
Assuming covalent radii to be additive property; The benzene ring is regular hexagon and each $ {\text{C}} - {\text{I}} $ bond lies on a line passing through the center of hexagon. The $ {\text{C}} - {\text{C}} $ bond length in $ {{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}} $ is $ {\text{1}}{\text{.40}}\mathop {\text{A}}\limits_{}^{\text{o}} $ and covalent radius of iodine and carbon atom are $ 1.33\mathop {\text{A}}\limits_{}^{\text{o}} $ and $ 0.77\mathop {\text{A}}\limits_{}^{\text{o}} $ . Also neglect different overlapping effects. The sum of iodine- iodine distances in o-, m-, p- di iodobenzene is $ {\text{X}}\mathop {\text{A}}\limits_{}^{\text{o}} $ . Value of $ 100{\text{X}} $ is:
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the structures and angles of the hexagonal structure of benzene. Each angle in a regular hexagon has an angle of $ {120^{\text{o}}}{\text{C}} $ and lengths of all the sides are equal.
Complete step by step solution:
First we consider the ortho- di- iodobenzene molecule.
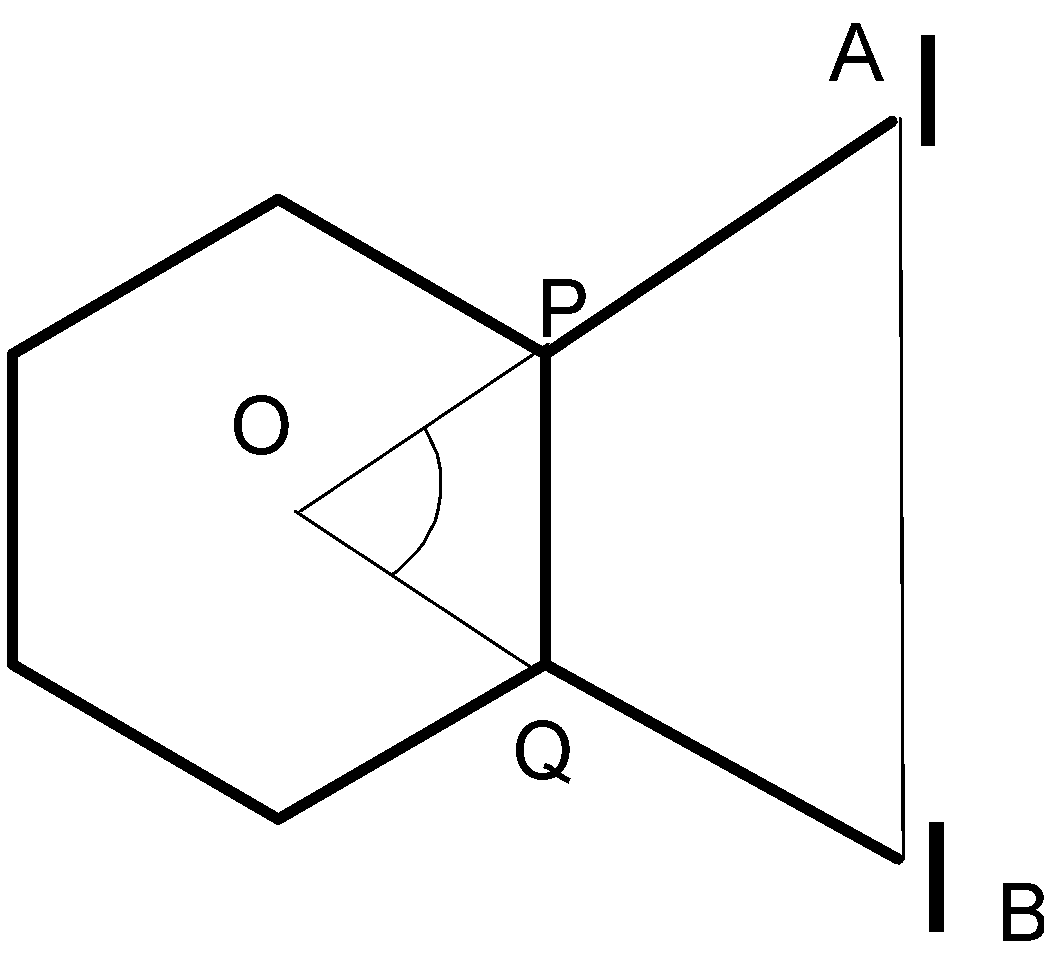
We are given that the carbon- iodine bond lies on the line passing through the center of the hexagon. Such a line also bisects the carbon- carbon bond angle thus, the angle becomes $ {60^{\text{o}}} $ . We know that both the carbon iodine bonds are identical, thus, the distance from the center of the hexagon to the iodine atoms will be equal.
