
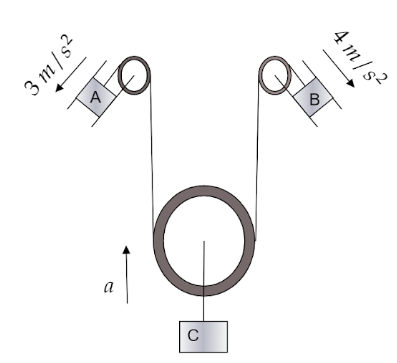
Assuming all the surfaces to be frictionless, acceleration of the block C, shown in the figure is _____ $\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$.

Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint: In this question above we have to find the acceleration of block C and the value of acceleration of block A and B are given. We will consider the distances that block A, B and C may cover due to tension of the string. Then, the double derivative of the equation will give the result.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider that the two bodies are suspended by a string. Forces are acting on them.The surfaces given here are also frictionless.Let us now consider that the block A having acceleration of $3{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$ moves by a distance $x$ as it is acted upon forces or tension of the string.Now, let us assume that block B which is moving with a velocity of ${\text{4 }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$ moves by a distance $y$ as it is also acted upon forces or tension of the string.
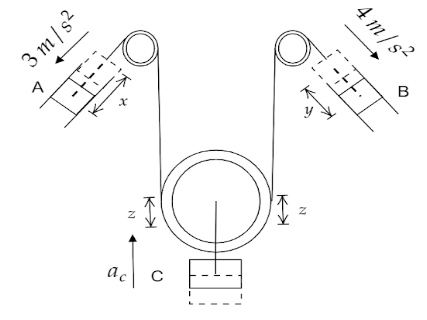
The block is also acted upon tension and its weight and lets it cover a distance of $z$. So, we can easily say that the distance moved by block C is equal to the distance moved by block A and C combined. As the block C is connected with two strings, we have
$z = x$ and $z = y$.
Thus, we now sum these two and get,
$2z = x + y$
$ \Rightarrow z = \dfrac{{x + y}}{2}$
Double derivative of the equation with respect to $t$, we get,
$\dfrac{{{d^2}z}}{{d{t^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{t^2}}} + \dfrac{{{d^{}}y}}{{d{t^2}}}} \right)$
Double derivative of distance with respect to time gives acceleration,
${a_c} = \dfrac{{{a_a} + {a_b}}}{2}$
Substituting the values of acceleration of block A and C we get,
$\therefore {a_c} = \dfrac{{3 + 4}}{2} = 3.5$
Therefore, the acceleration of block C is $3.5{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$.
Note:It must be noted that the first derivative of distance with respect to time gives velocity whereas the second derivative of distance with respect to time gives acceleration. As there is no friction there isn’t any opposition in forces, if there was friction between the surfaces, we have to use the tension formula. Also the Block A and B have the same angle of inclination with respect to C.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider that the two bodies are suspended by a string. Forces are acting on them.The surfaces given here are also frictionless.Let us now consider that the block A having acceleration of $3{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$ moves by a distance $x$ as it is acted upon forces or tension of the string.Now, let us assume that block B which is moving with a velocity of ${\text{4 }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$ moves by a distance $y$ as it is also acted upon forces or tension of the string.

The block is also acted upon tension and its weight and lets it cover a distance of $z$. So, we can easily say that the distance moved by block C is equal to the distance moved by block A and C combined. As the block C is connected with two strings, we have
$z = x$ and $z = y$.
Thus, we now sum these two and get,
$2z = x + y$
$ \Rightarrow z = \dfrac{{x + y}}{2}$
Double derivative of the equation with respect to $t$, we get,
$\dfrac{{{d^2}z}}{{d{t^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{t^2}}} + \dfrac{{{d^{}}y}}{{d{t^2}}}} \right)$
Double derivative of distance with respect to time gives acceleration,
${a_c} = \dfrac{{{a_a} + {a_b}}}{2}$
Substituting the values of acceleration of block A and C we get,
$\therefore {a_c} = \dfrac{{3 + 4}}{2} = 3.5$
Therefore, the acceleration of block C is $3.5{\text{ }}\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$.
Note:It must be noted that the first derivative of distance with respect to time gives velocity whereas the second derivative of distance with respect to time gives acceleration. As there is no friction there isn’t any opposition in forces, if there was friction between the surfaces, we have to use the tension formula. Also the Block A and B have the same angle of inclination with respect to C.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




