
At high concentration of soap in water, soap will behave as:
A.Molecular solid
B.Associated colloid
C.Macromolecular colloid
D.Lyophilic colloid
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:Soap is mainly made up of triglycerides and an alkaline strong base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. Hard soap is made of sodium as a base whereas soft soap is made up of potassium as a base. So in this we will see the reaction on how soap is made from sodium and potassium as a base.
Complete step by step answer:
At low concentration soap behaves as a normal electrolyte whereas in case of high concentration it acts as an ionic micelles.
Reaction of soap when it dissolves in water at low concentrations is as follows:
$RCOONa \to RCO{O^ - } + N{a^ + }$
It dissociates to give $RCO{O^ - }$ and $N{a^ + }$ .
So, at low concentrations carboxylate ion dissociates into two parts $RCO{O^ - }$
a) The part that loves water(hydrophilic): $CO{O^ - }$
b) Part that hates water(hydrophobic): $R$
So,here is an example of sodium stearate soap${C_{17}}{H_{35}}CO{O^ - }N{a^ + }$
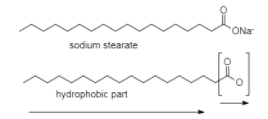
At lower concentrations the head part that is the carboxylate ion $CO{O^ - }$ dissolves in the water whereas the tail part that is $R$ stays on the surface.
Now, from all this we can say that at lower concentrations soap acts as an electrolyte.
Associated colloids are those substances that behave as normal electrolytes at low concentrations whereas in higher concentrations it behaves as a colloidal particle.
So, from this we can say that the soap behaves as associated colloids at higher concentrations.
So, the correct answer is option B i.e Associated colloid.
Note:
The concentration range at which a soap makes a micelles is known as critical micelle concentration (cmc). It ranges from ${10^{ - 4}} - {10^{ - 3}}mol/L$ . The soaps which are made of sodium and potassium as base are only used for cleaning purposes.
Complete step by step answer:
At low concentration soap behaves as a normal electrolyte whereas in case of high concentration it acts as an ionic micelles.
Reaction of soap when it dissolves in water at low concentrations is as follows:
$RCOONa \to RCO{O^ - } + N{a^ + }$
It dissociates to give $RCO{O^ - }$ and $N{a^ + }$ .
So, at low concentrations carboxylate ion dissociates into two parts $RCO{O^ - }$
a) The part that loves water(hydrophilic): $CO{O^ - }$
b) Part that hates water(hydrophobic): $R$
So,here is an example of sodium stearate soap${C_{17}}{H_{35}}CO{O^ - }N{a^ + }$

At lower concentrations the head part that is the carboxylate ion $CO{O^ - }$ dissolves in the water whereas the tail part that is $R$ stays on the surface.
Now, from all this we can say that at lower concentrations soap acts as an electrolyte.
Associated colloids are those substances that behave as normal electrolytes at low concentrations whereas in higher concentrations it behaves as a colloidal particle.
So, from this we can say that the soap behaves as associated colloids at higher concentrations.
So, the correct answer is option B i.e Associated colloid.
Note:
The concentration range at which a soap makes a micelles is known as critical micelle concentration (cmc). It ranges from ${10^{ - 4}} - {10^{ - 3}}mol/L$ . The soaps which are made of sodium and potassium as base are only used for cleaning purposes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