Thus, OA = OB and the angle is $ {60^{\text{o}}} $ . So, the triangle OAB is an equilateral triangle. In an equilateral triangle, all the sides are equal. So we can write $ AB = OA = OB $
Similarly the triangle OPQ is also equilateral. So, $ OP = OQ = PQ = 1.40{\text{ }}\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^0 $
We are supposed to find the distance between two iodine atoms, i.e. AB
$ AB = OA = OP + PA $
$ AB = 1.40 + 1.33 + 0.77 $
So, the distance between iodine atoms in ortho- di- iodobenzene is $ {\text{AB}} = {\text{3}}{\text{.50}}\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $
Now in meta- di- iodobenzene molecule,
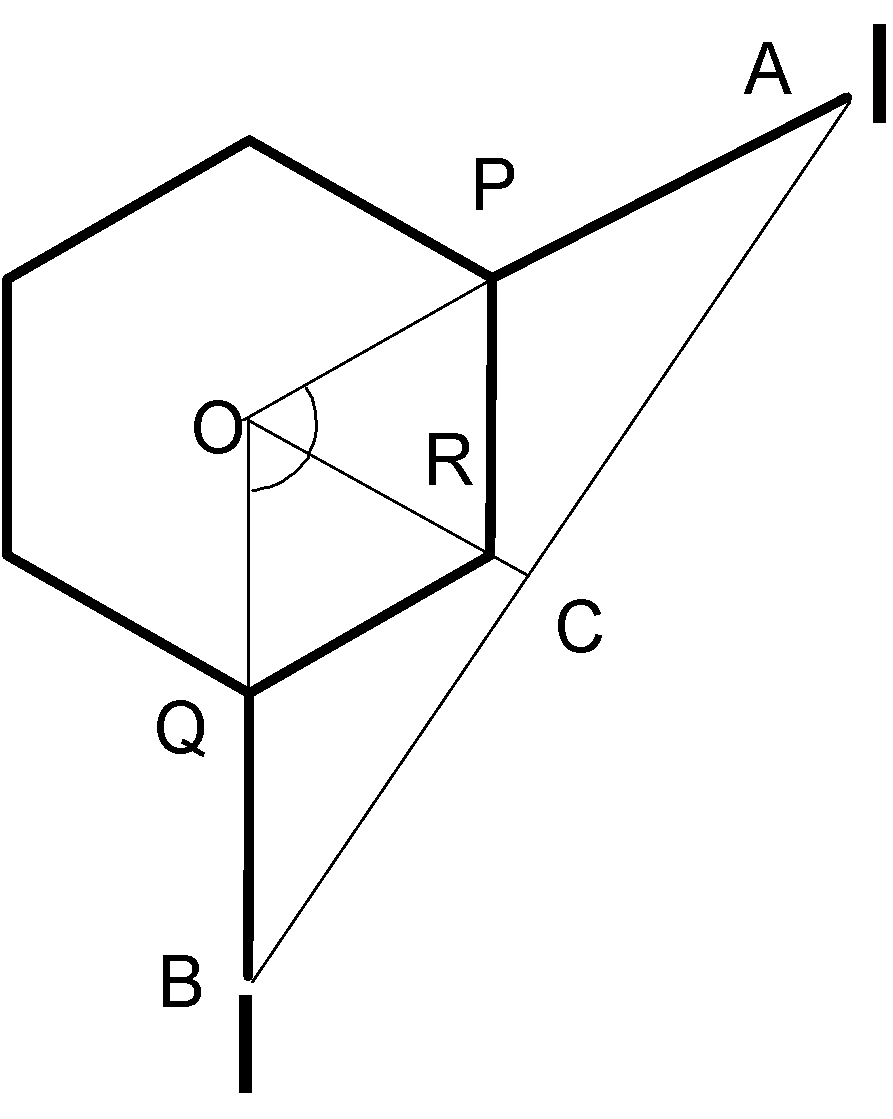
The angle formed at the center of the hexagon will be equal to $ {60^{\text{o}}} + {60^{\text{o}}} = {120^{\text{o}}} $ . Since we know from earlier calculations that OA must be equal to OQ, thus the angle A and angle B will be equal to $ {30^{\text{o}}} $ in the triangle OAB. The two triangles OAC and OBC are congruent since all sides are of equal lengths. We are supposed to find AB which is given by,
$ AB = AC + BC = 2AC $
Substituting:
$ \Rightarrow AB = 2AO\cos 30 = 2\left( {3.50} \right)\cos 30 $
Solving:
$ \Rightarrow AB = 6.06\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $
In Para- di- iodobenzene molecule,
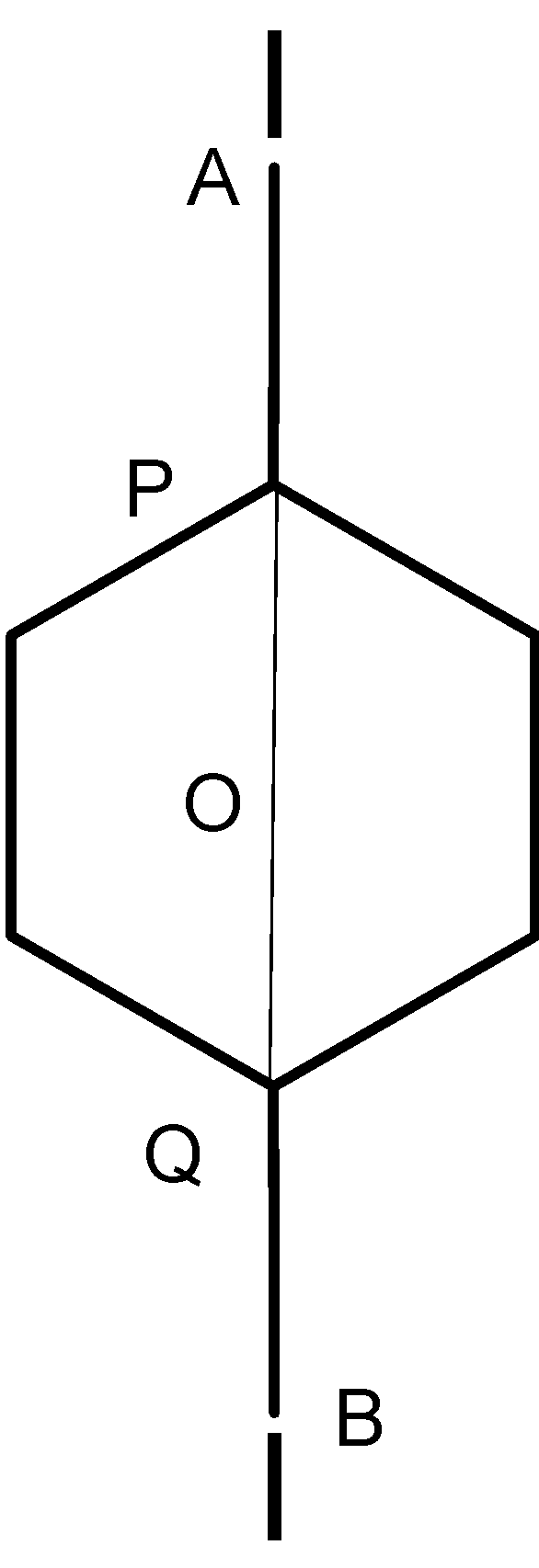
$ AB = OA + OB $
$ \Rightarrow AB = OP + OQ + PA + BQ $
Substituting:
$ \Rightarrow AB = 1.40 + 1.40 + 1.33 + 0.77 + 1.33 + 0.77 $
Solving:
$ \therefore AB = 7.0\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $
The sum of all three values of AB gives us X. So, $ X = 3.50 + 6.06 + 7 $
$ X = 16.56\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $
$ 100X = 1656 $ .
Note:
In an equilateral triangle, the angles at the bases of equal sides are equal. In an equilateral triangle, all the sides and angles are equal. Since the sum of all angles in the triangle is 180 degrees, each angle in an equilateral triangle is equal to 60 degrees.
Complete step by step solution:
First we consider the ortho- di- iodobenzene molecule.

