
At a point A, 20 meters above the level of water in a lake, then the angle of elevation of a cloud is $ {{30}^{o}} $ . The angle of depression of the reflection of the cloud in the lake at A is $ {{60}^{o}} $ . Find the distance of the cloud from sea level and also from A.
(a) Distance from $ A=20\sqrt{3}m $ , distance from sea level = 40m.
(b) Distance from A = 40m, distance from sea level = 40m.
(c) Distance from A=20m, distance from sea level = 40m.
(d) Distance from \[A=40\sqrt{3}m\], distance from sea level = 40m.
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: we use the given information and draw figure to get a better view of the figure. Once we draw a figure, we use trigonometric functions to get the relation between distance from A and distance from sea-level. Using these relations we solve for the required results.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that we have a point A, which is 20 meters above the level of water in the lake. There is a cloud in the sky and the angle of elevation of the cloud $ {{30}^{o}} $ with respect to point A.
We can see a reflection of the cloud in the lake which has an angle of depression $ {{60}^{o}} $ with respect to point A.
We need to find the horizontal distance between point A and cloud and also the vertical distance of cloud from sea level.
Let us assume the distance between point A and cloud be ‘x’ m and the vertical distance of cloud from point ‘A’ be ‘h’ m.
Let us draw all these so that we can have a detailed view of the information.
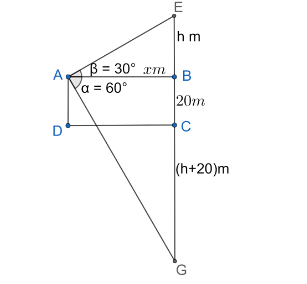
Since, the cloud is ‘h+20’m above the water level of the lake the reflection of cloud lies ‘(h+20)’m below the surface DC.
We know that in a right-angled triangle with an angle $ \theta $ (other than the right angle). $ \tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{opposite side length}}{\text{adjacent side length}} $
From $ \Delta ABE $ of the figure, we get
$ \tan \alpha =\dfrac{h}{x} $
$ \tan {{30}^{o}}=\dfrac{h}{x} $
$ \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{h}{x} $
$ x=h\sqrt{3}.......(1) $
From $ \Delta ABG $ of the figure, we get
$ \tan \beta =\dfrac{\left( h+20 \right)+20}{x} $
$ \tan {{60}^{o}}=\dfrac{h+40}{x} $
$ \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{h+40}{x} $
$ x\sqrt{3}=h+40 $
From equation (1), we have $ x=h\sqrt{3} $ . Substituting it we get,
$ \left( h\sqrt{3} \right)\sqrt{3}=h+40 $
$ 3h=h+40 $
\[3h-h=40\]
$ 2h=40 $
$ h=\dfrac{40}{2} $
$ h=20m $
The cloud is (h+20) m above the water level of lake. So, cloud is at a distance of (20+20) = 40m from sea level
From equation (1),
$ x=20\sqrt{3} $
∴ The cloud is at a distance of $ 20\sqrt{3}m $ from the point A.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We take horizontal and vertical distance unless it is stated otherwise. Whenever we get a problem involving angle of elevation and depression, draw a figure representing the information and try to solve the problem. Use all the information provided for us in the problem. On the problem side DC is considered as a surface and the portion below it is considered as a lake.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that we have a point A, which is 20 meters above the level of water in the lake. There is a cloud in the sky and the angle of elevation of the cloud $ {{30}^{o}} $ with respect to point A.
We can see a reflection of the cloud in the lake which has an angle of depression $ {{60}^{o}} $ with respect to point A.
We need to find the horizontal distance between point A and cloud and also the vertical distance of cloud from sea level.
Let us assume the distance between point A and cloud be ‘x’ m and the vertical distance of cloud from point ‘A’ be ‘h’ m.
Let us draw all these so that we can have a detailed view of the information.

Since, the cloud is ‘h+20’m above the water level of the lake the reflection of cloud lies ‘(h+20)’m below the surface DC.
We know that in a right-angled triangle with an angle $ \theta $ (other than the right angle). $ \tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{opposite side length}}{\text{adjacent side length}} $
From $ \Delta ABE $ of the figure, we get
$ \tan \alpha =\dfrac{h}{x} $
$ \tan {{30}^{o}}=\dfrac{h}{x} $
$ \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{h}{x} $
$ x=h\sqrt{3}.......(1) $
From $ \Delta ABG $ of the figure, we get
$ \tan \beta =\dfrac{\left( h+20 \right)+20}{x} $
$ \tan {{60}^{o}}=\dfrac{h+40}{x} $
$ \sqrt{3}=\dfrac{h+40}{x} $
$ x\sqrt{3}=h+40 $
From equation (1), we have $ x=h\sqrt{3} $ . Substituting it we get,
$ \left( h\sqrt{3} \right)\sqrt{3}=h+40 $
$ 3h=h+40 $
\[3h-h=40\]
$ 2h=40 $
$ h=\dfrac{40}{2} $
$ h=20m $
The cloud is (h+20) m above the water level of lake. So, cloud is at a distance of (20+20) = 40m from sea level
From equation (1),
$ x=20\sqrt{3} $
∴ The cloud is at a distance of $ 20\sqrt{3}m $ from the point A.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We take horizontal and vertical distance unless it is stated otherwise. Whenever we get a problem involving angle of elevation and depression, draw a figure representing the information and try to solve the problem. Use all the information provided for us in the problem. On the problem side DC is considered as a surface and the portion below it is considered as a lake.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




