
Assertion: Trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane is a chiral molecule.
Reason: All chiral molecules have chiral carbon atoms.
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: A atom (which is usually tetrahedral) of a molecule containing four different bonded groups, including lone pairs, is known as a chiral center or a chiral atom. They have a non-superimposable mirror image.
Complete answer:
The structure of a molecule can help in identifying the chiral centers. While looking at a structure of a molecule, look for an atom that is bonded through a single bond to four distinct ligands.
Now, the structure of trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane is
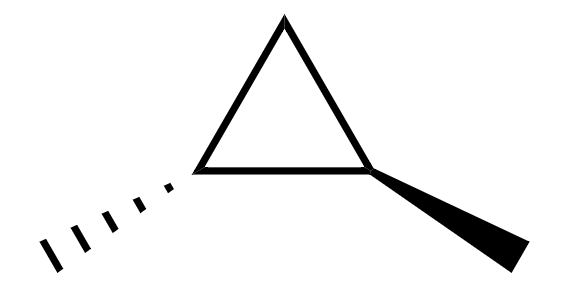
Here, we can see that both the carbon atoms which are attached to methyl groups have four different bonded groups, when looked at from the above,
1. hydrogen atom
2. methyl group
3. ring going clockwise
4. ring going anti-clockwise
Hence it is a chiral molecule.
Now, it is not necessary for a chiral molecule to have a chiral carbon or a center of chirality. Some of these chiral molecules are dimethylallene, dichloro spiro heptane, dibromobiphenyl, or trans-cyclooctene.
So, since the assertion is right but the reason is incorrect.
Hence the answer is option (C).
Additional Information:
Even though the terms chiral center and stereogenic center or stereocenter are used synonymously, not all stereocenters are considered to be chiral centers. But since stereocenters are bonded to three or more distinct groups, all chiral centers are stereocenters.
Note:
It should be noted that any atoms which have two or more identical groups attached to them cannot be a chiral center. For example, $(-C{{H}_{2}}\text{ or -C}{{\text{H}}_{3}})$.
A double-bonded or triple bonded carbon atom cannot be a chiral center as it can not form four distinct ligands.
Complete answer:
The structure of a molecule can help in identifying the chiral centers. While looking at a structure of a molecule, look for an atom that is bonded through a single bond to four distinct ligands.
Now, the structure of trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane is

Here, we can see that both the carbon atoms which are attached to methyl groups have four different bonded groups, when looked at from the above,
1. hydrogen atom
2. methyl group
3. ring going clockwise
4. ring going anti-clockwise
Hence it is a chiral molecule.
Now, it is not necessary for a chiral molecule to have a chiral carbon or a center of chirality. Some of these chiral molecules are dimethylallene, dichloro spiro heptane, dibromobiphenyl, or trans-cyclooctene.
So, since the assertion is right but the reason is incorrect.
Hence the answer is option (C).
Additional Information:
Even though the terms chiral center and stereogenic center or stereocenter are used synonymously, not all stereocenters are considered to be chiral centers. But since stereocenters are bonded to three or more distinct groups, all chiral centers are stereocenters.
Note:
It should be noted that any atoms which have two or more identical groups attached to them cannot be a chiral center. For example, $(-C{{H}_{2}}\text{ or -C}{{\text{H}}_{3}})$.
A double-bonded or triple bonded carbon atom cannot be a chiral center as it can not form four distinct ligands.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