We are given that the carbon- iodine bond lies on the line passing through the center of the hexagon. Such a line also bisects the carbon- carbon bond angle thus, the angle becomes $ {60^{\text{o}}} $ . We know that both the carbon iodine bonds are identical, thus, the distance from the center of the hexagon to the iodine atoms will be equal.
Thus, OA = OB and the angle is $ {60^{\text{o}}} $ . So, the triangle OAB is an equilateral triangle. In an equilateral triangle, all the sides are equal. So we can write $ AB = OA = OB $
Similarly the triangle OPQ is also equilateral. So, $ OP = OQ = PQ = 1.40{\text{ }}\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^0 $
We are supposed to find the distance between two iodine atoms, i.e. AB
$ AB = OA = OP + PA $
$ AB = 1.40 + 1.33 + 0.77 $
So, the distance between iodine atoms in ortho- di- iodobenzene is $ {\text{AB}} = {\text{3}}{\text{.50}}\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $
Now in meta- di- iodobenzene molecule,

The angle formed at the center of the hexagon will be equal to $ {60^{\text{o}}} + {60^{\text{o}}} = {120^{\text{o}}} $ . Since we know from earlier calculations that OA must be equal to OQ, thus the angle A and angle B will be equal to $ {30^{\text{o}}} $ in the triangle OAB. The two triangles OAC and OBC are congruent since all sides are of equal lengths. We are supposed to find AB which is given by,
$ AB = AC + BC = 2AC $
Substituting:
$ \Rightarrow AB = 2AO\cos 30 = 2\left( {3.50} \right)\cos 30 $
Solving:
$ \Rightarrow AB = 6.06\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $
In Para- di- iodobenzene molecule,

$ AB = OA + OB $
$ \Rightarrow AB = OP + OQ + PA + BQ $
Substituting:
$ \Rightarrow AB = 1.40 + 1.40 + 1.33 + 0.77 + 1.33 + 0.77 $
Solving:
$ \therefore AB = 7.0\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $
The sum of all three values of AB gives us X. So, $ X = 3.50 + 6.06 + 7 $
$ X = 16.56\mathop {\text{A}}\limits^{\text{o}} $
$ 100X = 1656 $ .
Note:
In an equilateral triangle, the angles at the bases of equal sides are equal. In an equilateral triangle, all the sides and angles are equal. Since the sum of all angles in the triangle is 180 degrees, each angle in an equilateral triangle is equal to 60 degrees.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




