
Assertion: The $B-F$ bond lengths in $B{{F}_{3}}$ and $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ are different
Reason: In $B{{F}_{3}}$, the $B-F$ bond acquires some double bond character.
A. Assertion and reason are true, reason is correct explanation for assertion
B. Assertion and reason are true, reason is correct explanation for assertion.
C. Assertion is true, reason is false.
D. Assertion is false, reason is true
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: $B{{F}_{3}}$ has resonance structures, so it has a partial double bond character, whereas there is no resonance structure in $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ion, so it acts like single bond. Strength of a double bond is more than a single bond.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about the structures of $B{{F}_{3}}$ and $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$. $B{{F}_{3}}$ is also known as bromine trifluoride and it has a total of 24 valence electrons. So, according to the VSEPR theory, the structure should be a triangle, with the boron atom, in the centre. The compound is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised. It happens as the s and the p orbitals of the Boron atom experience a combination, so that three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals are formed, all of which possess equal hybrid energy. The structure of $B{{F}_{3}}$ is:
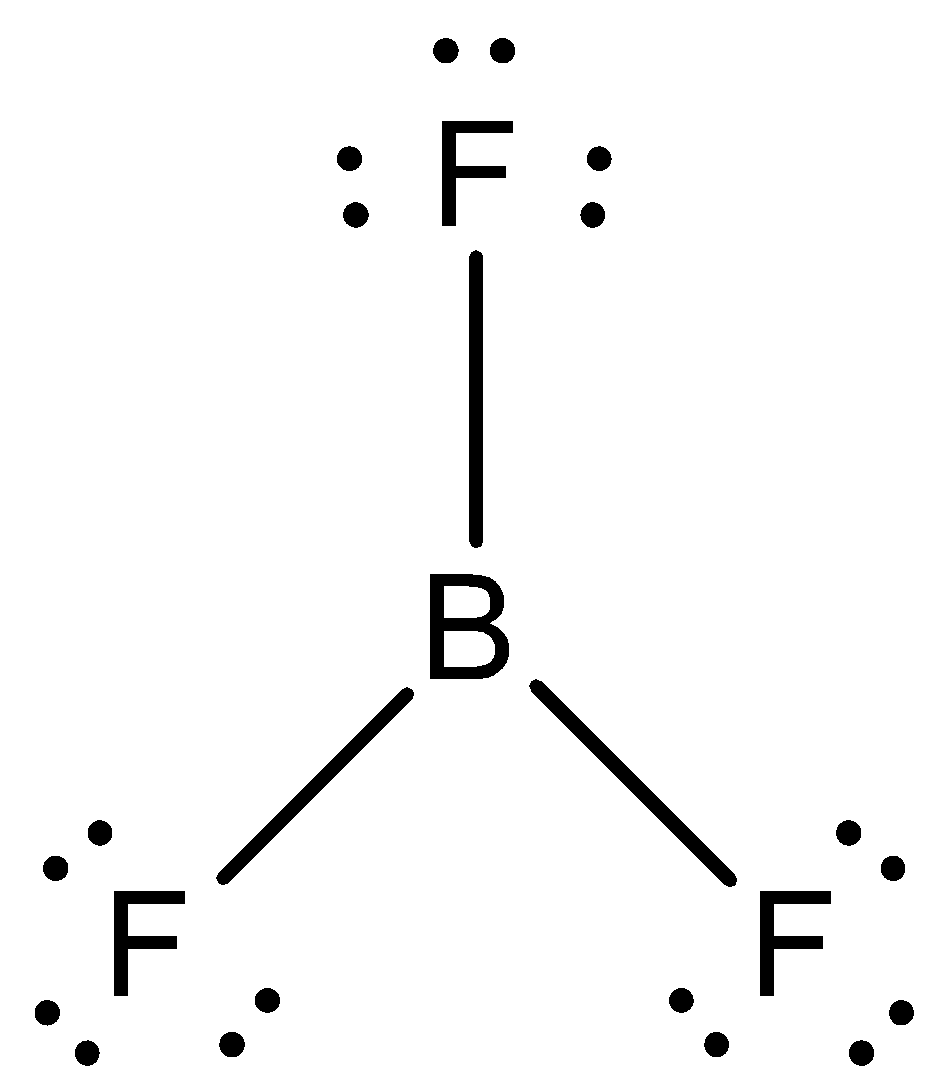
One electron of the boron in the ground state, remains unpaired. One 2s and two of the 2p orbitals hybridise. Now, let us know about the compound $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$. It is also known as the boron tetrafluoride ion and has the structure of a tetrahedron. Each of the 3 valence electrons of boron forms a covalent bond with all of the four fluorine atoms. One more electron is contributed by the overall negative charge of the molecule. The structure of $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ is:
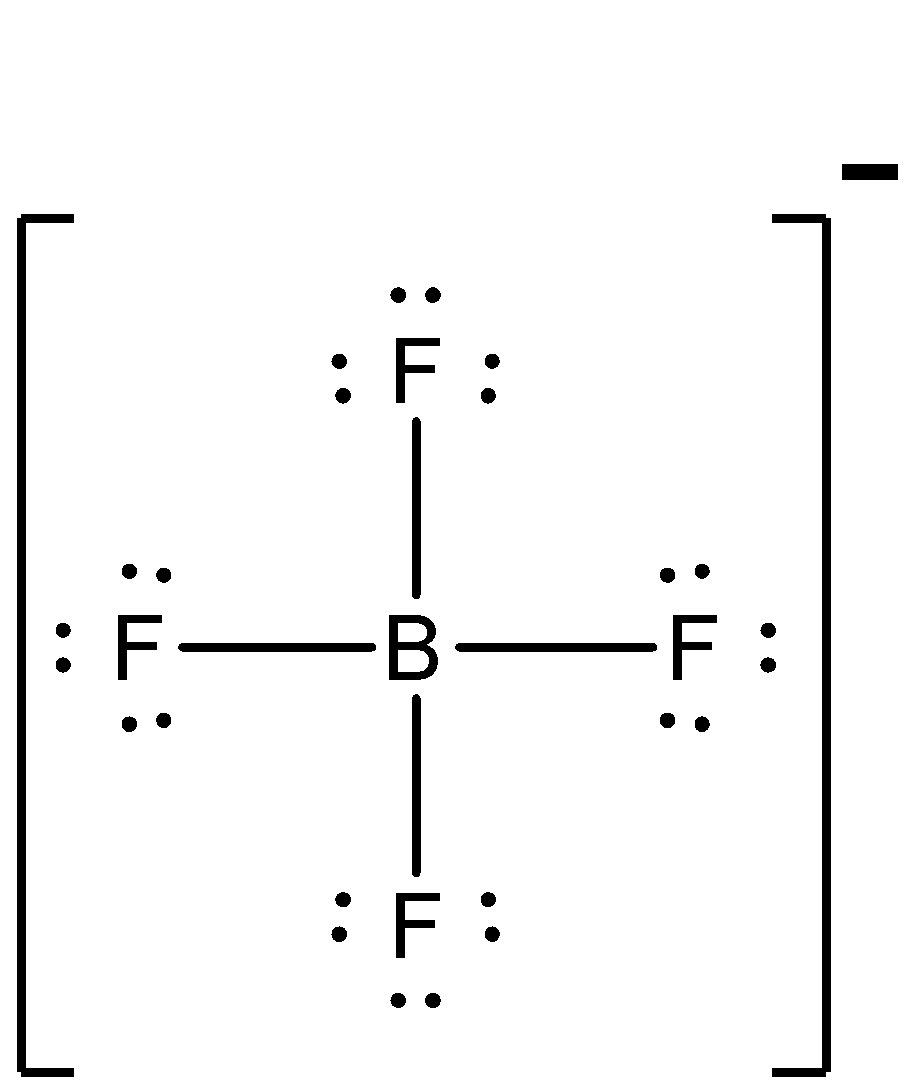
Now, $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ has some single bond character, whereas $B{{F}_{3}}$ has partial double bond character. So, the bond length of $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ will be more, as bond strength is less.
