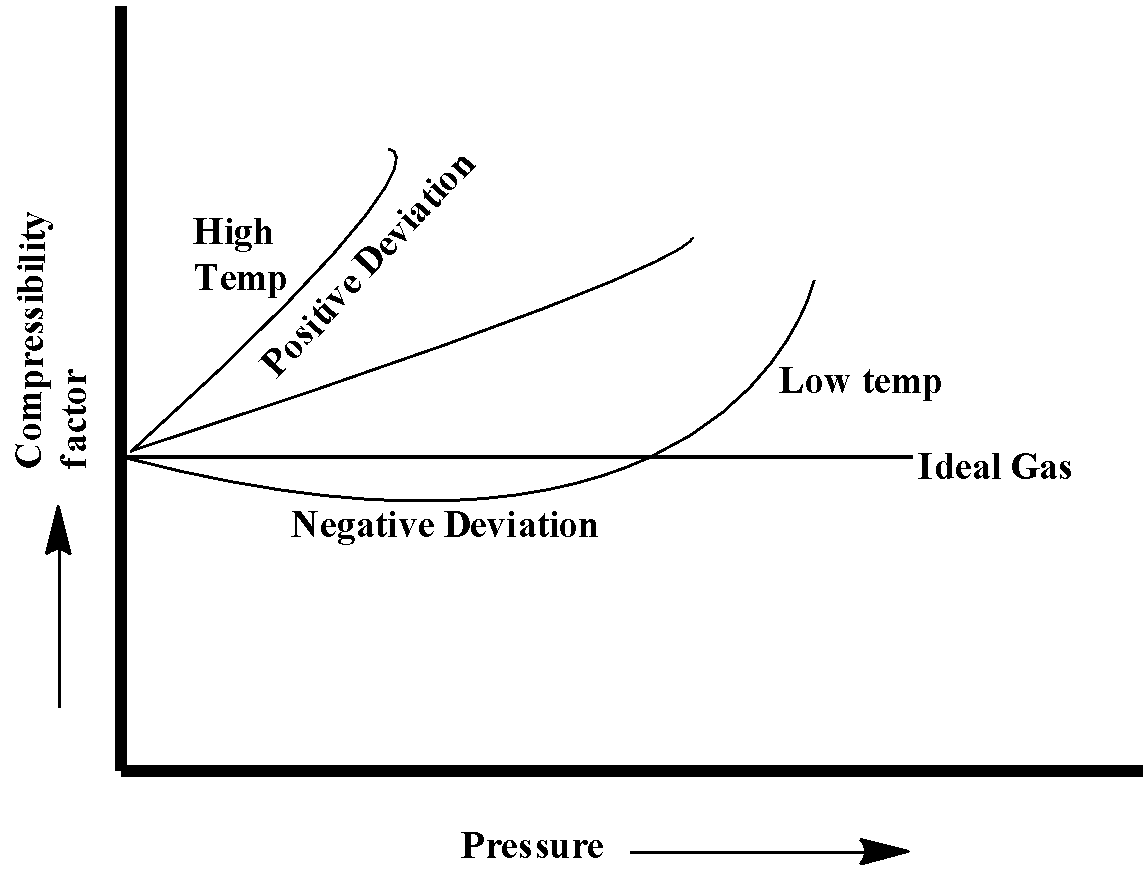
From the above diagram, we can conclude that under lower temperature real gases show negative deviation from ideal gases.
Correct option is A.
Note:
The real gases behaviour only satisfies with the ideal gas behaviour by five per cent under normal pressure and temperature. The kinetic theory of gases applies all the assumptions under ideal gases; there are several deviations from the kinetic theory when it comes to the real gases.
Complete step by step answer:
When real gases are under higher temperature and lower pressures, they deviate from the behaviour of ideal gases significantly. This was understood by Van der Waals as he saw that two assumptions of kinetic molecular theory do not satisfy the behaviour of real gases.
The first assumption of kinetic theory, which does not fit into the real gases, was that a negligible fraction of the total volume of the gas is occupied by gas particles. The thing is that it only works till one atmospheric pressure. When the gas gets compressed, this does not apply. As we apply high pressure to compress the gas, real gases do not compress to a higher extent which was believed to be true in case of an ideal gas.
The second assumption was that the attraction between the gas molecules. Also, the ideal gas is zero. Which is not in the case of the real gases they do possess is an attraction between the molecules.
These two factors lead to the deviation of real gases from the behaviour of ideal gas.
The below-given diagram shows the deviation of real gases from the ideal gases under lower and higher temperature.

From the above diagram, we can conclude that under lower temperature real gases show negative deviation from ideal gases.
Correct option is A.
Note:
The real gases behaviour only satisfies with the ideal gas behaviour by five per cent under normal pressure and temperature. The kinetic theory of gases applies all the assumptions under ideal gases; there are several deviations from the kinetic theory when it comes to the real gases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