So, the assertion and reason are true, reason is the correct explanation for assertion, which gives the correct answer as option A.
Note:
Boron trifluoride is a colourless and toxic substance which is generally present in the gaseous state. Fluorine is electronegative, but due to the arrangement of the fluorine atoms, the dipoles cancel out and net dipole becomes 0.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to learn about the structures of $B{{F}_{3}}$ and $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$. $B{{F}_{3}}$ is also known as bromine trifluoride and it has a total of 24 valence electrons. So, according to the VSEPR theory, the structure should be a triangle, with the boron atom, in the centre. The compound is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised. It happens as the s and the p orbitals of the Boron atom experience a combination, so that three $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybrid orbitals are formed, all of which possess equal hybrid energy. The structure of $B{{F}_{3}}$ is:

One electron of the boron in the ground state, remains unpaired. One 2s and two of the 2p orbitals hybridise. Now, let us know about the compound $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$. It is also known as the boron tetrafluoride ion and has the structure of a tetrahedron. Each of the 3 valence electrons of boron forms a covalent bond with all of the four fluorine atoms. One more electron is contributed by the overall negative charge of the molecule. The structure of $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ is:

Now, $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ has some single bond character, whereas $B{{F}_{3}}$ has partial double bond character. So, the bond length of $B{{F}_{4}}^{-}$ will be more, as bond strength is less.
So, the assertion and reason are true, reason is the correct explanation for assertion, which gives the correct answer as option A.
Note:
Boron trifluoride is a colourless and toxic substance which is generally present in the gaseous state. Fluorine is electronegative, but due to the arrangement of the fluorine atoms, the dipoles cancel out and net dipole becomes 0.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




